+86-159 9860 6917
info@geofantex.com
geofantex@gmail.com
+86-400-8266163-44899
The realm of civil engineering and construction has continually evolved, integrating advanced materials and methodologies to ensure the structural integrity and longevity of projects. One such innovation that has significantly impacted the industry is the use of geocomposite drainage systems. This article aims to elucidate the concept of geocomposite drain installation, a sophisticated solution that addresses complex drainage requirements while offering economic and environmental benefits. We will explore what geocomposite drainage layers are, delve into specifics such as thickness, compare geocomposites with geotextiles, and understand the role of composite materials in drainage solutions.
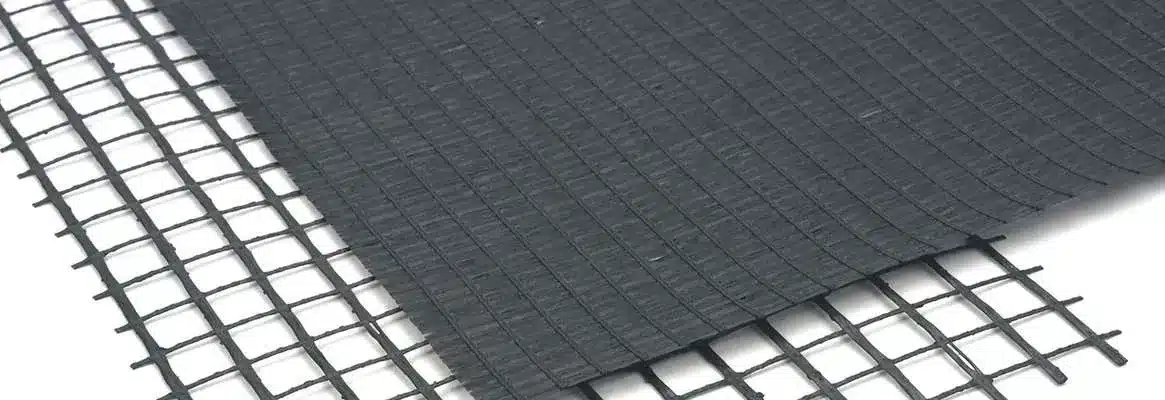

What is a Geocomposite Drainage Layer?
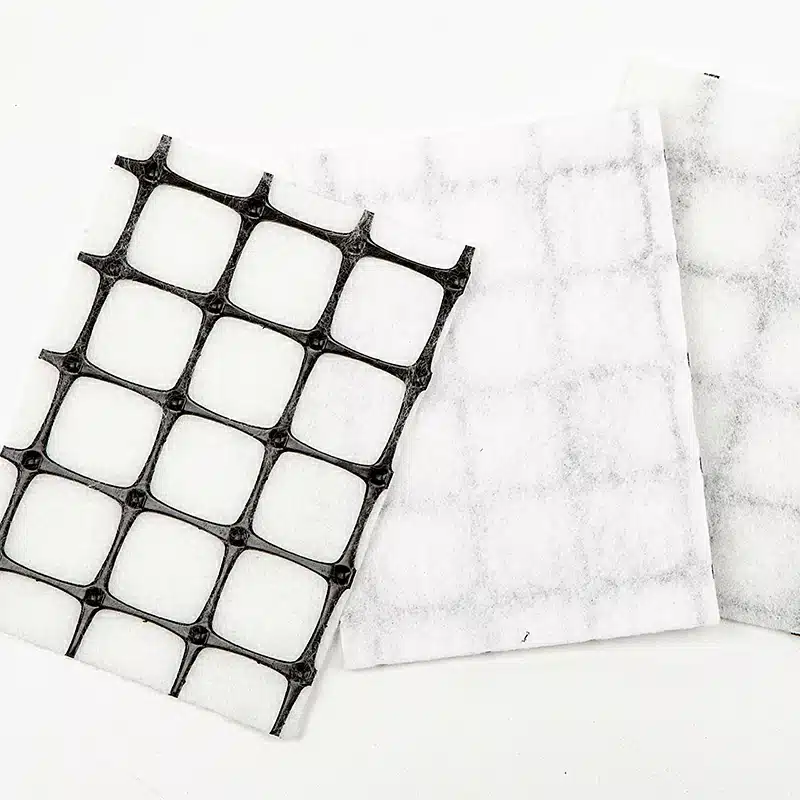
A Geocomposite Drainage Layer is a combination of geotextile and geonet (or other drainage materials) designed to enhance water drainage in construction and civil engineering projects. It improves drainage efficiency while maintaining soil stability.
