Geosynthetic products have become an integral part of the construction process for several key industries. Its price and physical properties are major advantages compared to traditional alternatives. Geosynthetics are manufactured from various man made polymers and are used in conjunction with soil or rock to enhance the stability of terrains. These products are used in civil, mining and transport infrastructure projects because of its ability to solve a range of engineering problems related to soil reinforcement, erosion control and containment. Geosynthetic products are classified into four types. Geomembranes, geotextiles, geocells and geocomposites. The most popular of these types is geomembrane.
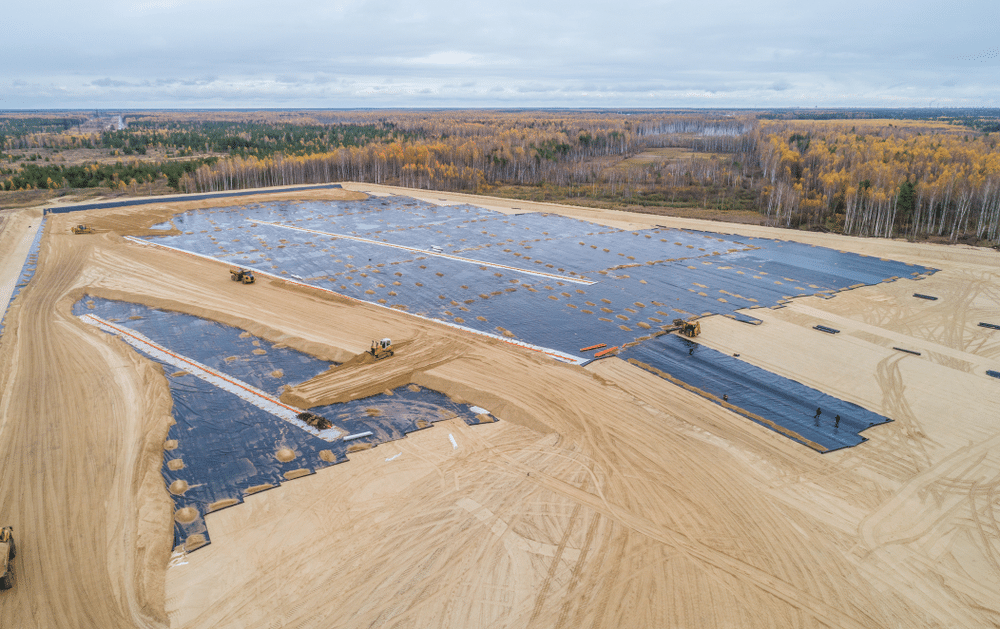
Geomembranes
Geomembranes are made from impermeable geosynthetic material consisting of thin continuous sheets of polymers. Geomembranes create an impermeable barrier that prevents the leakage of harmful contaminants or dangerous chemicals to surrounding environments. It is also regularly used as containment barriers for potable water and irrigation storage requirements to prevent leakage. Geomembranes are used in conjunction with other geosynthetic products to control fluid movement and provide containment in projects related to mining, sewage treatment and canal construction.
Applications
The growing application of geomembranes is noticeable in different industries due to the versatility of the product. Geomembranes have a wide range of applications in industries such as mining, marine, civil, water treatment and transportation. Some of the applications are detailed below.
Mining Industry
Usage of geomembrane in the mining industry started in the 1970s and has increased thereafter. It is used as a lining solution for evaporation ponds, heap leach pads and tailing impoundments.
The design and construction of these heap leach pads are regulated to protect the environment from exposure to harmful chemicals so a lining system, usually a HDPE geomembrane, forms a critical component in construction of these heap leach facilities.
Geomembranes are also used during the end of a mine’s lifespan. As a part of mine restoration, HDPE liners are used to seal the mine and prevent waste products from contaminating the surrounding environment. Overall, geomembrane lining is a safe and effective solution to protect the environment from harmful industries.
