+86-159 9860 6917
info@geofantex.com
geofantex@gmail.com
+86-400-8266163-44899
In the quest for sustainable construction and landscaping solutions, geocells have emerged as a revolutionary technology. These three-dimensional honeycomb-like structures are designed to stabilize and protect soil in various environmental and construction scenarios, effectively preventing erosion and reducing the risk of soil contamination. This article delves into the environmental benefits of geocells, exploring their applications, effects on soil behavior, and material properties. By understanding the multifaceted advantages of geocells, including their ability to prevent erosion and mitigate soil contamination, stakeholders can make informed decisions that contribute to ecological balance and long-term sustainability.
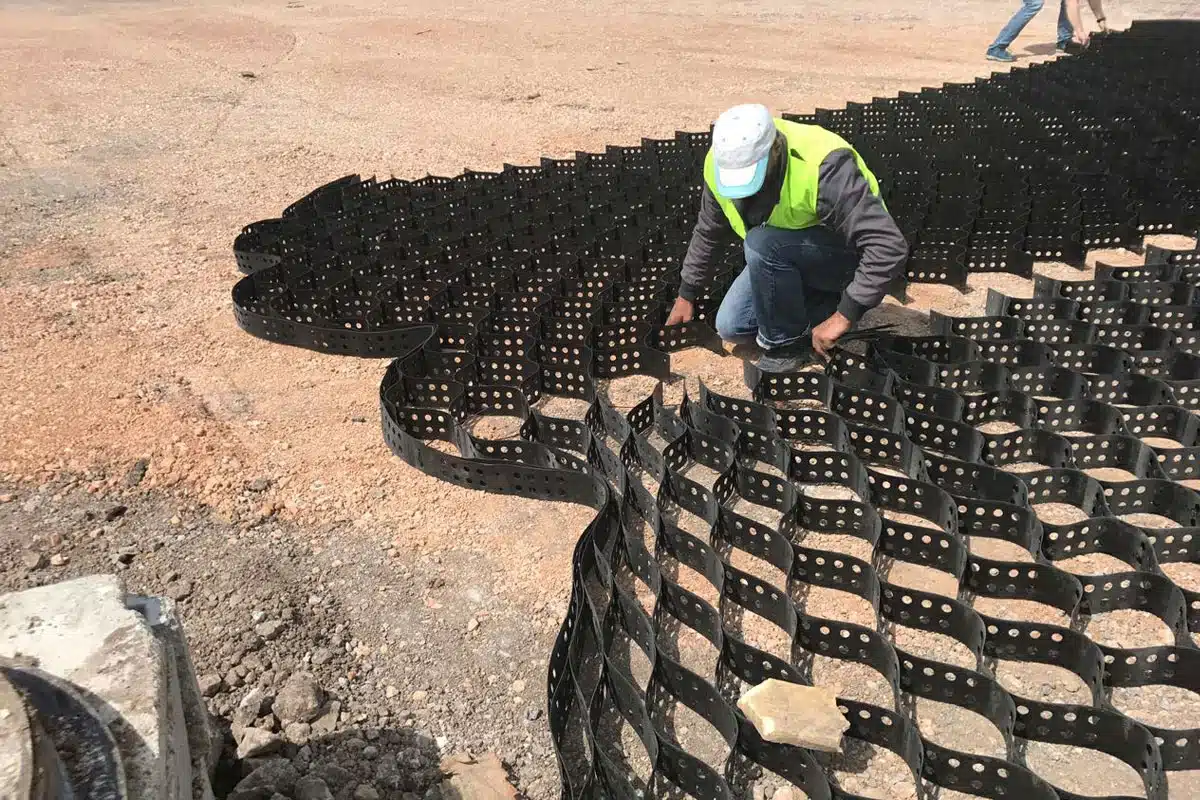

What are the benefits of geocells?
- Improved Load Distribution: Geocells distribute loads evenly over a larger area, reducing stress on underlying soil and preventing localized failures.
- Soil Stabilization: They reinforce weak soils, minimize settlement, and maintain the integrity of slopes, embankments, and foundations.
- Flexibility: Their honeycomb structure adapts to uneven terrain, making them ideal for slopes, embankments, and variable surfaces.
- Erosion Control: Geocells prevent soil erosion on hillsides, riverbanks, and slopes, protecting ecosystems and reducing sediment runoff.
- Vegetation Support: Filled with soil, geocells promote plant growth, further stabilizing ground and enhancing environmental benefits.
- Reduced Material Use: By improving the performance of local fill materials, they decrease the need for extra construction resources.
Where are Geocells used?
