Contents [hide]
- 1 What is Geotextile?
- 2 Types of Geotextiles
- 2.1 1) Non-woven Geotextile Fabric
- 2.2 2) Woven Geotextile Fabric
- 2.3 3) Knitted Geotextile
- 3 Functions of Geotextiles
- 3.0.1 1) Separation
- 3.0.2 2) Filtration
- 3.0.3 3) Reinforcement
- 3.0.4 4) Sealing
- 4 Geotextile Applications
- 5 FAQ Section
- 5.1 What is Woven geotextile fabric?
- 5.2 What is the Function of Geotextile?
- 5.3 What is the lifespan of Geotextile Fabric?
- 5.4 Is geotextile fabric necessary?
- 5.5 What is a geotextile membrane?
- 5.6 What are the types of Geotextile Fabrices?
What is Geotextile?
Geotextile is a permeable textile material used to increase soil stability, provide erosion control, or aid in drainage. Depending on their manufacturing method, they may be woven geotextile fabric or non-woven geotextile fabric, based upon the type of application they are intended for.
Woven and non-woven fabrics have different production methods. While non-woven geotextile fabrics comprise fibers, filaments, or other elements that are joined together randomly, in the case of woven fabrics, these yarns, fibers, or filaments are intertwined. In this new post, we will focus on the features of applications of woven geotextile fabrics.
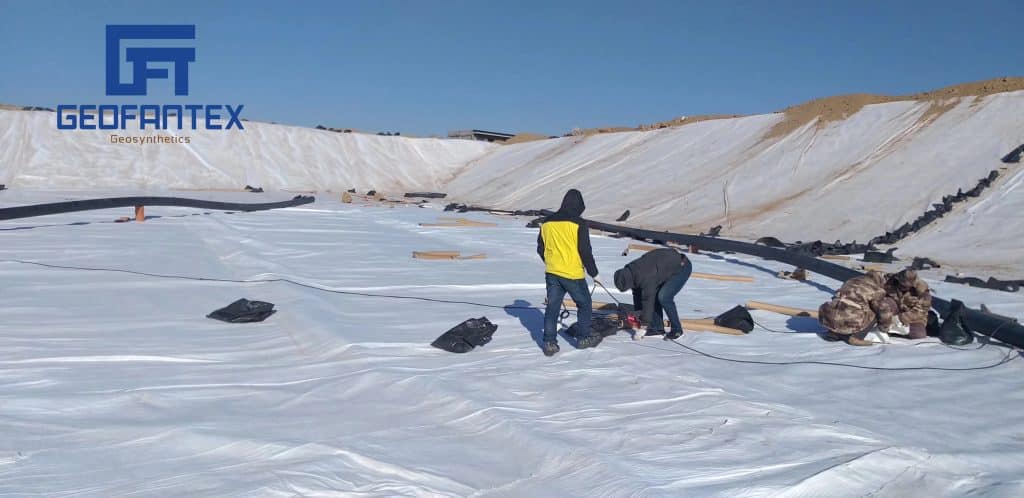

Types of Geotextiles
The geotextiles have the following types:
- Non-woven Geotextile Fabric
- Woven GeotextileFabric
- Knitted Geotextile
1) Non-woven Geotextile Fabric
They resemble felt and provide planar water flow. They are commonly known as filter fabrics, although woven monofilament geotextiles can also be referred to as filter fabrics.
Non-wovens in geotextiles laid to form a roll and are light and easy to handle, despite their strength and toughness.
It has higher flexibility and movement than woven geotextiles. As a result, it is ideal for use in separation. The thickness and puncture resistance of non-woven geotextile provides cushioning and protection to geomembranes in the areas of landfills, ponds, drainage, dams, river canals, coastal work, barriers, and mining design.
Non-woven geotextiles are also used in applications where filtration and drainage are required because of their smaller opening sizes and ability to filter smaller particle sizes which allow water to pass. It is ideal for separating paving applications in asphalt and concrete roadways.
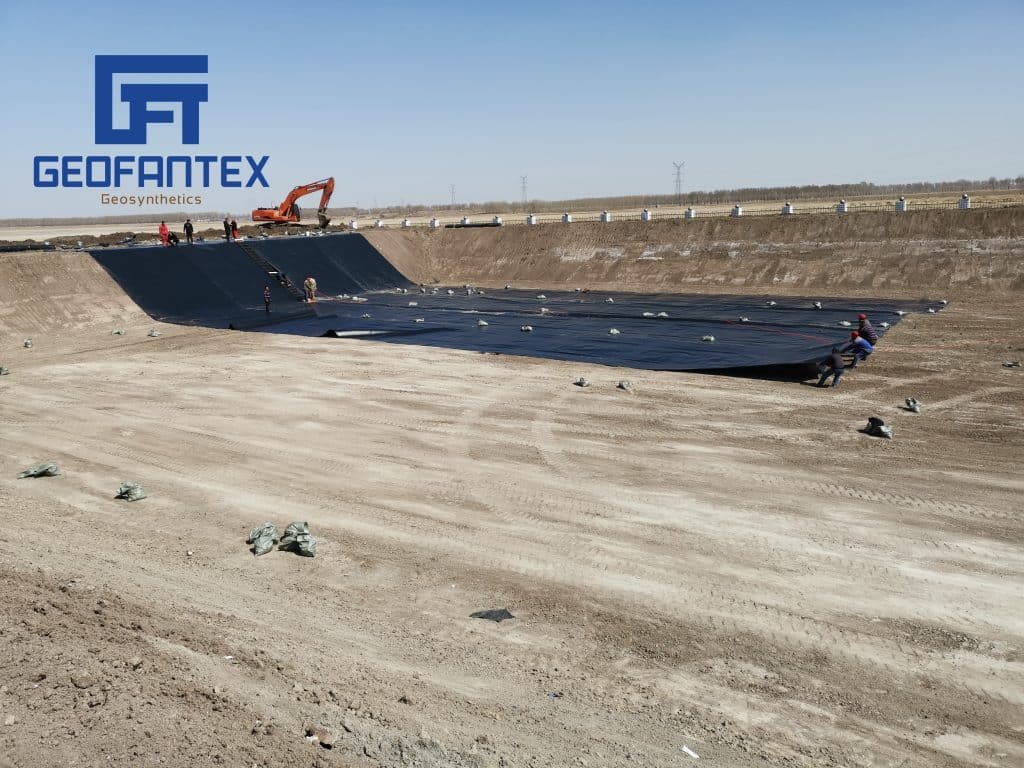

2) Woven Geotextile Fabric
Woven geotextile fabrics are defined as any material manufactured by intertwining two or more yarns, fibers, filaments, strips, or other elements, usually at right angles, i.e., both lengthwise and crosswise, by means of a textile process. These fabrics are mainly used in the construction sector.
