Filter fabric material, also known as geotextile fabric, is a versatile and essential textile widely used in construction, agriculture, landscaping, and environmental engineering. Engineered from durable synthetic fibers like polyester, polypropylene, or nylon, it allows water and fluids to pass through while blocking soil, sediment, and other particles, making it crucial for applications such as soil stabilization, drainage, erosion control, and industrial filtration.
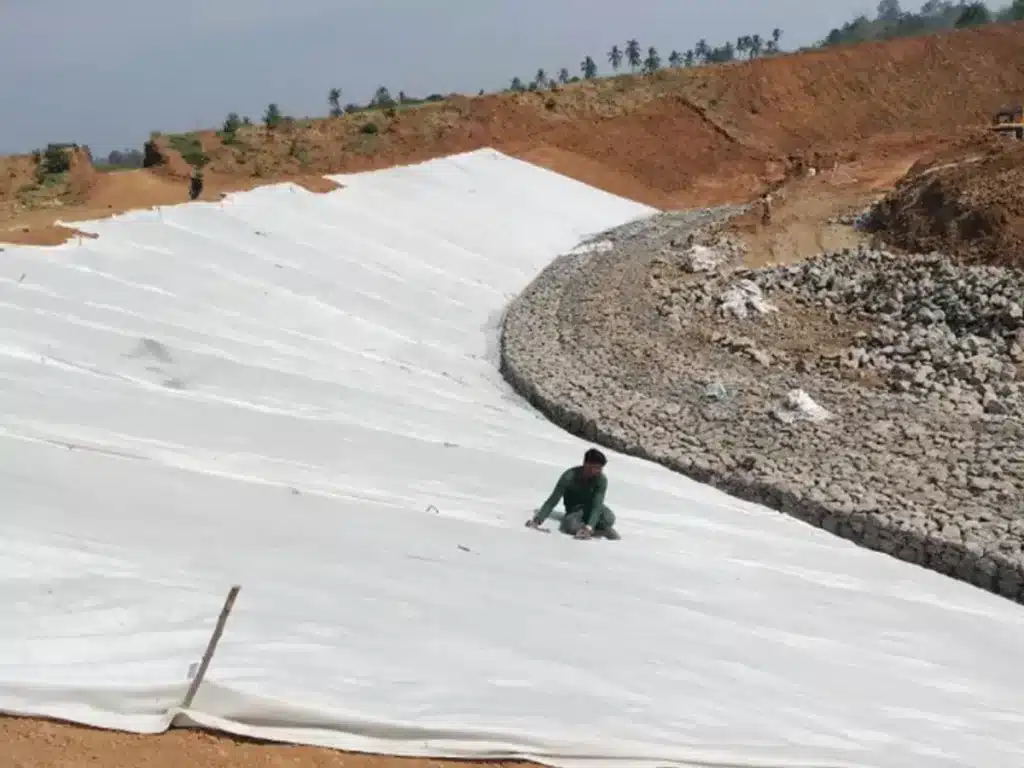

