+86-159 9860 6917
info@geofantex.com
geofantex@gmail.com
+86-400-8266163-44899
Geogrids are a revolutionary technology in the field of civil engineering, offering enhanced stability and support in various construction and landscaping projects. These grid-like synthetic materials are crucial for reinforcing soil, improving load capacity, and preventing erosion. This article explores the pivotal scenarios where geogrids play an essential role, specifically focusing on their applications in retaining walls and other structural needs.
When should you use Geogrid on a retaining wall?
You should use geogrid on a retaining wall when the wall is taller than 3-4 feet or when the wall is retaining a significant amount of soil or other material. Geogrid is particularly important in these situations because it reinforces the soil behind the wall, improving its stability and reducing the pressure exerted on the wall. Here are specific scenarios where geogrid is essential:
- Tall Walls: For retaining walls over 3-4 feet, geogrid helps to distribute the weight of the soil over a broader area, reducing the likelihood of wall failure.
- Poor Soil Conditions: If the soil behind the wall is loose, sandy, or clayey, geogrid provides additional reinforcement, preventing the soil from shifting and causing the wall to lean or collapse.
- Sloped Backfill: When the backfill material behind the wall is sloped or if the wall is on a slope, geogrid is necessary to stabilize the soil and prevent erosion or sliding.
- Heavy Loads: If the retaining wall is supporting heavy loads, such as driveways, parking areas, or structures, geogrid increases the wall’s strength and capacity to bear the extra weight.
- Water Management: In areas with high water tables or poor drainage, geogrid helps to manage hydrostatic pressure behind the wall by reinforcing the soil and allowing proper drainage.
Using geogrid in these situations ensures the longevity and stability of the retaining wall, reducing the risk of costly repairs or failures.
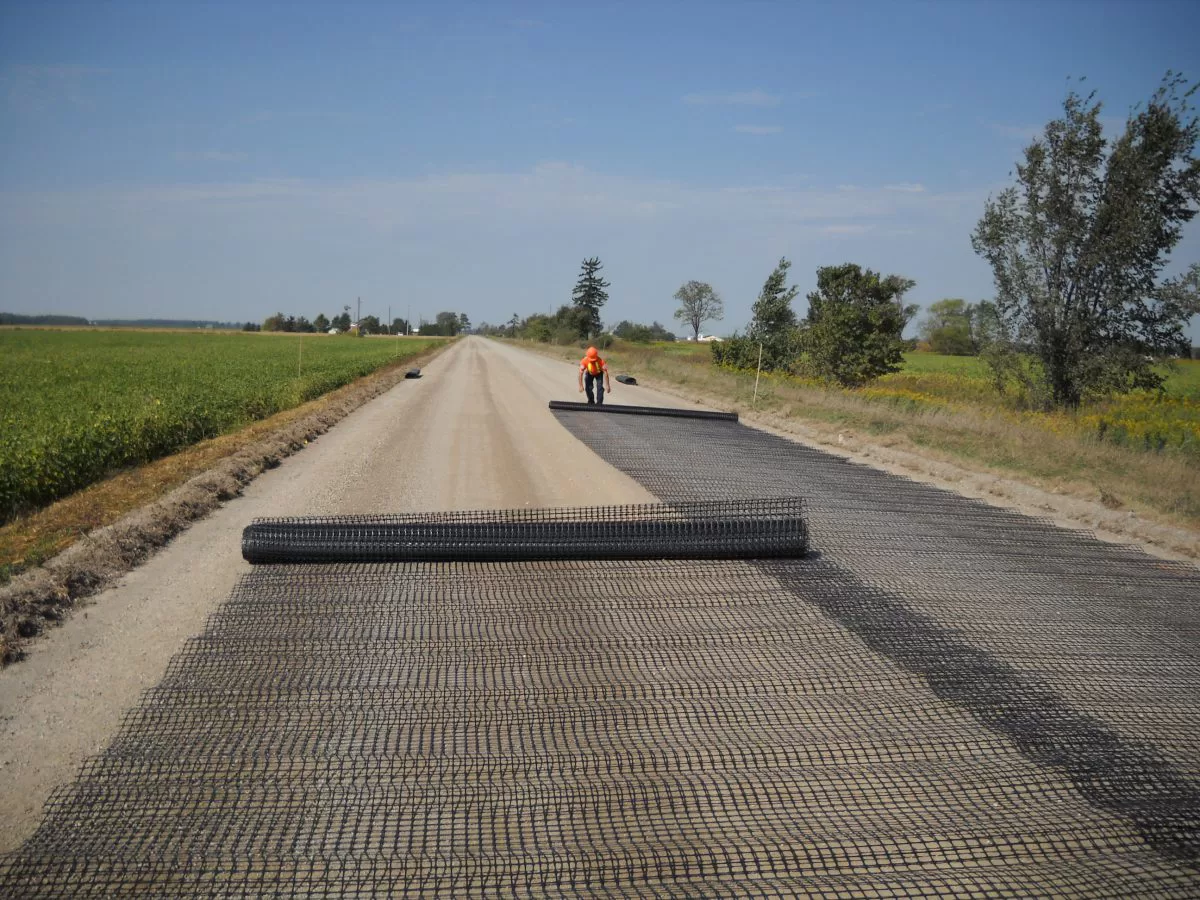

What is Geogrid used for?