Woven geotextile fabrics provide biaxial resistance, i.e., in the same direction as they were manufactured. Due to the structure and features of the strips used in their production, they usually have high resistance and low deformation, making them suitable for the reinforcement of roads, slopes, walls, and foundations.
There are two types of strands: slit films, which are flat, and monofilaments, which are round.
Woven slit-film geotextiles are generally preferred for applications where high strength properties are needed, and filtration requirements are less critical. These fabrics reduce localized shear failure in weak subsoil conditions and aid construction over soft subsoils.
3) Knitted Geotextile
Knitted geotextiles are manufactured by the process of interlocking a series of loops of yarn together. All of the knitted geosynthetics are formed by using the knitting technique in conjunction with some other method of geosynthetics manufacture, such as weaving.
Apart from these three geotextiles, other geosynthetics used are geonets, geogrids, geo-cells, geomembranes, geocomposites, etc., each having their own distinct features and uses for special applications.
Functions of Geotextiles
Six discrete functions define the mode of operation of a geotextile in any application:
1) Separation
The separation function of geotextile is majorly used in the construction of roads. Geotextile prevents the intermixing of two adjacent soils. For example, by separating fine subgrade soil from the base course aggregates, the geotextile preserves the drainage and the strength characteristics of the aggregate material.
Some of the application areas are:
- Between subgrade and stone base in unpaved and paved roads and airfields.
- Between subgrade in railroads.
- Between landfills and stone base courses.
- Between geomembranes and sand drainage layers.
2) Filtration
The equilibrium of the geotextile-to-soil system allows for adequate liquid flow with limited soil loss across the plane of the geotextile. Porosity and permeability are the major properties of geotextiles that involve infiltration action.
A common application illustrating the filtration function is the use of a geotextile in a pavement edge drain, as shown in the figure above.
3) Reinforcement
The introduction of geotextile in the soil increases the tensile strength of the soil the same amount steel does in concrete. The strength gained in soil due to the introduction of geotextile is by the following three mechanisms:
- Lateral restraint through interfacial friction between geotextile and soil/aggregate.
- Forcing the potential bearing surface failure plane to develop an alternate higher shear strength surface.
- Membrane type of support of the wheel loads.
4) Sealing
A non-woven geotextile fabric layer is impregnated between existing and new asphalt layers. The geotextile absorbs asphalt to become a waterproofing membrane minimizing the vertical flow of water into the pavement structure.
Geotextile Applications
- Railways: Geotextiles are used to separate the individual soil layers without impeding groundwater circulation where the ground is unstable. This also keeps the layer materials from shifting sideways under the constant shocks and vibrations from passing trains.
- Roads: Geotextiles are widely used in road construction, reinforcing the soil by adding tensile strength. Geotextiles can be used as a rapid dewatering layer in the roadbed.
- Agriculture: It is used for mud control. For the improvement of muddy paths and trails, those used by cattle or light traffic, non-woven fabrics are used and are folded by overlapping to include the pipe or a mass of grit.
- Coastal work: Geotextile fabric can help prevent erosion in river banks, canals, and other bodies of water.
- Drainage: Geotextiles are used as filtering mechanisms for drainage in roads, highways, earth dams, reservoirs, retaining walls, drainage trenches, and many other applications.
FAQ Section
What is Woven geotextile fabric?
Woven geotextile fabrics are defined as any material manufactured by intertwining two or more yarns, fibers, filaments, strips, or other elements, usually at right angles, i.e., both lengthwise and crosswise, by means of a textile process.
These fabrics are mainly used in the construction sector. This is, therefore, the simplest type of fabric manufacturing, also known as the “simple pattern” method, which results in a flat structure.
What is the Function of Geotextile?
The main function of the geotextile is to improve the soil characteristics. They are typically used to improve soil characteristics before building embankments, roads, pipelines, and earth-retaining structures. Geotextiles have several functions, which include filtration, drainage, reinforcement, cushioning, waterproofing and separation.
What is the lifespan of Geotextile Fabric?
The lifespan of the geotextile fabric can be stretched up to 20 years through various treatments and blending.
Is geotextile fabric necessary?
Yes, if you want your driveway to last. Having geotextile fabric under your gravel driveway will prevent you from continually needing to add more aggregate base to your road since the rock will drop into the subgrade layer.
What is a geotextile membrane?
Geotextile membranes are the name given to large sheets of fabric that are used in ground engineering and drainage applications, such as ground filtration, soil separation, ground reinforcement, and land drains.
What are the types of Geotextile Fabrices?
The geotextile fabric has the following types:
- Non-woven Geotextile Fabric
- Woven Geotextile Fabric
- Knitted Geotextile
