+86-159 9860 6917
info@geofantex.com
geofantex@gmail.com
+86-400-8266163-44899
Retaining walls, essential for landscaping and civil engineering, are designed to hold back soil and prevent erosion. These structures find application in various settings, from home gardens to large infrastructure projects. To enhance the stability and durability of these walls, geogrids are often employed. In this article, we will explore the benefits of using geogrids, how to select the appropriate geogrid for your project, and the methods for installing and maintaining geogrid-reinforced retaining walls.
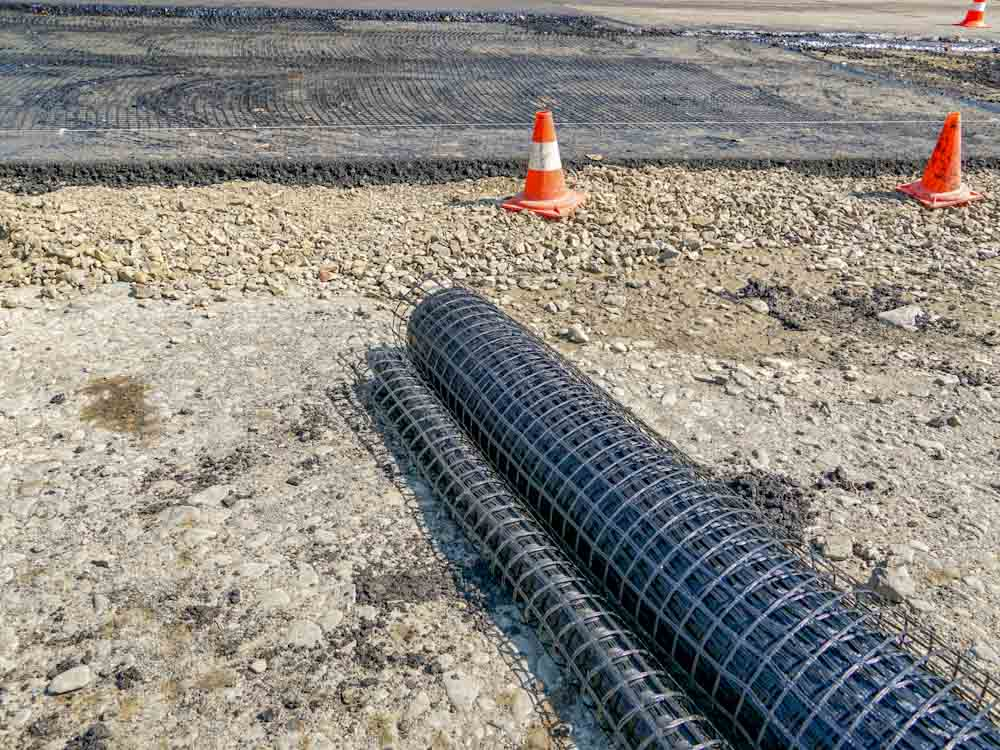

About Geogrids
Purpose of Geogrids: Geogrids are synthetic materials used to reinforce soils and similar materials. They are primarily employed to enhance the mechanical properties of soil, providing stability and support in various construction and civil engineering projects.
Construction of Geogrids
Geogrids are manufactured through various processes:
- Extrusion: Creating a flat, sheet-like structure with uniform apertures.
- Knitting or Weaving: Producing grids by interlacing yarns or fibers, often coated for additional strength.
- Bonding: Joining materials together, usually through thermal, chemical, or mechanical means, to form a grid structure.
Applications in Civil Engineering
- Road Construction: Geogrids reinforce the subgrade and improve the load-bearing capacity of roads.
- Retaining Walls: They provide stability to retaining structures by reinforcing the backfill.
- Railway Construction: Used to stabilize the track bed and improve its durability.
- Slope Stabilization: Prevent landslides and erosion by reinforcing slopes.
- Foundation Reinforcement: Enhance the stability and load distribution of foundations.
Benefits and Advantages
- Improved Load Distribution: Geogrids distribute loads more evenly, reducing stress on the subgrade.
- Increased Stability: They provide greater stability and reduce deformation and settlement.
- Cost-Effective: Reduces the need for over-excavation and replacement of poor soils, leading to cost savings.
- Durability: Geogrids are resistant to environmental degradation, ensuring long-term performance.
- Environmental Benefits: By reducing the need for excavation and new materials, geogrids contribute to more sustainable construction practices.
The Benefits of Using Geogrids
- Increased Stability and Load-Bearing Capacity: Geogrids enhance the stability and load-bearing capacity of retaining walls by reinforcing the soil and distributing loads more evenly. This reduces the risk of wall failure and soil movement.
- Cost Savings: By reducing the need for fill material and allowing for steeper wall designs, geogrids lower construction costs. The enhanced stability provided by geogrids also minimizes the need for maintenance and repairs, leading to long-term cost savings.