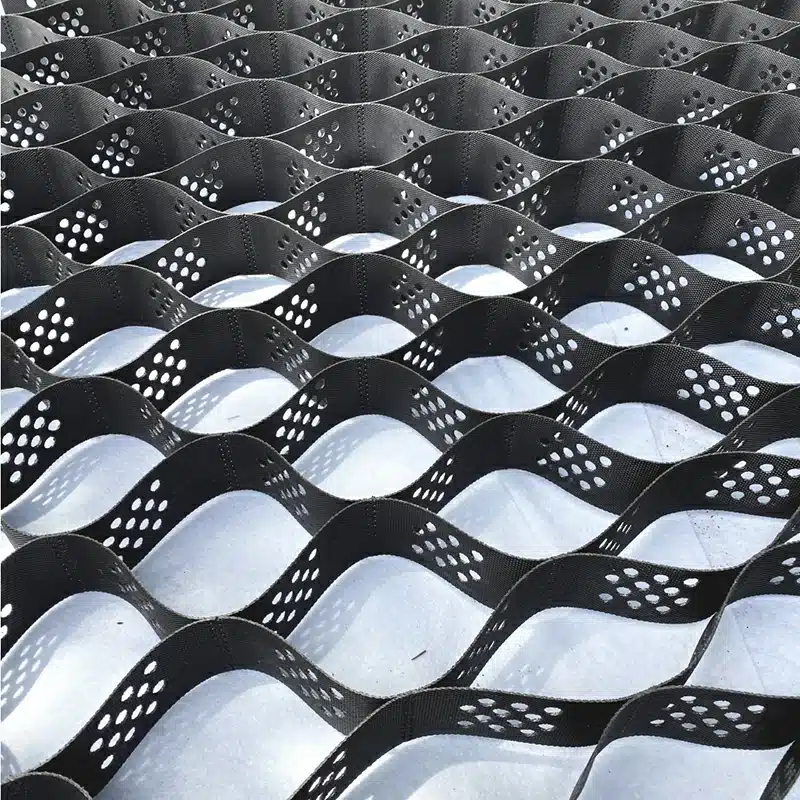
Geocells are three-dimensional, honeycomb-like structures made from polymeric materials (e.g., HDPE) and are used in various civil engineering and construction applications. They provide soil stabilization, erosion control, and load support. Common uses include:
- Slope and Erosion Control: Stabilizing steep slopes and embankments.Preventing soil erosion on hillsides and riverbanks.
- Load Support and Soil Stabilization: Reinforcing weak soils for road and railway foundations.Supporting heavy loads in parking lots, construction sites, and airport runways.
- Retaining Walls: Creating reinforced retaining structures for landscaping or infrastructure.
- Channel and Shoreline Protection: Protecting waterways, shorelines, and coastal areas from erosion.
- Earth Retention: Stabilizing earth in embankments, dams, and landfills.
- Green Infrastructure: Supporting vegetation growth in eco-friendly projects like green roofs or vegetated slopes.
Geocells are versatile, cost-effective, and widely used in infrastructure, environmental protection, and landscaping projects.
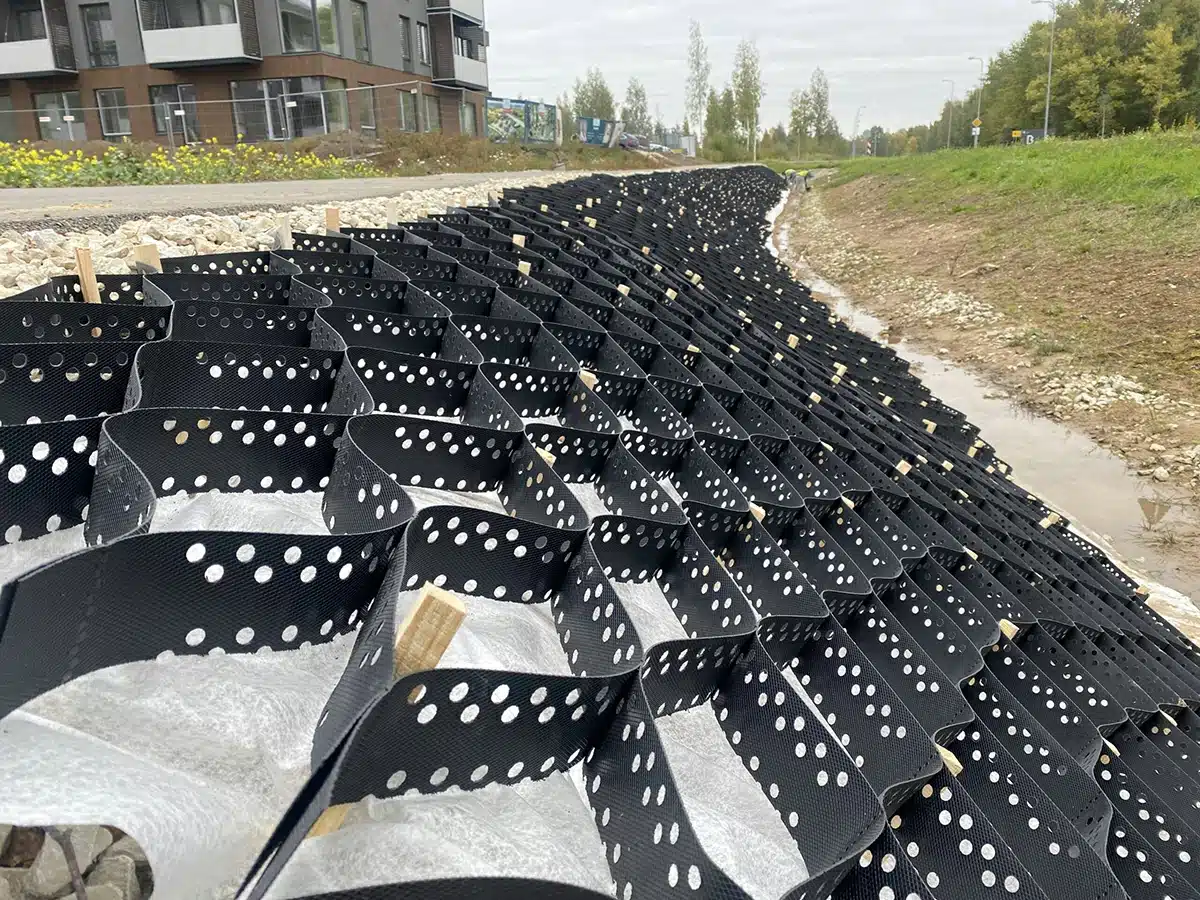

What is the effect of Geocell on soil’s behavior?
