+86-159 9860 6917
info@geofantex.com
geofantex@gmail.com
+86-400-8266163-44899
Geocell slope protection is an innovative technology designed to stabilize and protect slopes from erosion and other forms of degradation. This article delves into the intricacies of geocell technology, exploring its definition, applications, limitations, and overall purpose in slope management. By addressing common inquiries about geocell slope protection, we aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of how this technology contributes to more sustainable and secure land management practices.
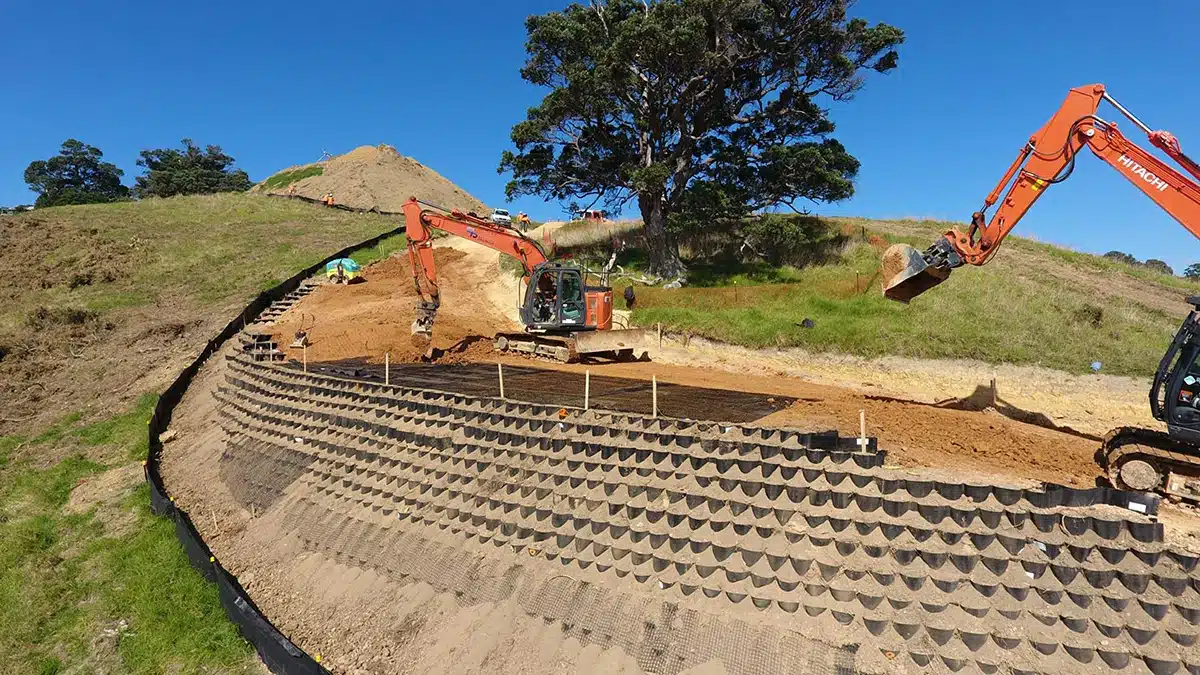

What is geocell in slope protection?
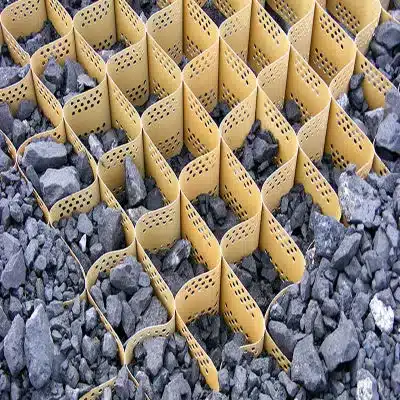
A geocell is a three-dimensional, honeycomb-like structure used in slope protection. Typically made from high-density polyethylene (HDPE) or other durable materials, the geocell is expanded on-site and filled with soil, gravel, or other materials. Its purpose is to reinforce the slope, distribute loads evenly, and prevent erosion by keeping the fill material securely in place. Here’s a breakdown of its function:
- Purpose: The primary purpose is to provide structural reinforcement to the slope. It prevents surface runoff and minimizes soil erosion by confining the fill material within its cells.
