Erosion Control
+86-159 9860 6917
info@geofantex.com
geofantex@gmail.com
+86-400-8266163-44899
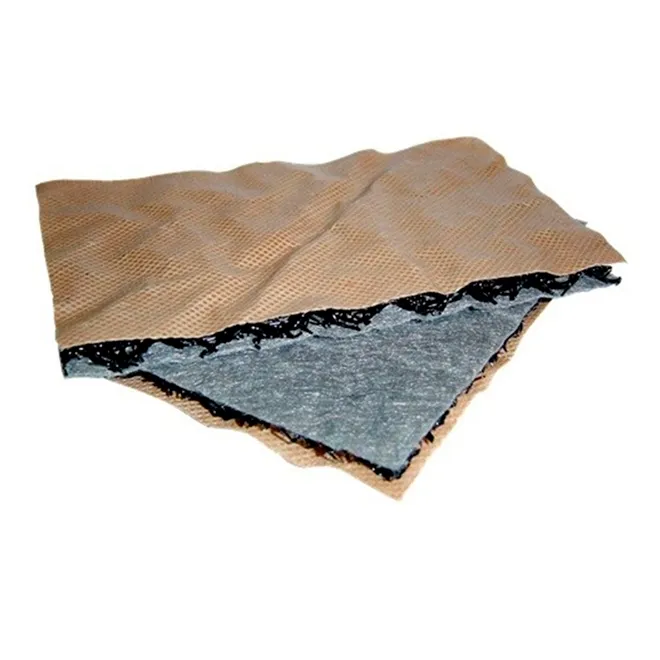
Geosynthetics play a crucial role in enhancing hydraulic structures and managing erosion and sediment control. Geofantex offers high-performance, non-degradable products that improve durability, reliability, and performance in watercourses by enhancing flow velocities and shear resistance. These solutions, whether used with or without vegetation, effectively reduce or eliminate soil erosion of the underlying subgrade. Additionally, Geofantex’s erosion and site management systems provide temporary and permanent erosion control solutions, replacing traditional materials like rock or concrete and offering cost-saving opportunities while protecting the environment. From hydraulic mulch fibers to erosion control geotextiles, Geofantex offers a comprehensive suite of products to meet various erosion control needs, ensuring stability and cost-effectiveness in slope and channel stabilization.
The Main Functions of Various Geosynthetics:
| SEPARATION | REINFORCEMENT | FILTRATION | DRAINAGE | WATERPROOF | PREVENTION | POLLUTION PREVENTION | PROTECTION | CONSOLIDATE | |
| GEOTEXTILE | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||
| GEOMEMBRANE | √ | √ | √ | ||||||
| GEOGRID | √ | √ | |||||||
| GEONET | √ | ||||||||
| GEOTUBE | √ | ||||||||
| GEOCELL | √ | √ | |||||||
| GCL | √ | √ | |||||||
| GEOCOMPOSITE | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||
| GEOCONCRETE BLANKET | √ | √ | √ | ||||||
| Drainage Board B | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||
| Storage and Drainage Board | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||
| Grass Paver | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||
| Macmat | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||
| GeoFanTex®GD 2L | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||
| GeoFanPipe® FP | √ | ||||||||
| GeoFanDrain® BC | √ | √ | √ | ||||||
| GeoFanPipe® DCP | √ | √ | |||||||
| GeoFanTRM® Geomantles | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ |
Get Free Sample
We’ll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)