+86-159 9860 6917
info@geofantex.com
geofantex@gmail.com
+86-400-8266163-44899
Geocell retaining walls have emerged as a cost-effective and sustainable solution for soil stabilization and erosion control. In this article, we will explore what geocell retaining walls are, the role of geogrid in retaining walls, and whether you should use geogrid for your project. Additionally, we’ll delve into the working principles of geotextile retaining walls to help you make informed decisions for your construction needs.
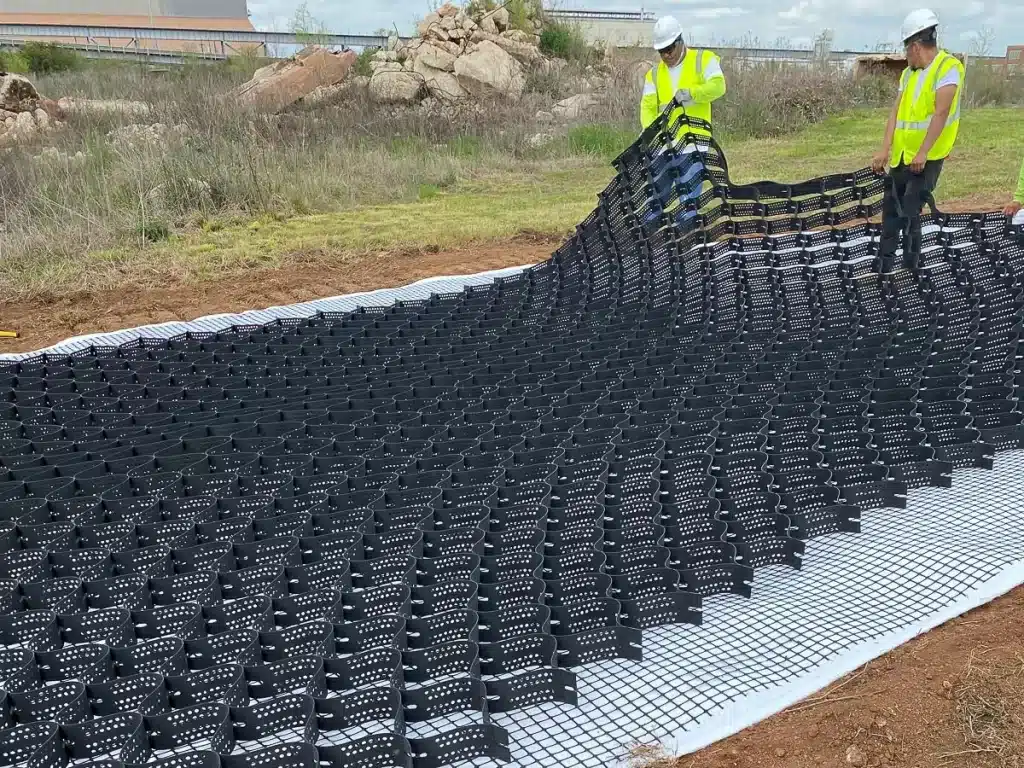

