+86-159 9860 6917
info@geofantex.com
geofantex@gmail.com
+86-400-8266163-44899
Biaxial geogrids are an essential component of modern civil engineering projects. In this article, we will explore what biaxial geogrids are, the various types available, and their wide range of applications, and address important questions related to this versatile material.
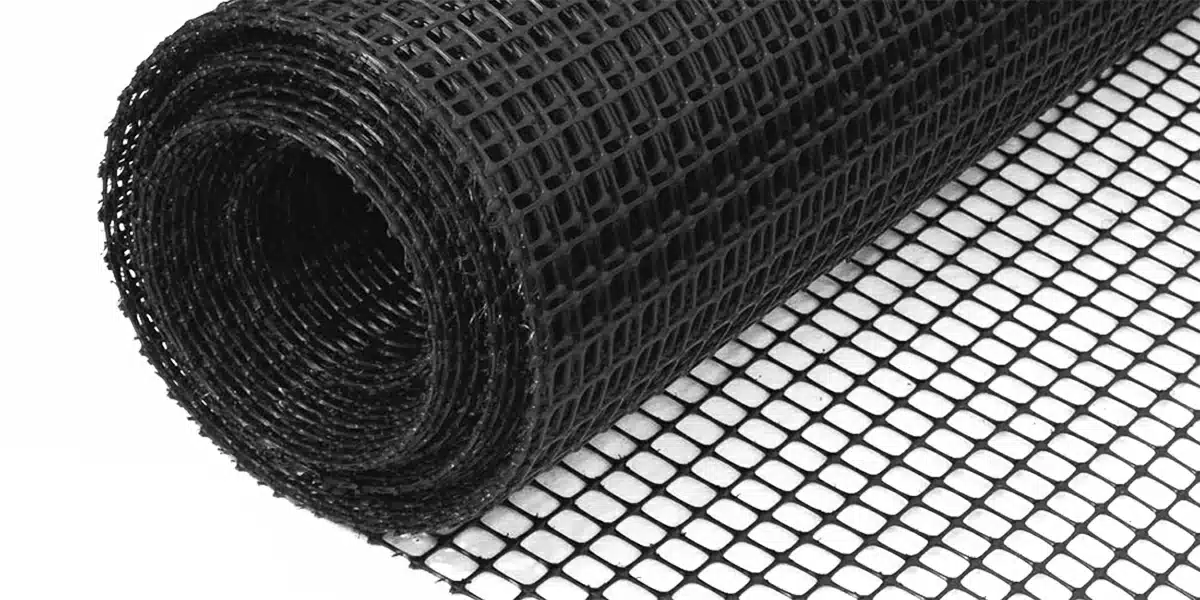

