Mining
+86-159 9860 6917
info@geofantex.com
geofantex@gmail.com
+86-400-8266163-44899
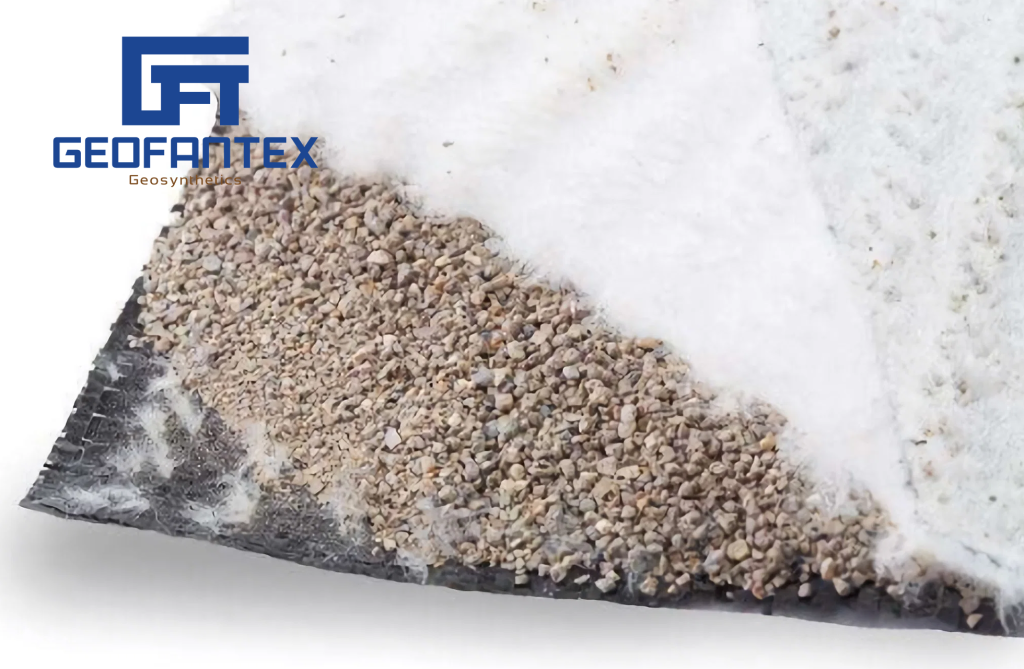
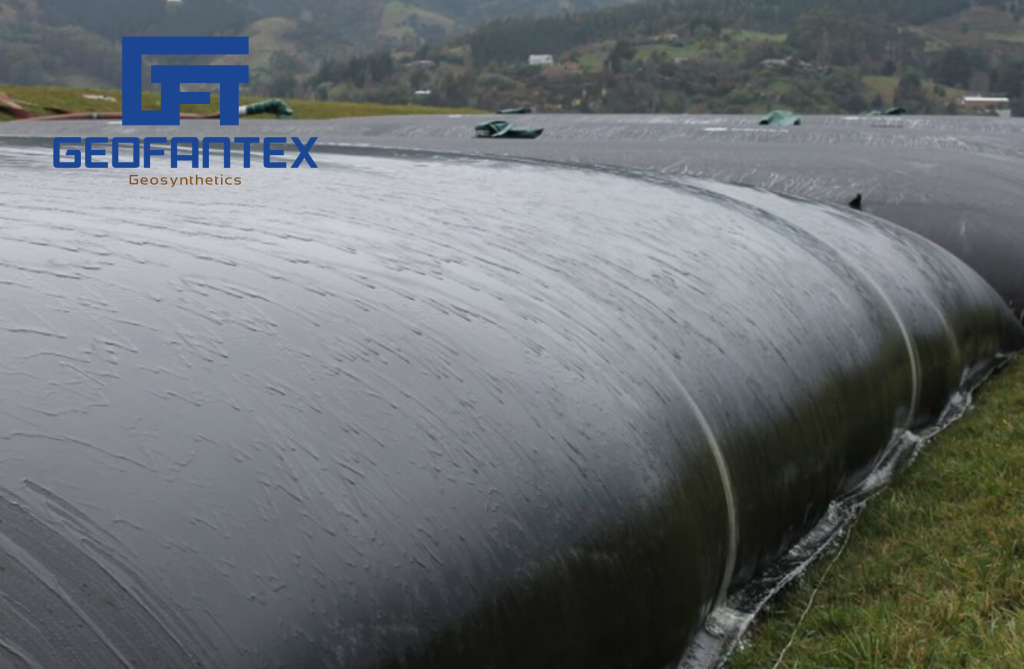
The annual growth of Geosynthetics’ usage in the mining industry is attributed to their durability and ability to meet economic and environmental goals. Common applications include tailing dams, secondary containments, heap leach pads, landfill ponds, and rehabilitation, as well as stabilization and reinforcement of tunnels to prevent rockfalls. Geofantex’s range of geosynthetic products finds diverse applications in mining development, operation, and closure, including access road construction, sediment control, pond lining, and tailings containment. Geomembranes and geosynthetic clay liners are primarily utilized for liquid containment and basal liners, while geotextiles provide crucial separation and cushioning layers. Geogrids stabilize soft soils for various construction purposes, and drainage systems are essential for leakage control and protection of lining systems. During site closure, materials are capped, and embankments are reinforced to facilitate vegetation growth.
The Main Functions of Various Geosynthetics:
| SEPARATION | REINFORCEMENT | FILTRATION | DRAINAGE | WATERPROOF | PREVENTION | POLLUTION PREVENTION | PROTECTION | CONSOLIDATE | |
| GEOTEXTILE | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||
| GEOMEMBRANE | √ | √ | √ | ||||||
| GEOGRID | √ | √ | |||||||
| GEONET | √ | ||||||||
| GEOTUBE | √ | ||||||||
| GEOCELL | √ | √ | |||||||
| GCL | √ | √ | |||||||
| GEOCOMPOSITE | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||
| GEOCONCRETE BLANKET | √ | √ | √ | ||||||
| Drainage Board B | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||
| Storage and Drainage Board | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||
| Grass Paver | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||
| Macmat | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||
| GeoFanTex®GD 2L | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||
| GeoFanPipe® FP | √ | ||||||||
| GeoFanDrain® BC | √ | √ | √ | ||||||
| GeoFanPipe® DCP | √ | √ | |||||||
| GeoFanTRM® Geomantles | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ |
Get Free Sample
We’ll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)