Geocell technology involves the use of three-dimensional honeycomb-like structures made from high-density polyethylene or other polymeric materials. These structures are used to confine soil, providing enhanced mechanical properties and stability.
Impact on Soil Behavior
- Shear Strength: Geocells significantly increase the shear strength of the soil. The confinement provided by the Geocell limits the lateral movement of soil particles, enhancing inter-particle friction and cohesion. This leads to an overall increase in the shear strength, making the soil more resistant to shear forces.
- Compaction: The use of Geocells improves soil compaction. The confined cells allow for a uniform distribution of compaction effort, resulting in higher density and reduced void spaces within the soil. This uniform compaction ensures better load-bearing capacity and reduces the likelihood of settlement.
- Settlement: Geocells reduce both immediate and long-term settlement of soil. The confinement restricts soil displacement and helps maintain the soil structure under load. This is particularly beneficial in soft or loose soils, where settlement can be a significant issue.
- Overall Stability: The overall stability of soil is enhanced by the use of Geocells. They provide a stable framework that distributes loads evenly and prevents localized failures. This leads to improved performance of the soil in various applications such as road construction, embankments, and slope stabilization.
Potential Drawbacks and Limitations
- Cost: One of the primary drawbacks of using Geocells is the cost. The initial investment in materials and installation can be higher compared to traditional soil stabilization methods. However, this cost is often offset by the long-term benefits and reduced maintenance requirements.
- Installation Challenges: Proper installation of Geocells requires skilled labor and careful preparation of the site. Incorrect installation can lead to suboptimal performance and reduced effectiveness of the technology.
- Environmental Concerns: While Geocells are generally considered environmentally friendly, the use of synthetic materials can raise concerns. The production and disposal of polymeric materials can have environmental impacts, and there is ongoing research into biodegradable alternatives.
Geocell technology offers significant benefits in enhancing the mechanical properties and behavior of soil. It improves shear strength, and compaction, reduces settlement, and enhances overall stability. However, considerations such as cost, installation challenges, and environmental impacts need to be addressed to fully realize the potential of this technology in soil stabilization applications.
What are the properties of Geocell material?
- Benefits of Geocells: They improve load distribution on the soil, reinforce weak soils, prevent erosion, support vegetation growth, adapt to uneven terrain, and reduce the need for additional materials.
- Main Applications: Slope and erosion control on roads and riverbanks, soil reinforcement for roads, railways, and airport runways, reinforced retaining walls, protection of canals and coastal areas, and green infrastructure such as vegetated roofs and stabilized slopes.
- Effect on Soil Behavior: They increase shear strength, improve compaction, reduce immediate and long-term settlement, and provide overall stability by creating a stable matrix that distributes loads and prevents localized failures.
- Geocell Material Properties: Manufactured from HDPE or other polymers with UV and chemical resistance additives, they feature a flexible honeycomb structure, high tensile strength and load-bearing capacity, and resistance to UV rays, chemicals, and extreme environmental conditions. Their lightness and flexibility facilitate installation and transport.
Geocells represent an innovative and sustainable solution for soil stabilization and erosion control, improving soil strength, compaction, and load distribution, while also supporting vegetation and reducing the need for additional construction materials.
Geocells represent a cutting-edge solution in the field of environmental conservation and sustainable construction. Their benefits extend beyond soil stabilization, encompassing erosion control, vegetation support, and enhanced load distribution. By understanding the applications, effects on soil behavior, and material properties of geocells, stakeholders can leverage this technology to mitigate environmental impacts and promote sustainability in construction projects. As the world moves towards greener construction practices, the role of geocells in environmental preservation and sustainable development becomes increasingly significant.


Get Free Sample
We’ll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)






















