What Is a Geogrid?
Learn how geogrids reinforce soil, stabilize slopes, and strengthen roadways for durable, cost-effective infrastructure.
Tel: +86-411-39569550 | E-mail: info@geofantex.com/geofantex@gmail.com
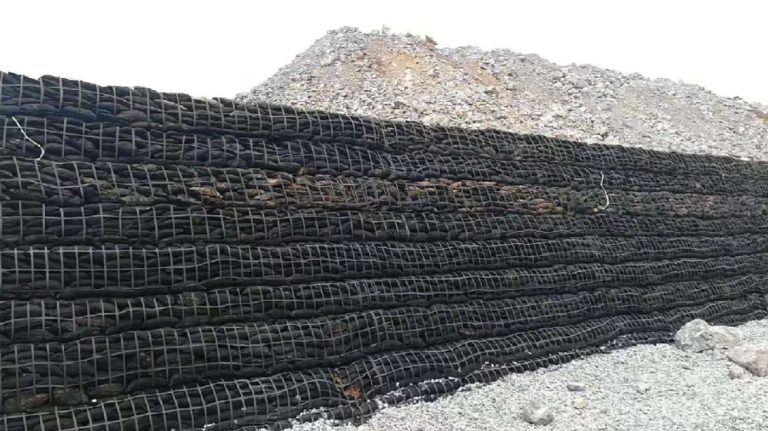

Learn how geogrids reinforce soil, stabilize slopes, and strengthen roadways for durable, cost-effective infrastructure.
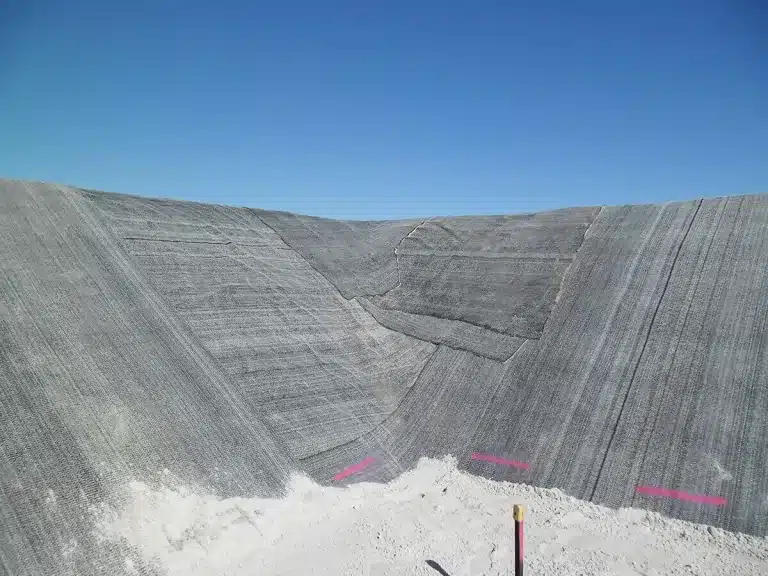

A geosynthetic reinforced integrated bridge is a structure where geosynthetic materials—such as geogrids or geotextiles.
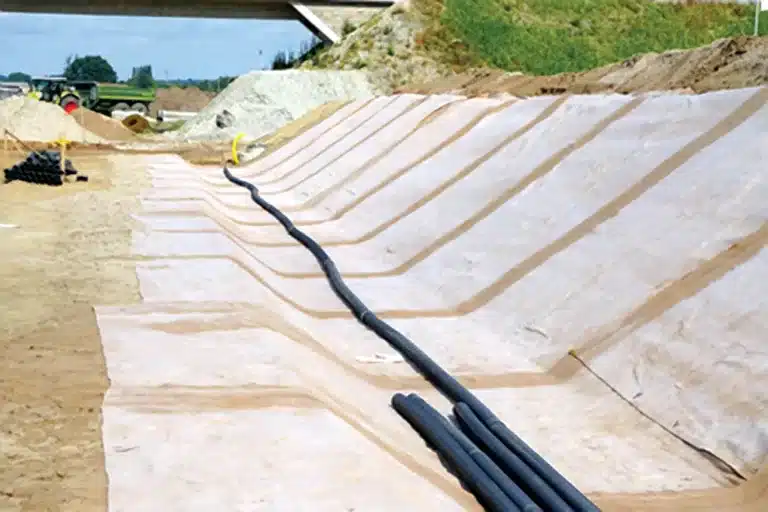

Geosynthetic reinforced retaining walls provide effective solutions for a range of construction challenges.

Using geotextile fabric in various civil engineering applications provides several environmental benefits.

When it comes to geosynthetics, two materials that often come up in discussions are geogrid vs geotextile.

The geocomposite supplier provided a customized geocomposite material designed to offer both filtration and separation.