Geogrid is a geosynthetic material used primarily for soil reinforcement. It is a grid-like structure made from materials such as polymeric plastic, polyester, or fiberglass. The open grid structure allows soil or aggregate to interlock with the geogrid, providing enhanced stability and strength to the soil or other materials it is used with. Here are the primary uses of geogrid:
- Reinforcement of Retaining Walls: Geogrid is commonly used to reinforce retaining walls by improving the wall’s ability to withstand lateral earth pressures. The geogrid is layered between the blocks or stones of the wall and the backfill material, creating a reinforced soil structure that holds together more effectively.
- Slope Stabilization: On slopes, geogrid is used to stabilize the soil and prevent erosion. By reinforcing the soil, geogrid helps maintain the slope’s integrity, reducing the risk of landslides or soil movement. It is particularly useful in steep slope situations where soil stability is a concern.
- Pavement Support: Geogrid is also used in road construction and other paved areas to improve the load-bearing capacity of the soil. It is laid beneath the pavement or road base, where it distributes the load more evenly, reducing the likelihood of rutting or cracking in the pavement.
- Embankment Reinforcement: In the construction of embankments or raised areas of earth, geogrid is used to reinforce the fill material, ensuring that the embankment remains stable and can support additional loads. This is particularly important in areas with weak or soft soils.
- Foundation Reinforcement: Geogrid is sometimes used beneath building foundations, particularly in areas where the underlying soil is weak or prone to settling. The geogrid helps distribute the load of the building more evenly, reducing the risk of uneven settling or structural damage.
- Landfill and Environmental Applications: Geogrid is used in landfill construction to reinforce the layers of waste and soil, ensuring the stability of the landfill structure. It is also used in other environmental applications, such as reinforcing soil in areas subject to heavy erosion or where vegetation needs support.
Overall, geogrid is a versatile material that provides essential reinforcement in a wide range of civil engineering and construction projects, enhancing the stability, durability, and load-bearing capacity of the structures it supports.
At what height do you need a geogrid?
The requirement for geogrids in retaining wall projects generally starts when the wall height reaches about 3 feet (about 0.9 meters) or greater. This threshold can vary based on the type of soil, the slope of the ground, and the load expected on or near the wall. Consulting with a geotechnical engineer is advisable to assess specific needs based on these factors.
What is the spacing between geogrids?
The spacing between layers of geogrids in a retaining wall or other structures depends on the soil type, wall height, and expected loads. Typically, the spacing ranges from 0.3 to 0.8 meters. Accurate spacing is crucial for ensuring that the geogrid layers effectively share the load and enhance the stability of the soil or structure they are reinforcing. Again, specific projects should be evaluated by a professional to determine the optimal spacing for geogrid layers.
Geogrids are an essential tool in modern construction, offering significant benefits for soil stabilization and structural support. Their use in retaining walls is particularly noteworthy, providing necessary reinforcement that enhances safety and durability. Whether you are planning a small garden wall or a major highway embankment, understanding when and how to effectively utilize geogrids can lead to more successful and sustainable construction projects. By consulting with professionals and adhering to recommended practices for geogrid use, engineers and contractors can ensure that their structures stand the test of time.


Get Free Sample
We’ll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)






