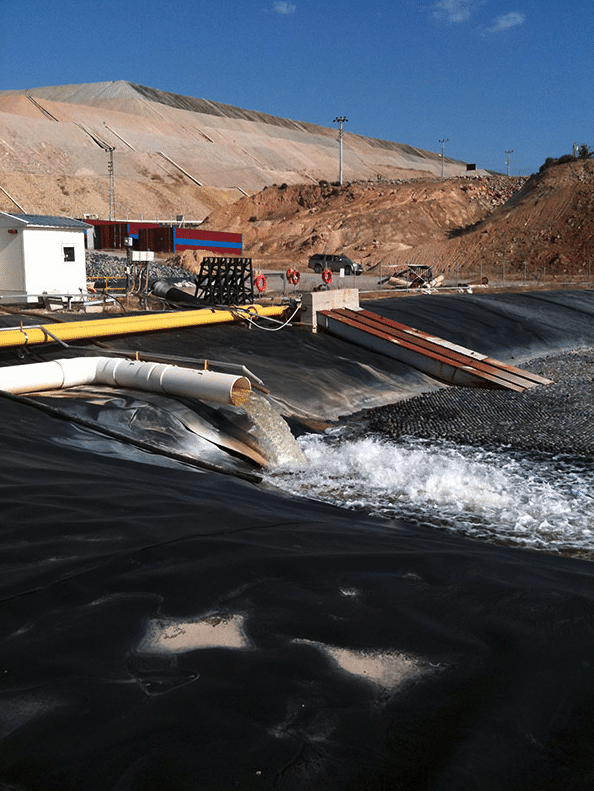

Water Industry
HDPE geomembranes play a major role in delivering clean water to the community. They are used in services related to drinking water and wastewater including sewage treatment. When canals, dams and reservoirs are sealed with geomembrane liners they avoid contamination from groundwater.
Geomembrane is also used to prevent contamination of potable water from soil and other pollutants as well as preventing loss of water through infiltration of the water into the surrounding soil. Lining a dam or canal can minimise seepage thereby improving the efficiency of storage and transportation. Geomembranes are also used as a secondary containment for underground storage tanks, solar ponds and brine solution.

Marine (Pontoon Construction)
HDPE geomembranes are used widely in the marine industries, particularly in the construction of floating docks or jetty platforms supported by pontoons. In the construction process, HDPE geomembrane is wrapped around the flotation foam of the pontoon to provide a protective barrier that increases the durability of the product. By lining it with a HDPE geomembrane the foam is protected from damage by marine life, environmental forces and other contaminants in the water.
It also adds additional buoyancy to the pontoons and prevents deterioration from extreme weather conditions, improving the overall longevity of the pontoon. Please refer to Pond and Pontoon Plastic Liner Applications for more information.
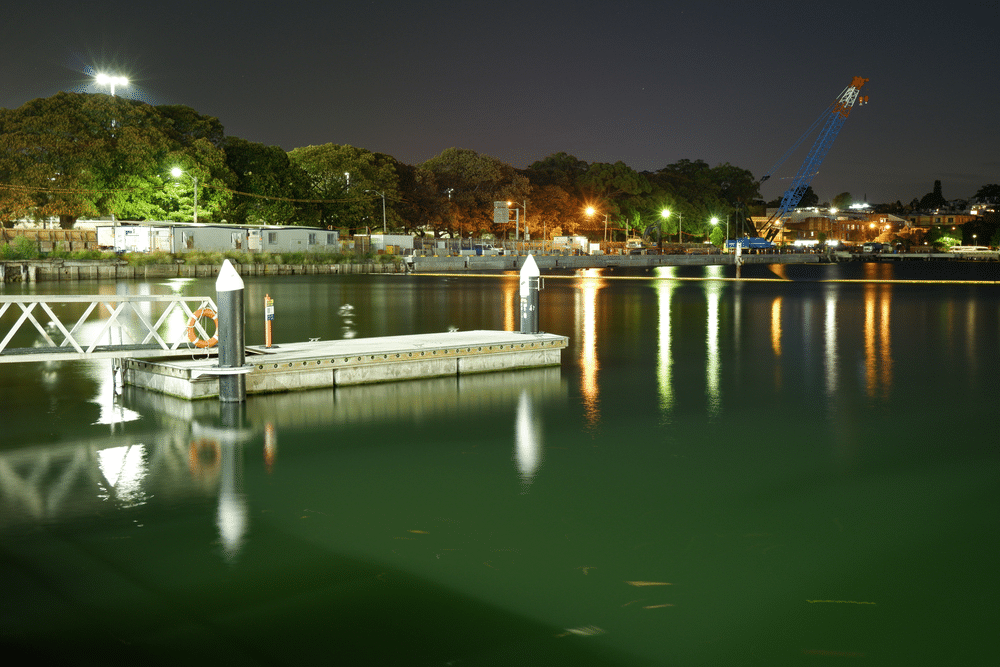
Agriculture and Nurseries
HDPE liners are extensively used by farmers in lining dams and ponds as they provide cost effective and reliable containment solutions.