- Components: The geocell comprises interconnected strips of polymer material that form a honeycomb pattern. The cells are filled with different materials like soil or gravel, depending on the intended application.
- How it Works: When laid out on the slope, the geocell’s interconnected cells confine the fill material. This confinement increases the shear strength of the slope, reduces the movement of soil particles, and provides stability even on steep gradients. By evenly distributing the load, it helps slopes withstand environmental stresses like heavy rain or surface runoff.
Geocells are popular in civil engineering projects for protecting embankments, roadside slopes, riverbanks, and retaining structures.
What is the maximum slope for geocell?
The maximum slope for geocell reinforcement generally depends on the project’s requirements and the specific geocell product used. In practice:
- General Slopes: Geocells can typically reinforce slopes up to about 45 degrees (1:1 slope).
- Steep Slopes: For slopes ranging from 45 to 70 degrees, specially designed geocells combined with additional reinforcement measures (e.g., anchors or specific soil mixes) may be required.
- Very Steep Slopes: For slopes over 70 degrees, the system often requires engineering analysis, specialized materials, and additional support mechanisms.
Always consult the geocell manufacturer’s guidelines and work with geotechnical engineers to ensure proper design.
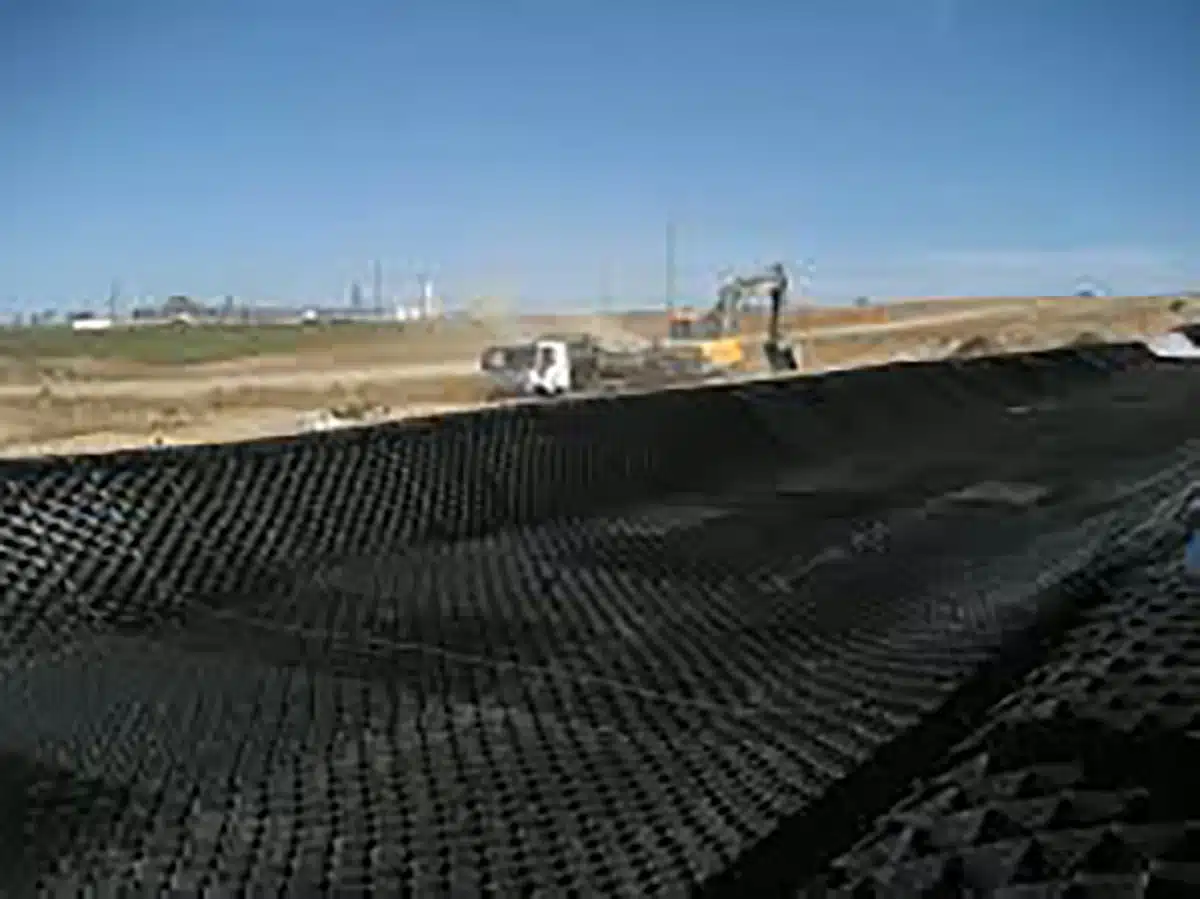

What is the purpose of Geocell?