What fabric can be used as a filter?
Various fabrics can be used as filters depending on the application and the type of filtration required. Here are some commonly used fabrics for different types of filtration:
- Cotton: Widely used in medical and laboratory settings. It is effective for filtering out large particles and is breathable.
- Polyester: Common in air and water filtration. It is durable, resistant to chemicals, and can be manufactured with different pore sizes for varied filtration levels.
- Nylon: Often used in liquid filtration. It is strong, has good chemical resistance, and can filter small particles effectively.
- Polypropylene: Used in industrial and commercial filtration. It is resistant to most chemicals, and its non-woven versions are effective in capturing fine particles.
- Activated Carbon Fabric: Used for filtering gases and odors. It has a high surface area that absorbs impurities effectively.
- Fiberglass: Common in high-temperature applications and air filtration. It can withstand high temperatures and has good filtration efficiency for small particles.
- Microfiber: Effective in capturing fine particles due to its dense structure. It is used in various applications, including household cleaning and air filtration.
- Non-woven Fabrics: Made from fibers bonded together, used in medical masks, vacuum bags, and air filters. They are efficient at filtering out small particles.
- Silk: Natural and has been studied for use in filtration, including mask filters. It offers good breathability and can filter out particles effectively.
The choice of fabric depends on the specific requirements, such as the size of particles to be filtered, chemical compatibility, temperature resistance, and desired durability.
Is Filter Fabric the Same as Landscape Fabric?
- Filter fabric and landscape fabric are not the same, although they may look similar and are sometimes confused in practice. They are engineered for different primary functions.
- Filter fabric (geotextile fabric) is designed mainly for filtration and separation. It allows water to pass through while retaining soil particles, sediment, and fines. It is commonly used in drainage systems, French drains, retaining walls, road construction, erosion control, and other civil engineering applications.
- Landscape fabric, also known as weed barrier fabric, is intended primarily for weed suppression in gardens and landscaping. It blocks sunlight to inhibit weed growth while allowing limited water and air penetration to the soil.
- Permeability difference: Filter fabric has controlled pore sizes engineered to balance water flow and particle retention, while landscape fabric prioritizes light blockage rather than precise filtration performance.
- Durability and standards: Filter fabric is manufactured to meet engineering standards and withstand long-term mechanical, hydraulic, and environmental stresses. Landscape fabric is generally lighter-duty and not designed for structural or drainage performance.
- Interchangeability: While heavy-duty landscape fabric may provide minimal filtration in light-duty situations, it is not a reliable substitute for filter fabric in drainage or soil stabilization applications.
In summary, filter fabric is an engineered filtration solution, while landscape fabric is a weed control product. Choosing the correct fabric ensures proper performance, longevity, and project reliability.
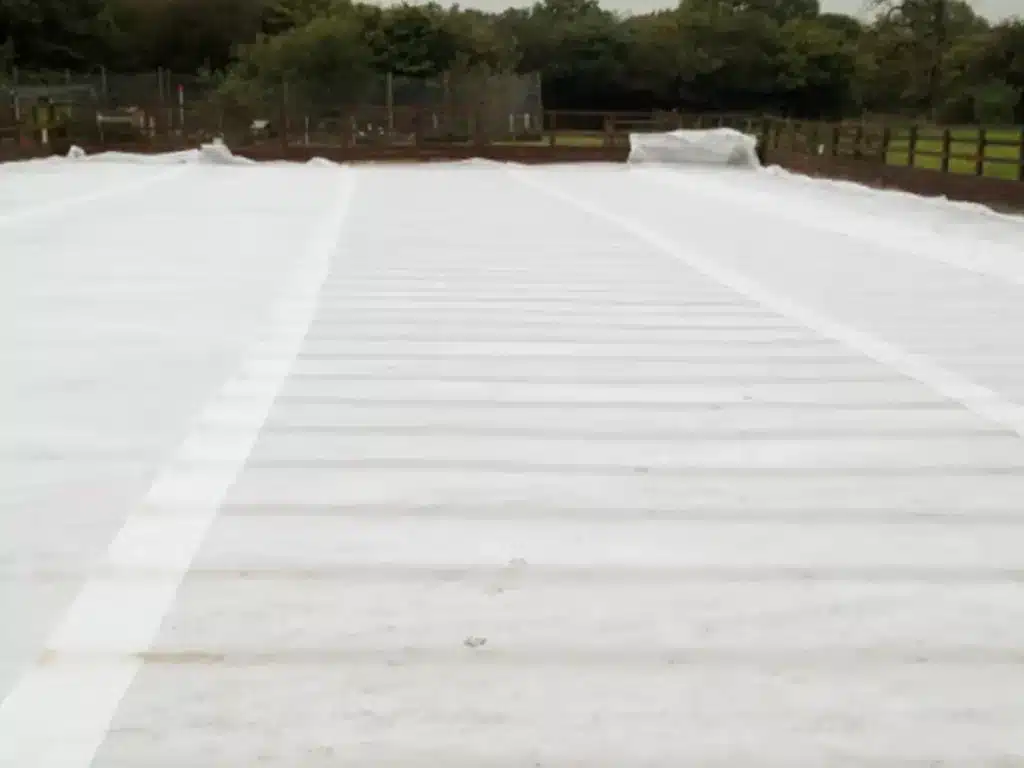

What is the best cloth for filtering?
The best cloth for filtering depends on what you’re filtering and the desired filtration level. Here are some commonly used cloths for various filtering purposes:
- Cotton Muslin: This lightweight, breathable fabric is excellent for straining liquids like stocks, soups, or cheese curds. It has a fine weave that allows liquids to pass through while trapping larger particles.
- Cheesecloth: Often used in cooking and cheese-making, cheesecloth is a loosely woven cotton fabric. It’s ideal for straining liquids, making spice sachets, and filtering fine solids.
- Nonwoven Geotextile Fabric: In industrial or large-scale applications, nonwoven geotextile fabrics are used for filtering soil and debris from water, often in drainage systems or as part of erosion control measures.
- Polyester Mesh: Polyester mesh fabrics are durable, resistant to chemicals, and can be used for filtering fine particles. They are commonly used in air and liquid filtration in industrial settings.
- Silk: For very fine filtration, such as in laboratory settings or for certain culinary applications, silk can be used because of its tightly woven structure.
Each of these fabrics is suited to different applications, so the best choice depends on your specific filtration needs.
What Is the Purpose of Filter Fabric in Construction and Engineering Applications?
The primary purpose of filter fabric (geotextile fabric) in construction and engineering is to control the movement of water while preventing soil and fine particles from migrating, thereby maintaining the stability and functionality of engineered systems.
In geotechnical and civil applications, filter fabric serves several critical functions:
- Filtration: It allows water to pass through while retaining soil particles, preventing clogging in drainage systems such as French drains, subdrains, and retaining wall backfills.
- Separation: Filter fabric keeps different material layers—such as soil and aggregate—separate, preserving the structural integrity and load-bearing performance of roads, foundations, and embankments.
- Drainage protection: By preventing fine particles from entering drainage media, filter fabric ensures long-term hydraulic efficiency and reduces maintenance requirements.
- Erosion control: It stabilizes soil surfaces by controlling sediment movement caused by water flow, rainfall, or runoff, especially on slopes and embankments.
- System protection: Filter fabric protects pipes, gravel layers, and other structural components from sediment intrusion, abrasion, and premature failure.
Unlike general-purpose fabrics, filter fabric used in engineering applications is manufactured to meet specific performance criteria for permeability, strength, durability, and chemical resistance. When properly selected and installed, it plays a vital role in extending the service life of drainage systems, soil stabilization works, and environmental protection projects.
Filter fabric is more than just a textile; it is a versatile engineering solution that ensures effective fluid management while protecting soil and environmental quality. Choosing the right type of fabric for your specific application is crucial, whether in construction, landscaping, or industrial processes. By understanding its properties, functions, and applications, filter fabric can optimize both project performance and sustainability.


Get Free Sample
We’ll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)






