Geocomposite layer was employed to create an impermeable barrier between the waste and the surrounding soil.
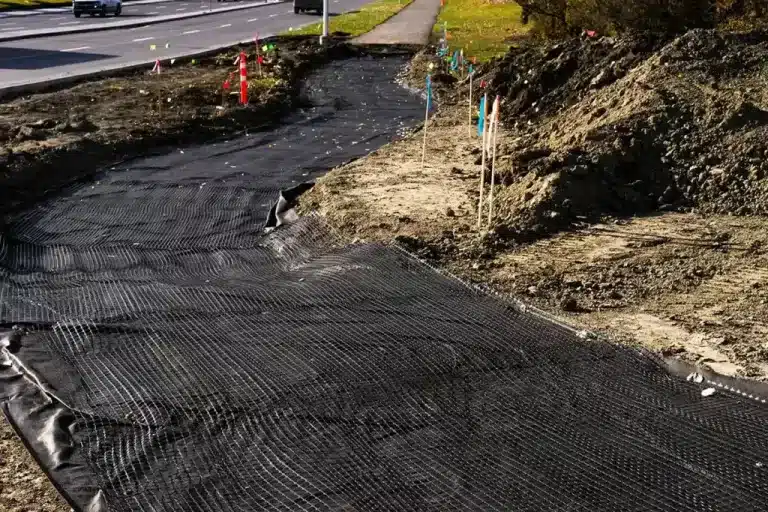

These advancements underscore the industry’s commitment to addressing geonet questions through innovation and strategic investments.
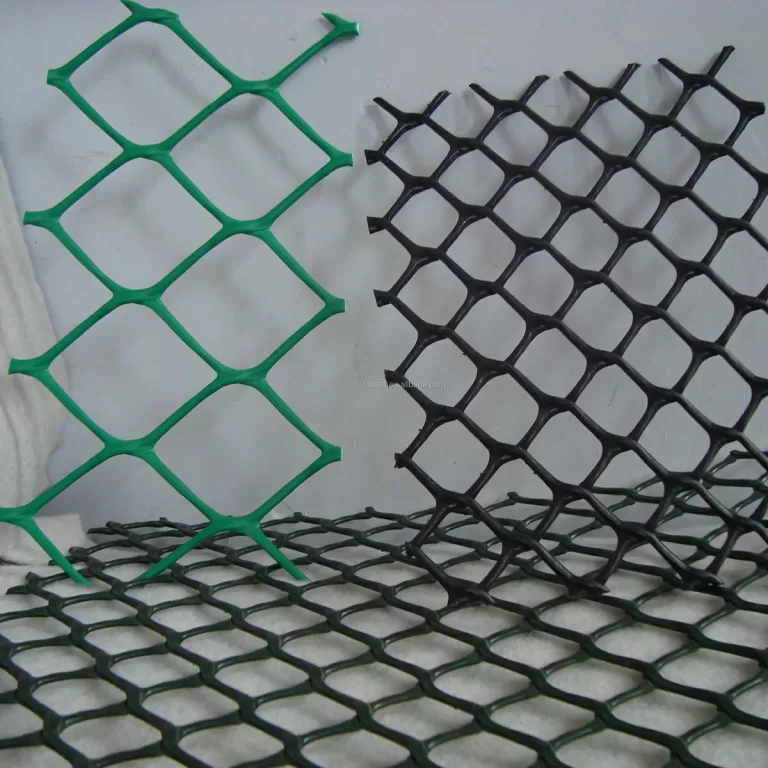
In recent industry developments, geonet for gravel has emerged as a game-changer in infrastructure projects worldwide.
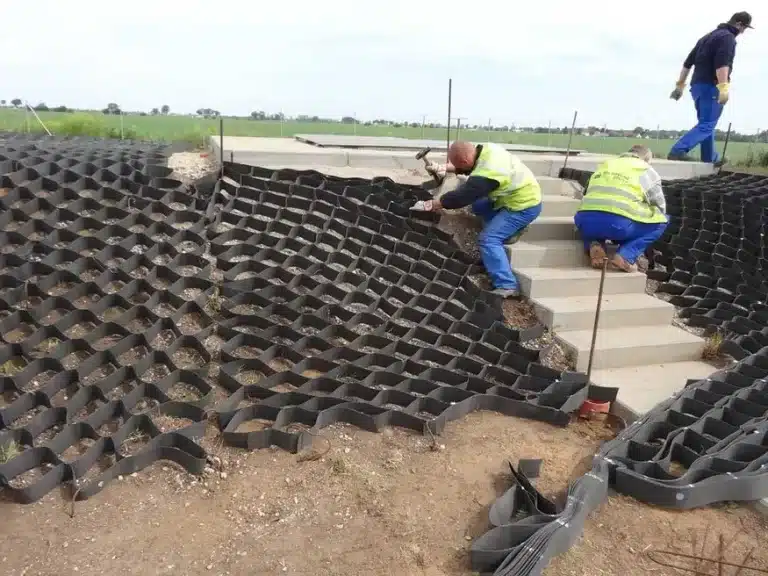

In today’s fast-evolving construction landscape, geocell roofing is setting a new standard for efficiency and sustainability.
End of content
End of content
WhatsApp us