+86-159 9860 6917
info@geofantex.com
geofantex@gmail.com
+86-400-8266163-44899
In the realm of civil engineering and landscape architecture, the concept of using geocells as a wall has gained significant traction. This innovative approach to soil stabilization and retention offers a blend of strength, flexibility, and environmental friendliness. This article delves into the basics of geocell walls, exploring their definition, comparison with geo retaining walls, benefits, and material properties. By understanding these aspects, we can appreciate the role of geocells in modern construction and environmental conservation.
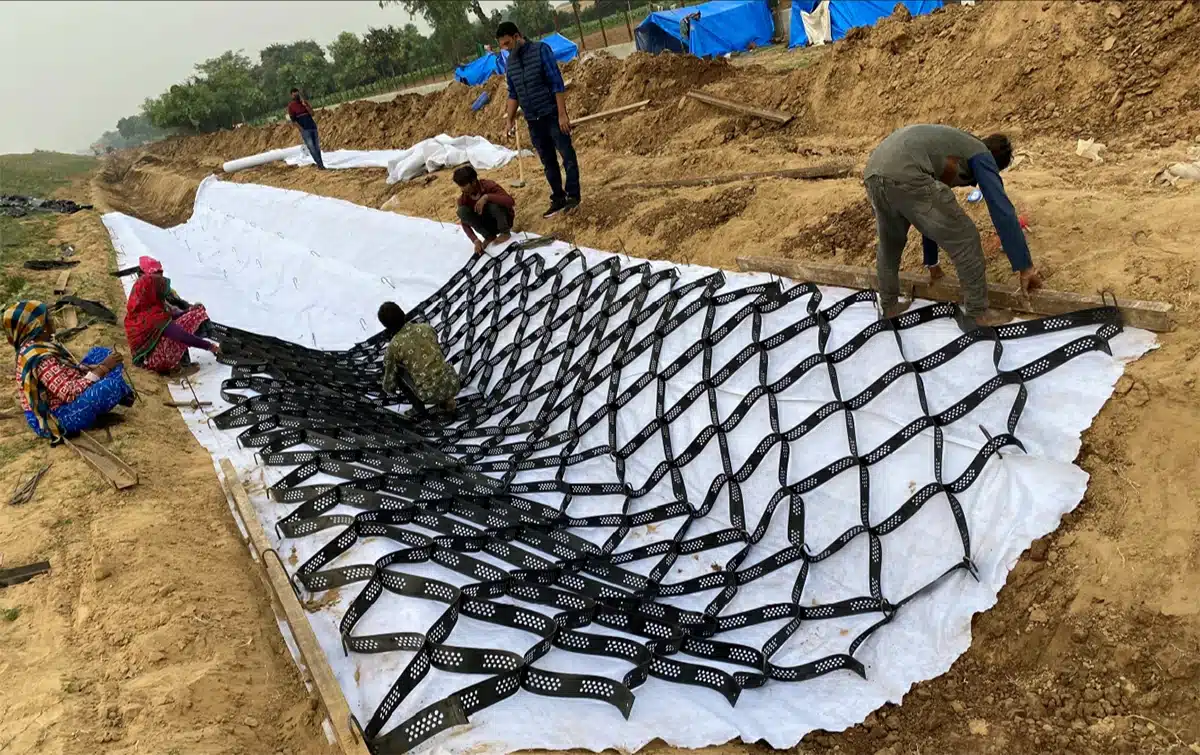

What is a GeoCell Wall?