Key Components:
- Geotextile – Acts as a filter, allowing water to pass while preventing soil clogging.
- Geonet/Core – Provides a structured drainage path for water movement.
- Geocomposite Sheet/Mat – Can include multiple layers for enhanced drainage capacity.
Applications:
- Retaining Walls – Reduces hydrostatic pressure by directing water away.
- Roadways & Railways – Prevents water buildup under pavements.
- Landfills – Facilitates leachate drainage in waste containment.
- Green Roofs & Basements – Manages water infiltration effectively.
Would you like recommendations on selecting a geocomposite for a specific project?
How Thick is a Geocomposite Drain?
The thickness of a geocomposite drain can vary based on its specific application and the materials used in its construction. Here is a structured overview of the factors and standards related to the thickness of geocomposite drains:
Standard Thickness Range
- Typical Thickness: Geocomposite drains generally range in thickness from 5 mm to 10 mm.
- Common Variations: Depending on the application, the thickness can vary, with some specialized geocomposite drains being as thin as 3 mm or as thick as 20 mm.
Variations Based on Applications
- Civil Engineering Projects: Thicker geocomposites (10-20 mm) are often used in road construction, landfills, and retaining walls for better drainage capacity.
- Landscaping and Roof Gardens: Thinner geocomposites (3-5 mm) are used where space constraints require minimal thickness while still providing adequate drainage.
Factors Influencing Thickness
- Load Bearing Requirements: Higher loads require thicker geocomposites to prevent deformation.
- Flow Rate Needs: Applications needing higher water flow rates may use thicker geocomposites with larger flow channels.
- Environmental Conditions: Conditions such as soil type, presence of chemicals, and UV exposure can influence the choice of thickness.
Industry Standards and Guidelines
- ASTM Standards: The American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) provides guidelines for the testing and application of geocomposites, including considerations for thickness.
- ISO Standards: The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) also offers specifications that dictate appropriate thickness for various applications of geocomposite drains.
- Local Regulations: Different regions may have specific building codes and regulations that influence the required thickness of geocomposite drains.
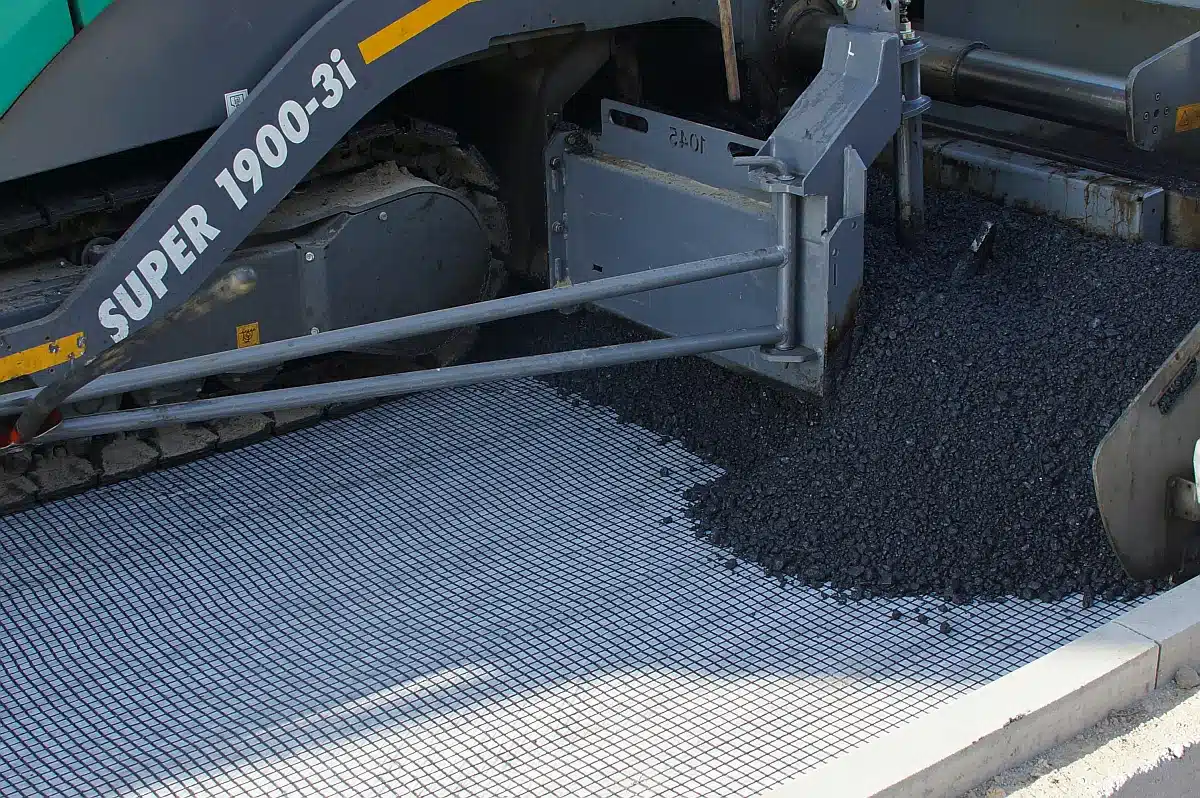

What is the Difference Between Geocomposite and Geotextile?
The difference between geocomposite and geotextile lies in their composition and functionality:
Geotextile
- A single-layer fabric made from synthetic fibers (polypropylene, polyester).
- It is primarily used for filtration, separation, reinforcement, and drainage in soil and construction applications.
- Comes in woven (stronger, used for reinforcement) and non-woven (better for filtration and drainage) types.
Geocomposite