Geomembranes are also used for various applications in nurseries including waterproofing and containment of soils. HDPE liner usage in commercial nurseries is increasing as customers transition from using PVC and LDPE liners. For example, gardeners are now showing an increased interest in HDPE geomembranes as a permanent solution for nursery bed lining and basket lining applications.
Additionally, HDPE liners are used to provide lining for secondary containment in chemical and fertilizer storage tanks due to the immense versatility of the product’s applications and its durability.

Manufacturing Process
The process begins by choosing the suitable polymer resin which is normally in pellet form. Next, different additives such as carbon black, plasticizers, antioxidants and lubricants are added. The formulation of resin and additives are then fed into a hopper which leads to an horizontal extruder. This formulation is transported via a continuous screw through feed section, compression, metering and filtering stages, after which it is pressure fed into a die to create sheets of varying widths and thicknesses by calendering.
Additives are added in the formulation to prevent oxidation and increase durability. Carbon black is sometimes added to the formulation to improve its stability under ultraviolet light, making black HDPE one of the most UV resistant products on the market.
Types of Geomembranes
Depending on the parent resin used several types of geomembranes are available. The most commonly used geomembranes are listed below.
HDPE Geomembrane
HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene) is the most widely used geomembrane and is the preferred choice for lining projects due to its durability, strong UV resistance and relatively inexpensive material cost.
HDPE geomembranes are often selected for use in exposed applications such as landfill, reservoir covers as well as pond and canal liners. This is due to the low initial material cost and its high resistance to chemicals. It is available in higher thicknesses which other geomembrane types do not offer. HDPE geomembrane is also very strong relative to its weight and can resist higher temperatures.
One of the best characteristics of this geomembrane is its chemical and UV resistance, making it suitable for large area applications where high quality installation is required. Additionally, HDPE is food safe, allowing it to be used in storage of potable water.
LLDPE Geomembrane
Linear Low-Density Polyethylene (LLDPE) geomembranes provide more flexibility compared to HDPE, making it more appropriate for installers who require an impermeable geomembrane. It is made with virgin polyethylene resins, making it resistant to low temperature and ultraviolet exposure.
LLDPE geomembranes are also meant for long term use and will remain strong and durable for years. Its best use relates to industrial applications, such as liquid storage tanks, environmental and animal waste containments.
PVC Geomembrane
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) geomembranes is a thermoplastic waterproofing material made with vinyl, plasticisers and stabilisers. The polyvinyl chloride resin used for PVC geomembranes is made by cracking ethylene dichloride into a vinyl chloride monomer. It is then polymerized to make PVC resin.
It is tear, puncture and abrasion resistant meaning the material is perfect for preventing contaminants from entering water sources and maintaining potable drinking water. PVC geomembranes are highly flexible and are best suited for landfills and canals, tank linings, soil remediation and wastewater lagoon liners.
EPDM Geomembrane
Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) geomembrane is a flexible and durable material that can resist punctures and extreme weather conditions. It has a rubber-like texture and is UV-stable with great strength.
EPDM geomembranes are typically used as surface barriers for dams and other irrigation sites. It’s also easy to install, which is why backyard landscapers use this type of geomembrane. It’s suitable for agricultural applications such as irrigation ponds as well as liners and covers.
RPP Geomembrane
Reinforced Polypropylene (RPP) geomembranes are polyester reinforced liners for long term water containment and industrial waste applications. It’s made from a UV-stabilized polypropylene copolymer that gives the material flexibility, stability and chemical resistance.
RPP geomembranes are perfect for applications where folds appear due to uneven and inconsistent weather conditions. It is supported with nylon scrim to ensure it remains strong and durable. This geomembrane type is typically used in municipal applications, aqua and horticulture, evaporation pond liners and mine tailings.
TRP Geomembrane
Reinforced Polyethylene (TRP) geomembranes are almost the same as the RPP, but use polyethylene fabric instead of polyester. This is an ideal option for lining your temporary retaining ponds.