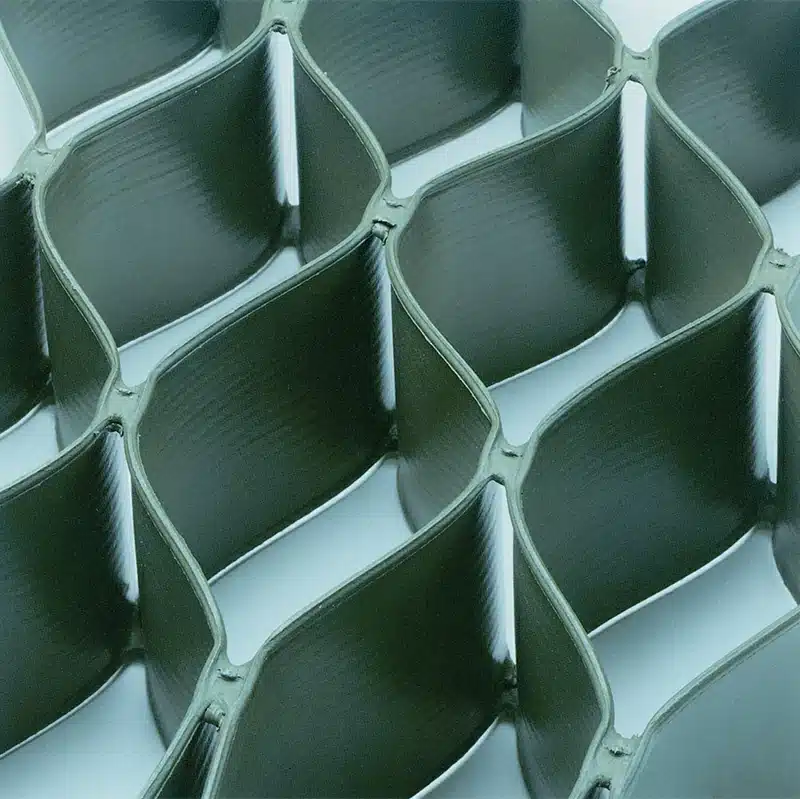
A GeoCell Wall, also known as a cellular confinement system, is an advanced geosynthetic material used in construction and civil engineering. It is designed to improve the performance and longevity of various structural applications. Here is a detailed explanation:
Purpose: The primary purpose of a GeoCell Wall is to provide soil stabilization, erosion control, and load support. It is used in various applications such as retaining walls, slope protection, channel lining, and road construction.
Construction: GeoCell Walls are constructed using high-density polyethylene (HDPE) strips that are connected to form a honeycomb-like structure. This cellular grid is then filled with soil, gravel, concrete, or other infill materials. The cells confine the infill, which significantly enhances its strength and stability.
Materials Used
- High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE): This is the most common material used for GeoCell Walls due to its durability, flexibility, and resistance to chemicals and UV degradation.
- Infill Materials: Soil, gravel, sand, and concrete are typically used as infill materials. The choice of infill depends on the specific application and required performance characteristics.
Benefits
- Improved Load Distribution: The cellular structure distributes loads over a larger area, reducing pressure on underlying soils.
- Erosion Control: GeoCell Walls prevent soil erosion by confining the infill materials and providing structural stability to slopes and embankments.
- Versatility: They can be used in various applications, including road construction, slope stabilization, retaining walls, and channel protection.
- Cost-Effective: GeoCell systems can reduce the need for extensive excavation and the use of imported fill materials, lowering overall construction costs.
- Durability: Made from HDPE, GeoCell Walls are highly durable and resistant to environmental degradation.
Drawbacks
- Installation Complexity: Proper installation requires skilled labor and precise engineering to ensure effectiveness and longevity.
- Initial Cost: While cost-effective in the long run, the initial investment in materials and installation can be higher compared to traditional methods.
- Limited Availability: Depending on the region, GeoCell materials may not be readily available, leading to potential delays and additional costs for procurement.
GeoCell Walls are a modern, effective solution for soil stabilization and erosion control, offering significant benefits in terms of durability and versatility, despite some challenges in installation and initial costs.
What is a Geo Retaining Wall?
A Geo Retaining Wall, also known as a Geosynthetic Reinforced Soil (GRS) wall, is a type of retaining wall that utilizes geosynthetic materials to reinforce soil. These walls are designed to retain soil at different levels on the two sides, preventing erosion and providing stability in various construction projects.
Purpose
- Soil Retention: Primarily used to hold back soil and prevent erosion in areas with varying elevations.
- Slope Stabilization: Stabilizes slopes and prevents landslides in hilly or mountainous regions.
- Structural Support: Provides support for roads, bridges, and other infrastructure projects.
Construction
- Excavation: The area is excavated to the desired depth and shape.
- Foundation Preparation: A stable and level foundation is prepared, often with a gravel base for drainage.
- Geosynthetic Placement: Geosynthetic materials, such as geogrids or geotextiles, are placed in layers within the soil to provide reinforcement.
- Backfilling: Soil is placed and compacted over each layer of geosynthetic material.
- Facing Installation: A facing system, which can be made of concrete, stone, or other materials, is installed to provide the wall with its final appearance and additional stability.
- Finishing: Final adjustments and aesthetic finishes are applied.
Materials Used
- Geosynthetics: Geogrids, geotextiles, geomembranes, and geocells.
- Soil: Select granular fill material that provides adequate compaction and drainage.
- Facing Elements: Concrete blocks, natural stones, or other durable materials.
Design Considerations
- Soil Type: The type of soil affects the choice of geosynthetic materials and the overall design of the wall.