Geocells, also known as cellular confinement systems, are a type of geosynthetic product used in civil engineering and construction to provide soil stabilization and erosion control. Their primary purposes include:
- Soil Stabilization: Geocells reinforce weak soils by confining and stabilizing the fill material within their cellular structure. This improves load-bearing capacity and prevents lateral movement of the soil.
- Erosion Control: By containing soil and preventing it from being washed away, geocells help to control erosion on slopes, embankments, and channels.
- Load Distribution: When used under pavements or railways, geocells distribute loads more evenly, reducing stress on the subgrade and increasing the lifespan of the structure.
- Slope Protection: Geocells are effective in protecting slopes from erosion and landslides by stabilizing the soil and vegetation cover.
- Retention and Detention Systems: In stormwater management, geocells can be used to create permeable retaining walls and detention basins, allowing water to be stored and gradually released.
- Environmental Benefits: By reducing the need for extensive earthworks and minimizing the environmental footprint of construction projects, geocells contribute to more sustainable construction practices.
Overall, the primary function of geocells is to provide a robust and versatile solution for soil reinforcement, erosion control, and load support in various civil engineering applications.
How does geocell contribute to environmental sustainability?
Soil Stabilization:
- Erosion Control: Geocells prevent soil erosion by confining the soil within a cellular structure, reducing the impact of water and wind.
- Slope Protection: They provide stability to slopes and embankments, reducing the risk of landslides and soil degradation.
Water Conservation:
- Rainwater Harvesting: Geocells can be used in rainwater harvesting systems to enhance water infiltration and reduce runoff.
- Moisture Retention: They help in maintaining soil moisture levels, promoting healthy vegetation growth.
Reduced Carbon Footprint:
- Material Efficiency: Geocells often use recycled materials, reducing the demand for new raw materials and associated carbon emissions.
- Transportation Savings: The lightweight nature of geocells reduces transportation energy and emissions compared to traditional materials.
Enhancing Vegetation:
- Plant Growth: Geocells provide a stable environment for plant roots, promoting vegetation in areas prone to erosion.
- Green Roofs and Walls: They are used in constructing green roofs and walls, which improve air quality and provide insulation.
Infrastructure Longevity:
- Durability: Geocell-reinforced structures have a longer lifespan, reducing the need for frequent repairs and replacements.
- Sustainable Construction: They enable the construction of more durable and sustainable infrastructure, such as roads and pathways.
Pollution Control:
- Filtration: Geocells can be used in filtering pollutants from stormwater, reducing the contamination of water bodies.
- Sediment Control: They help in trapping sediments and preventing them from entering water systems.
In conclusion, geocell slope protection is a versatile and effective solution for managing and stabilizing slopes. By understanding its application, limitations, and benefits, stakeholders can make informed decisions that lead to safer, more sustainable, and cost-effective land management practices. Whether for infrastructure development, landscape restoration, or erosion control, geocell technology offers a promising approach to addressing some of the most challenging issues in slope management and environmental conservation.


Get Free Sample
We’ll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)






