TRP geomembranes are also a durable solution for soil remediation. Its physical properties include chemical resistance, low temperature range and ultraviolet stability. This type of geomembrane is used for canals, industrial tarps, landfills, agricultural and municipal applications.
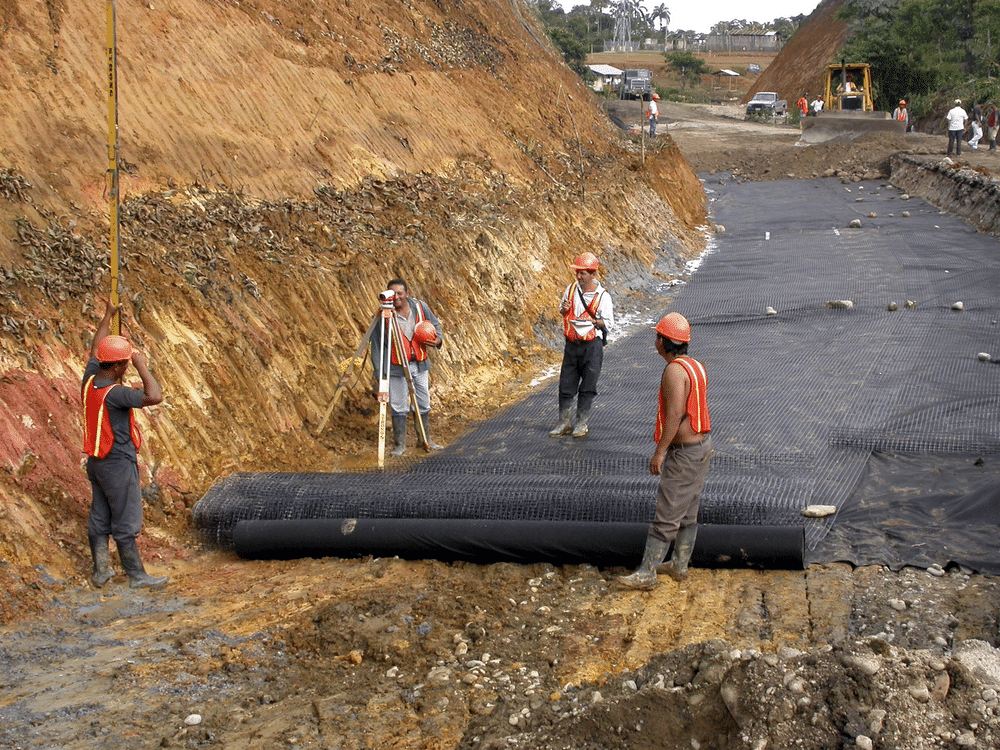
Installation
Geomembrane liner installation is very technical. It requires welding equipment and a qualified welder to install them properly on site. Please see our HDPE Liner Installation manual for more information. The most common method of securing the liners on side slopes is by means of an anchor trench around the perimeter.

Relevant Regulations
Quality standards are crucial when purchasing geomembrane liner for your project. HDPE geomembrane’s physical properties such as tensile strength and tear resistance are calculated based on test methods specified by ASTM and GSI.
ASTM International
Because of their extensive history in this field, the American Society of Testing and Materials (ASTM) is responsible for the bulk of generic geomembrane test methods.
Geosynthetic Institute (GSI)
Geosynthetic Institute (GSI) is a group of organisations involved in geosynthetics. They provide comprehensive standards, specifications, guidelines and practices for all types of polymeric geosynthetic materials through Geosynthetic Research Institute (GRI.)
GSI includes test methods that are not addressed by ASTM.
Geomembrane Durability
Several factors affect the degradation of polymers within the geomembranes. Factors like UV exposure, chemical impact, biological contaminants (animal, fungi) and thermal expansion impact the life span of the geomembranes.
Technical expertise is necessary when selecting the right type and thickness for the project. This is generally based on the depth of the containment and the geo technical conditions of the site.
Please see the corresponding depth and thickness chart for a general overview. This is for guidance only, speak to one of our technical consultants for advice relevant to your requirements.
|
Liquid depth ≤ 1m |
0.5mm thickness |
|
Liquid depth 1m to 2m |
1.0mm thickness |
|
Liquid depth 2m to 4m |
1.5mm thickness |
|
Liquid depth ≥ 4m |
2.0mm thickness |