- Load Requirements: Consider the load that the wall needs to support, including soil pressure, surcharge loads, and environmental factors.
- Drainage: Proper drainage is essential to prevent water accumulation behind the wall, which can compromise its stability.
- Height and Slope: The height and slope of the wall need to be carefully designed to ensure stability and effectiveness.
- Environmental Impact: Consideration of the environmental impact and the use of sustainable materials where possible.
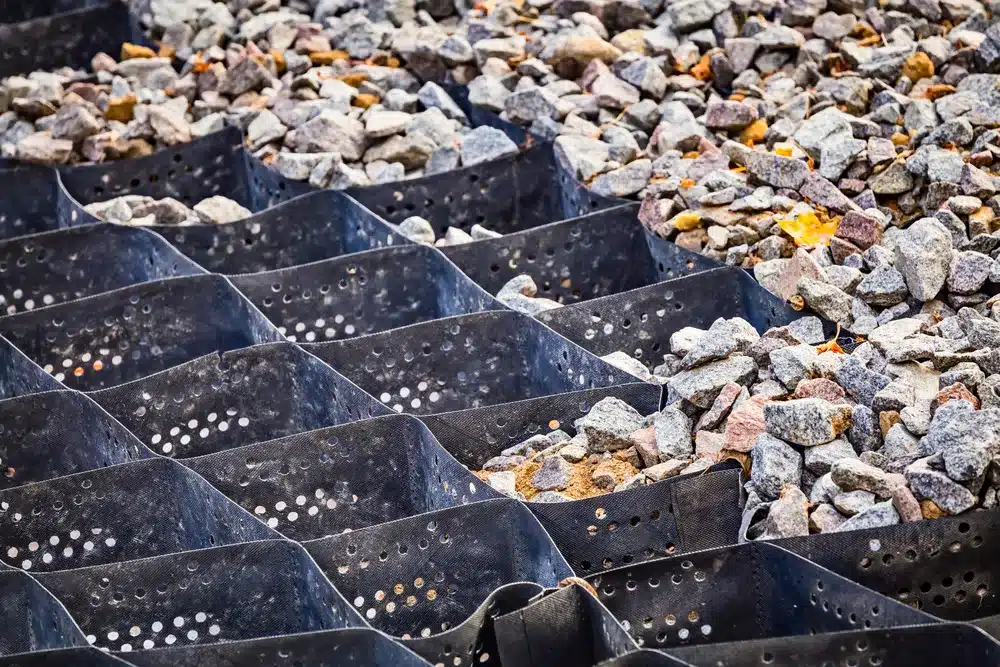

What are the Benefits of Geocells?
Geocells offer numerous advantages in construction and environmental applications, designed to reduce erosion, stabilize soil, protect channels, and provide structural reinforcement for load support and earth retention:
- Enhanced Stability: They improve the load-bearing capacity of the soil, making it more stable and effectively stabilizing soil.
- Erosion Control: Geocells are effective in preventing soil erosion, especially on slopes and in areas prone to water runoff, thereby reducing erosion.
- Cost-Effective: They often reduce the need for expensive, imported materials and heavy construction equipment.
- Environmentally Friendly: Geocells are usually made from recyclable materials and encourage vegetation growth, blending with the natural environment, and protecting channels.
- Versatility: Suitable for a wide range of applications, including roads, railroads, airfields, and earth retention systems, they provide structural reinforcement for load support and earth retention.
- Durability: Resistant to chemicals, ultraviolet radiation, and mechanical damage, ensuring long-term stability and protection.
What are the Properties of Geocell Material?
Geocell materials, typically made from HDPE or other polymeric alloys, exhibit several key properties:
- High Tensile Strength: They can withstand significant stress without breaking.
- Elasticity and Flexibility: Allows them to conform to varying terrain and withstand differential settlement.
- Chemical Resistance: They are resistant to a wide range of chemicals, making them suitable for various environments.
- UV Resistance: Geocell materials are often treated to be resistant to ultraviolet light, enhancing their longevity.
- Permeability: The design allows for water drainage, which is crucial for soil health and erosion control.
Geocell technology, particularly in the form of geocell walls, represents a significant advancement in soil stabilization and erosion control. By understanding what geocell walls are, their comparison with traditional geo retaining walls, their benefits, and the properties of the materials used, we gain insight into their importance in modern construction and environmental management. The versatility, cost-effectiveness, and environmental benefits of geocells make them a preferred choice in various applications, marking a shift towards more sustainable and resilient construction practices.


Get Free Sample
We’ll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)






















