Landfill
+86-159 9860 6917
info@geofantex.com
geofantex@gmail.com
+86-400-8266163-44899
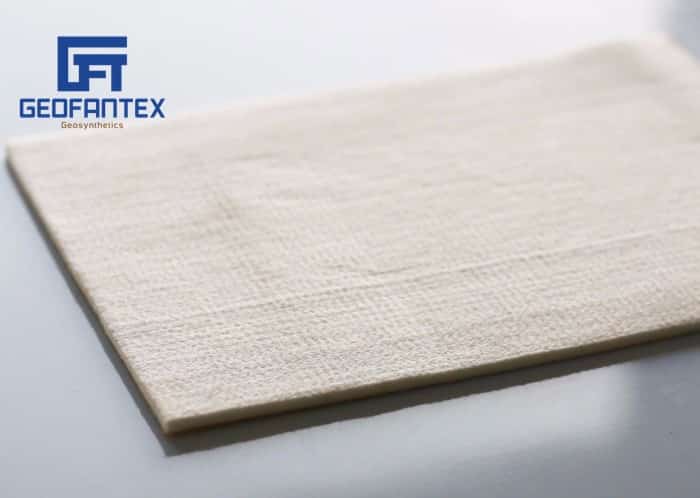
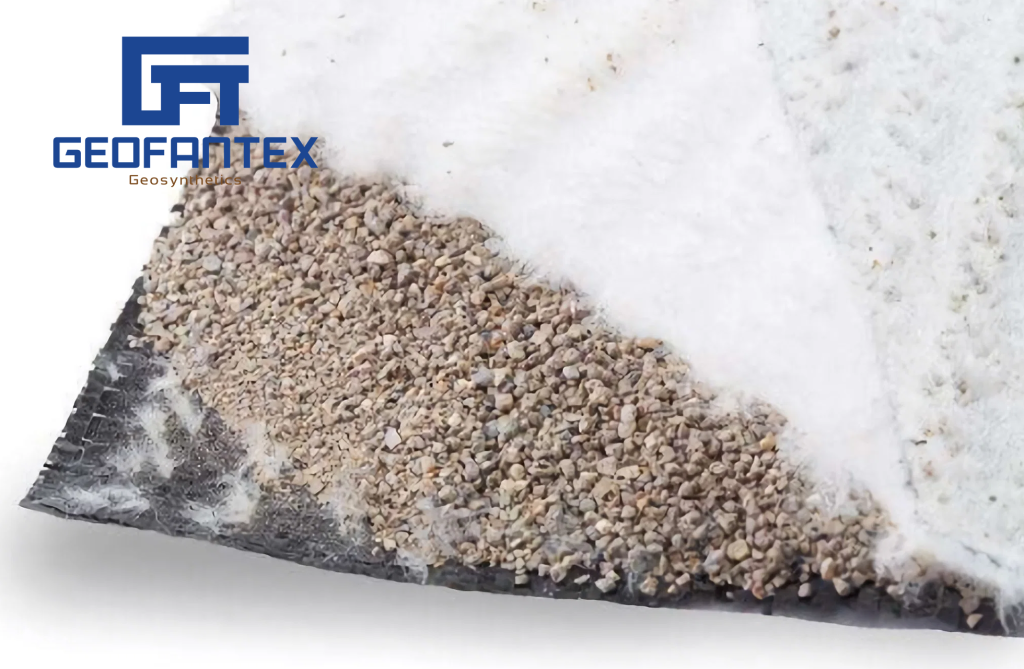
Landfills, serving as disposal facilities for various types of waste including domestic, municipal, industrial, contaminated, and hazardous waste, aim to contain waste in a manner protective of human health and the environment. Geosynthetics play a crucial role in landfill operations, serving two primary functions: in base barrier systems, they minimize leachate escape into the foundation and prevent groundwater contamination, while in cap barrier systems, they control moisture filtration, collect gas flows, prevent odors and disease sources, and meet erosion and aesthetic criteria.
Geofantex offers high-quality HDPE geomembranes, certified by government regulators, for use in landfill applications. Additionally, protective cushion geotextiles and drainage systems, such as geonets or geocomposites, ensure effective fluid collection and diversion while safeguarding against potential contamination. These geosynthetic solutions not only ensure environmental protection and groundwater safety but also offer durability, cost-effectiveness, and resource efficiency compared to conventional construction methods.
The Main Functions of Various Geosynthetics:
| SEPARATION | REINFORCEMENT | FILTRATION | DRAINAGE | WATERPROOF | PREVENTION | POLLUTION PREVENTION | PROTECTION | CONSOLIDATE | |
| GEOTEXTILE | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||
| GEOMEMBRANE | √ | √ | √ | ||||||
| GEOGRID | √ | √ | |||||||
| GEONET | √ | ||||||||
| GEOTUBE | √ | ||||||||
| GEOCELL | √ | √ | |||||||
| GCL | √ | √ | |||||||
| GEOCOMPOSITE | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||
| GEOCONCRETE BLANKET | √ | √ | √ | ||||||
| Drainage Board B | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||
| Storage and Drainage Board | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||
| Grass Paver | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||
| Macmat | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||
| GeoFanTex®GD 2L | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||
| GeoFanPipe® FP | √ | ||||||||
| GeoFanDrain® BC | √ | √ | √ | ||||||
| GeoFanPipe® DCP | √ | √ | |||||||
| GeoFanTRM® Geomantles | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ |
Get Free Sample
We’ll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)