What is biaxial geogrid?
Biaxial geogrid is a high-strength, polymeric grid-like material designed to provide reinforcement, stabilization, and confinement in various civil engineering applications. It consists of a grid structure formed by intersecting sets of ribs, creating a mesh-like pattern that can withstand significant tensile forces. The primary purpose of biaxial geogrids is to improve the mechanical properties of soils and other construction materials.
What are the different types of biaxial geogrids?
Biaxial geogrids come in different forms to suit specific project requirements. The most common types include:
- Uniaxial Biaxial Geogrid: This geogrid offers strength in one primary direction, making it suitable for applications that require reinforcement in a single plane.
- Polypropylene Biaxial Geogrid: Known for its resistance to chemical and biological degradation, this type of geogrid is often used in environments where exposure to harsh substances is a concern.
- High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) Biaxial Geogrid: This geogrid type is highly durable and capable of withstanding heavy loads, making it ideal for load-bearing applications.
- Polyester Biaxial Geogrid: Polyester geogrids are known for their exceptional tensile strength and are often used in applications requiring long-term stability.
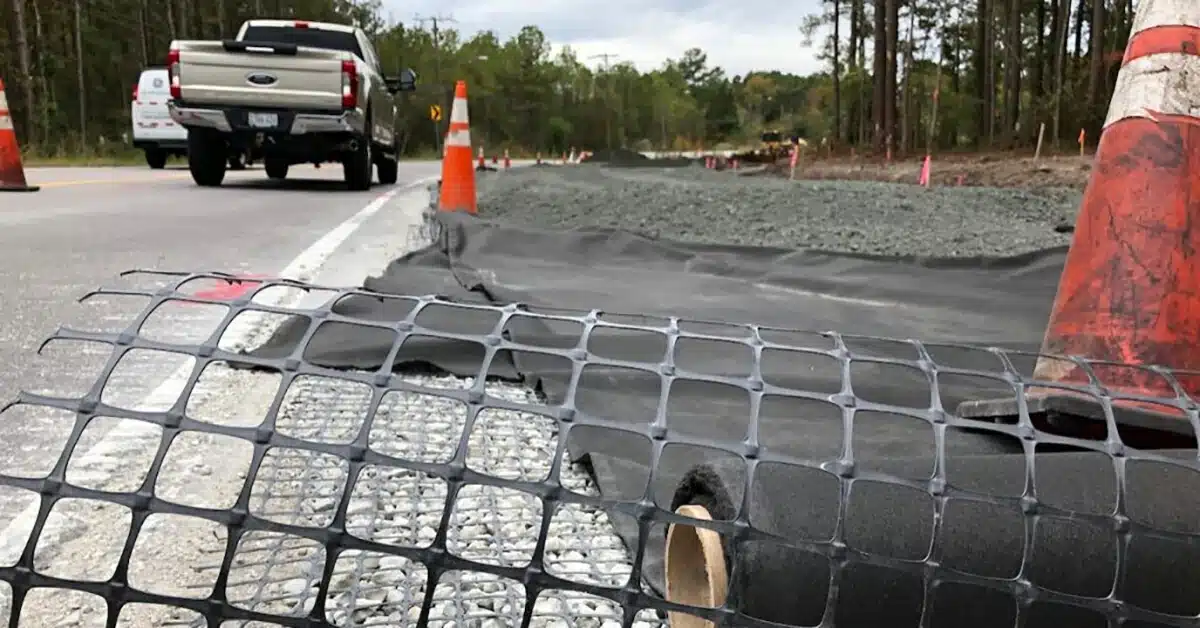

What are the applications of biaxial geogrid?
Biaxial geogrids are versatile materials used in various civil engineering and construction applications due to their strength, durability, and reinforcement properties. Some of their applications include:
- Road Construction: Biaxial geogrids are commonly used in road construction to improve the stability and strength of the pavement layers. They help reduce rutting, extend the road’s life, and distribute the load more uniformly.
- Railway Embankments: They are used in railway track construction to enhance the stability of embankments, prevent soil erosion, and provide reinforcement to the subgrade.
- Slope Reinforcement: Biaxial geogrids are employed in stabilizing slopes and retaining walls. They prevent soil erosion, reinforce steep slopes, and aid in creating more structurally stable surfaces.
- Foundation Support: These grids are used in foundation systems to improve the load-bearing capacity of weak soils, reducing settlement and increasing the stability of foundations for buildings, bridges, and other structures.
- Landfill Construction: Biaxial geogrids play a role in landfill construction by reinforcing the landfill structure, preventing soil erosion, and providing stability to the waste containment system.
- Soil Stabilization: They are employed for stabilizing soil in various applications like parking lots, airports, and industrial yards, reducing the potential for soil movement and improving load distribution.
- Erosion Control: Biaxial geogrids help in erosion control by stabilizing soil on slopes, shores, and embankments, preventing the loss of soil due to water flow or wind.
- Pipeline Trenches: They are used in pipeline construction to improve the load distribution and prevent soil movement in the trench.
How can one choose the right biaxial geogrid for a specific project?
Selecting the appropriate biaxial geogrid for a project depends on several factors, including soil type, project requirements, and budget constraints. Consider the following when making a choice:
- Soil characteristics: Understanding the soil’s properties and behavior is crucial. Different geogrids may be required for cohesive and granular soils.
- Load requirements: Determine the load-bearing requirements of the project, as this will impact the choice of geogrid type and strength.
- Installation conditions: Consider the installation environment, including weather conditions, site access, and equipment availability.
- Budget considerations: Evaluate the project budget and select a geogrid that balances performance and cost-effectiveness.
In conclusion, biaxial geogrids are essential tools in the world of civil engineering and construction. They offer improved stability, durability, and load-bearing capacity, making them a valuable asset in a wide range of applications. Understanding the types, applications, and selection criteria for biaxial geogrids is key to ensuring the success of your infrastructure projects.


Get Free Sample
We’ll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)






