What Is a Geocell Retaining Wall?
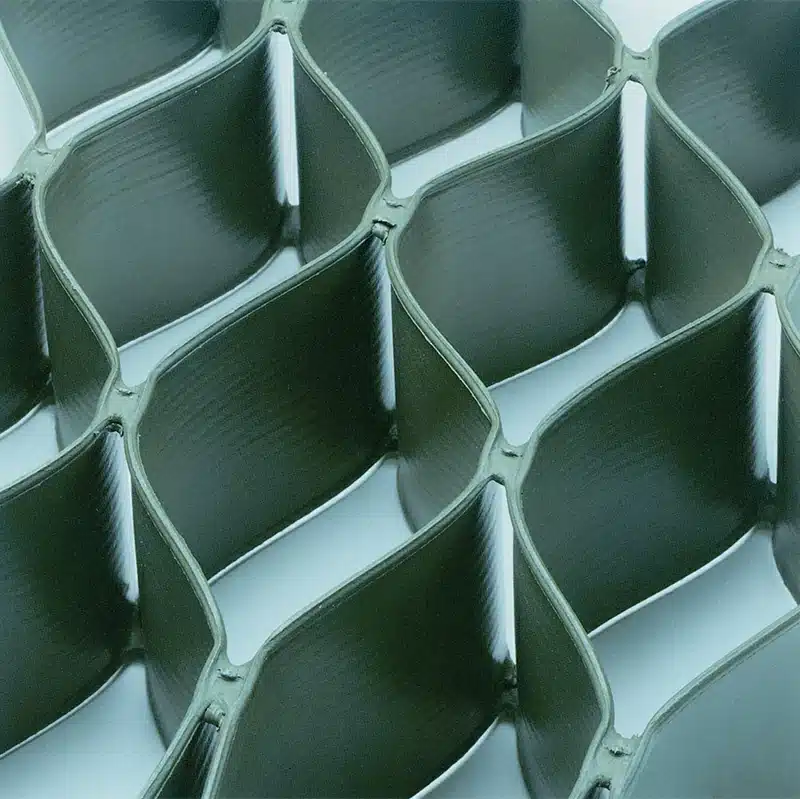
A geocell retaining wall is a modern soil-retention system designed to stabilize slopes, embankments, and earth walls using a three-dimensional cellular structure.
- Structure: It is made of interconnected HDPE strips that expand on site to form a 3D honeycomb, which is filled with soil, gravel, or concrete.
- Stability mechanism: The cellular confinement increases shear strength, limits lateral soil movement, and improves resistance to erosion and deformation.
- Performance advantages: Geocell retaining walls are lightweight, flexible, and able to accommodate minor ground movement, making them suitable for weak soils and seismic zones.
- Applications and benefits: They are widely used on steep slopes, load-bearing embankments, and environmentally sensitive areas, offering faster installation, lower costs, and optional vegetated or finished facings.
What is Geocell for a Retaining Wall?
A geocell for a retaining wall is a three-dimensional honeycomb structure made from high-density polyethylene (HDPE), used to reinforce soil and improve wall stability. It provides several key benefits:
- Soil reinforcement: Confines and stabilizes soil within its cells, increasing load-bearing capacity.
- Erosion control: Reduces surface runoff and prevents soil erosion on slopes or wall facings.
- Load distribution: Distributes pressure evenly, reducing stress on the wall foundation.
- Flexibility: Adapts to various terrains, including curves and slopes.
- Eco-friendly: Supports vegetation for green wall applications.
- Cost-effective and easy to install: Offers a practical alternative to traditional retaining systems like concrete or gabions.
Overall, geocells improve the durability, efficiency, and sustainability of retaining wall systems.
Should I Use Geocell to Retain the Wall?
Yes—geocell is an excellent choice for retaining walls when flexibility, cost efficiency, and sustainability are priorities, especially in the following conditions:
- Weak or loose soils: Geocells confine soil effectively, improving stability and load-bearing capacity.
- Slope and erosion control needs: Ideal for preventing erosion on steep or exposed areas behind the wall.
- Irregular or curved terrain: The flexible structure adapts easily to complex geometries and uneven ground.
- Eco-friendly design goals: Can be filled with soil and vegetation for a natural, green retaining wall.
- Cost and time constraints: Faster installation and lower material costs compared to traditional concrete or masonry walls.
In summary, geocell retaining walls are best suited for projects requiring flexible design, soil reinforcement, and sustainable performance without the expense of rigid retaining systems.
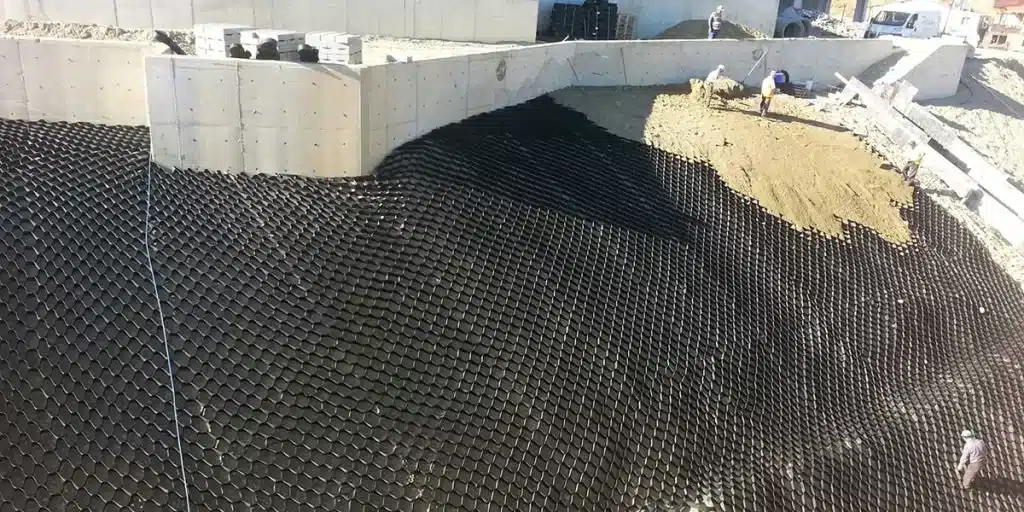

How Do Geocell Retaining Walls Work?
Geocell retaining walls work by using a 3D honeycomb structure that stabilizes and strengthens soil through cellular confinement. Here’s how they function:
- Cellular confinement: The geocell forms a honeycomb grid that holds soil or gravel in place, preventing lateral movement.
- Load distribution: It spreads vertical and horizontal loads evenly, reducing pressure on the retaining wall and its base.
- Friction and interlock: The confined fill creates strong internal friction and interlocking, enhancing wall stability.
- Erosion control: Geocells protect exposed surfaces from erosion, especially on slopes or vegetated walls.
- Flexibility: The structure adapts to uneven terrain, curves, and step formations, making it suitable for complex sites.
Together, these features make geocell retaining walls durable, stable, and efficient for soil retention and slope protection.
In conclusion, geocell retaining walls, with the assistance of geogrid and geotextile materials, offer innovative solutions for soil stabilization and erosion control. By understanding their functions and consulting with professionals, you can make informed decisions to ensure the success of your retaining wall project. Proper planning, quality materials, and expert guidance are key to achieving a durable and reliable retaining structure.


Get Free Sample
We’ll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)






