- A multi-layered system that combines two or more geosynthetic materials (e.g., geotextiles, geogrids, geomembranes, or drainage cores).
- Designed to enhance specific functions such as drainage, reinforcement, containment, and protection.
- Examples:
- Geotextile-Geonet Geocomposite (for drainage)
- Geotextile-Geomembrane Geocomposite (for containment)
Key Difference:
- Geotextile is a single material mainly for separation, filtration, and reinforcement.
- Geocomposite is a combination of materials designed for multiple functions, offering better performance in specific applications.
What is a Composite Material for Drainage?
A composite material for drainage is a combination of different materials designed to improve water flow, filtration, and soil stabilization in construction and landscaping applications. These materials typically consist of geotextiles, geonets, geocomposites, or drainage cores that enhance drainage efficiency while preventing soil erosion.
Types of Composite Drainage Materials:
- Geocomposite Drains – A combination of geotextiles and geonets or perforated drainage cores to improve water flow and filtration.
- Geonet Drainage Systems – High-density polyethylene (HDPE) nets sandwiched between geotextiles to allow rapid water movement in landfill liners, retaining walls, and roadbeds.
- Drainage Geomats – Three-dimensional polymer structures that provide excellent drainage while preventing soil displacement.
- Prefabricated Vertical Drains (PVDs) – Used for accelerating soil consolidation in soft ground projects.
Key Benefits:
- Efficient Water Management – Facilitates quick water movement, preventing waterlogging.
- Erosion Control – Protects slopes and embankments from soil loss.
- Lightweight & Easy Installation – Reduces construction time and labor costs.
- Improves Soil Stability – Reinforces soft or weak soils while maintaining permeability.
- Durable & Long-Lasting – Resistant to chemicals, biological degradation, and UV exposure.
These materials are widely used in road construction, retaining walls, landfills, green roofs, and sports fields to enhance drainage performance and extend structural lifespan.
Geocomposite drain installation represents a pivotal advancement in construction and civil engineering, offering a multifaceted approach to solving complex drainage problems. Through the integration of different materials, geocomposite drains provide superior drainage, filtration, and protection functionalities. Understanding the nuances of geocomposite layers, from their thickness to their comparison with geotextiles, and recognizing the role of composite materials in drainage, is crucial for professionals aiming to implement effective water management solutions in their projects. As the construction industry continues to evolve, the application of geocomposite drainage systems is set to become increasingly prevalent, underscoring the importance of staying informed about these innovative materials and techniques.


Get Free Sample
We’ll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)






















