+86-159 9860 6917
info@geofantex.com
geofantex@gmail.com
+86-400-8266163-44899
In the vast field of civil engineering and construction, the search for materials that combine durability, flexibility, and cost-efficiency is endless. Among the innovations that have made a significant impact in recent years is the biaxial woven geogrid made from polyester. This advanced material has not only revolutionized the way infrastructures are built but also enhanced their longevity and performance. This article dives deep into the fabric of this remarkable technology, answering key questions about its nature, its differences from other materials, and its unparalleled benefits in modern construction.
What is Polyester Geogrid?
Composition: Polyester geogrid is made from high-tenacity polyester yarns that are coated with a polymeric or PVC coating to enhance durability and resistance to environmental factors. The geogrid is designed with a grid-like structure, which provides its primary function of reinforcement.
Properties:
- High Tensile Strength: Polyester geogrid offers excellent tensile strength, making it ideal for reinforcing soil and other construction materials.
- Durability: It is resistant to biological degradation, chemicals, and UV radiation, ensuring long-term performance.
- Flexibility: The material is flexible enough to conform to various surfaces and conditions without losing its structural integrity.
Uses:
- Soil Reinforcement: Polyester geogrid is commonly used to reinforce weak soils, improving their load-bearing capacity.
- Retaining Walls: It is used in the construction of retaining walls to provide additional stability and prevent wall collapse.
- Road Construction: Used in road construction to enhance the strength and longevity of road bases and asphalt layers.
- Slope Stabilization: Helps in stabilizing slopes and preventing landslides by reinforcing the soil.
Benefits:
- Improved Structural Integrity: Enhances the structural integrity of construction projects, reducing the risk of failure.
- Cost-Effective: Reduces the need for extensive excavation and foundation work, leading to cost savings.
- Extended Lifespan: Increases the lifespan of structures by providing long-term reinforcement and stability.
- Environmental Protection: Minimizes the environmental impact by reducing soil erosion and promoting sustainable construction practices.
What is Biaxial Geogrid?
Biaxial Geogrid is a geosynthetic material made from polymers such as polypropylene or polyester. It is manufactured through a process of extruding and stretching the polymer sheets to form a grid-like structure with uniform apertures.
Purpose: The primary purpose of a Biaxial Geogrid is to reinforce soil and aggregate materials. It is designed to provide high tensile strength in both longitudinal and transverse directions. This dual-direction strength helps in distributing loads more effectively and prevents soil and aggregate movement.
Applications
- Road Construction: Used in the subgrade stabilization of roads and highways. Enhances the load-bearing capacity and extends the lifespan of pavements.
- Railway Construction: Reinforces the ballast and sub-ballast layers. Reduces maintenance requirements and improves track stability.
- Retaining Walls: Supports the construction of retaining walls by providing additional strength to the soil. Reduces the need for deep foundations.
- Landfills: Used in landfill liners and covers to prevent erosion and maintain structural integrity.
- Embankments and Slopes: Reinforces embankments and slopes, preventing landslides and erosion. Used in areas with weak or unstable soil conditions.
Benefits
- Increased Durability: Enhances the structural integrity of construction projects.
- Cost-Effective: Reduces the need for additional materials and maintenance.
- Environmental Protection: Helps in soil erosion control and slope stabilization.
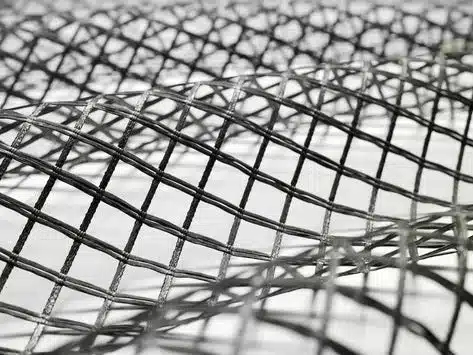
What is the difference between Uniaxial and Biaxial Geogrids?
Structural Characteristics
Uniaxial Geogrids:
- Strength Direction: Designed to provide high tensile strength in one principal direction (typically along the roll length).
- Material: Often made from high-density polyethylene (HDPE) or polypropylene.
- Structure: Elongated rectangular apertures, reinforcing strength predominantly in the longitudinal direction.
Biaxial Geogrids:
- Strength Direction: Provide high tensile strength in both longitudinal and transverse directions.
- Material: Commonly manufactured from polypropylene or polyester.
- Structure: Square or rectangular apertures, distributing strength equally in both directions.
Applications
Uniaxial Geogrids:
- Primary Use: Retaining walls, embankments, and slope stabilization.
- Function: Reinforcement for structures requiring strength in one primary direction, such as tall retaining walls.
Biaxial Geogrids:
- Primary Use: Road and railway base reinforcement, parking lots, and load transfer platforms.
- Function: Reinforcement for surfaces requiring multidirectional strength, enhancing load distribution and preventing subsidence.
Advantages
Uniaxial Geogrids:
- Specialization: Ideal for applications with unidirectional stress, ensuring stability and strength in specific construction scenarios.
- Efficiency: Often more cost-effective for specific reinforcement needs due to focused material usage.
Biaxial Geogrids:
- Versatility: Suitable for a wide range of applications requiring multidirectional stability.
- Load Distribution: Excellent for spreading loads over a larger area, reducing the risk of deformation and prolonging the lifespan of infrastructure.
Uniaxial Geogrids and Biaxial Geogrids serve distinct purposes in civil engineering based on their tensile strength directions and structural applications. Understanding these differences allows for the appropriate selection of geogrids to enhance the durability and performance of construction projects.
What is the difference between Geogrid and Woven Geotextile?
Composition
- Geogrid: Made from polymers such as polypropylene, polyethylene, or polyester. They are created by stretching sheets of material to form a grid-like pattern.
- Woven Geotextile: Constructed by weaving together fibers of polypropylene or polyester to form a fabric.
Structure
- Geogrid: Characterized by a grid structure with open spaces between the ribs. The open grid pattern allows for interlocking with surrounding materials like soil or aggregate.
- Woven Geotextile: Has a tightly woven fabric structure with small openings. The woven pattern gives it high tensile strength.
Functions
- Geogrid: Primarily used for reinforcement. It enhances the structural integrity of soils, provides stability, and distributes loads over a wider area.
- Woven Geotextile: Used for separation, filtration, reinforcement, and stabilization. It prevents the mixing of different soil layers, allows water to pass while retaining soil particles, and provides structural support.
Applications
- Geogrid: Reinforcement of retaining walls and slopes. Base reinforcement for roads, pavements, and railway tracks. Erosion control. Subgrade stabilization.
- Woven Geotextile: Road construction to separate and reinforce soil layers. Erosion control in riverbanks and coastal areas. Filtration in drainage systems. Soil stabilization in construction projects.
The introduction of biaxial woven geogrids made from polyester into the construction and civil engineering sectors has marked a significant advancement in materials technology. Offering superior durability, flexibility, and multidirectional strength, these materials address a myriad of challenges faced by traditional construction methods. Whether it’s enhancing the load-bearing capacity of soil, extending the lifespan of infrastructure projects, or providing cost-effective solutions for complex engineering problems, biaxial woven geogrids from polyester stand out as a cornerstone of modern construction techniques. As we continue to explore and understand their potential, it’s clear that these innovative materials will play a crucial role in shaping the future of construction and engineering.



Get Free Sample
We’ll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)






