- Adaptability: Geogrids are suitable for various types of retaining walls, including gravity walls, reinforced soil walls, and hybrid systems, making them ideal for both residential and commercial projects.
- Improved Appearance: Geogrids enable the design of steeper walls that blend seamlessly with the surrounding landscape, enhancing the visual appeal of retaining walls, especially in residential and public areas.
- Environmental Benefits: Geogrids reduce the environmental impact of retaining wall construction by decreasing the need for concrete and other materials, making them a more sustainable option for soil reinforcement.
Selecting the Right Geogrid
Choosing the right geogrid for your project involves considering several factors:
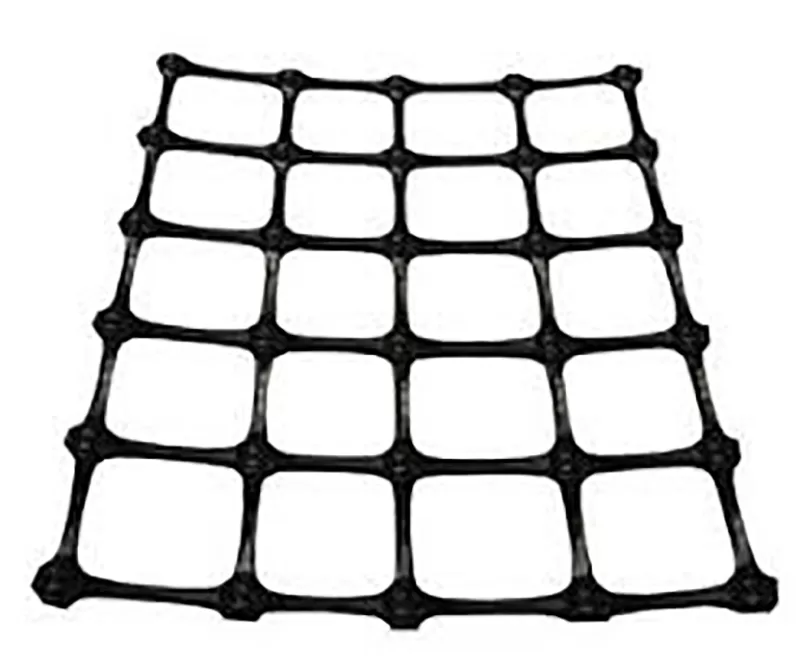
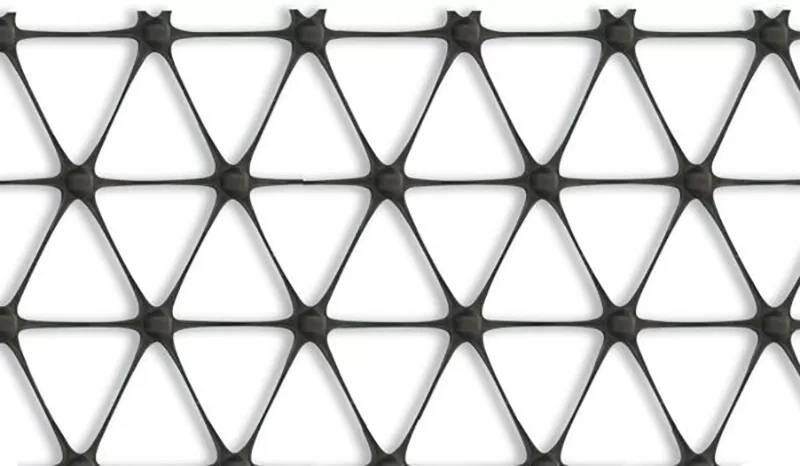
- Type of Geogrid: There are three types of geogrids—uniaxial, biaxial, and triaxial. Uniaxial geogrids are designed to bear loads in one direction and are commonly used for retaining walls. Biaxial and triaxial geogrids provide reinforcement in multiple directions and are often used in road construction and ground stabilization.
- Materials: Geogrids are made from various materials, including HDPE, polyester, and polypropylene, each with different properties such as tensile strength, durability, and chemical resistance. Select the material that meets the specific requirements of your project.
- Opening Size: The size of the openings in the geogrid affects how well soil particles interlock. Larger openings are suitable for coarse soils, while smaller openings are better for fine-grained soils. Ensure the opening size matches the type of soil you are working with.
- Tensile Strength: The tensile strength of the geogrid determines its ability to bear loads and reinforce the soil. Choose a geogrid with sufficient tensile strength to meet your project’s needs.
Maintaining the Reinforced Retaining Wall
Regular maintenance is crucial for the longevity and performance of a retaining wall. Follow these steps:
- Inspect Regularly: Check the wall for signs of cracking, movement, or erosion. Early detection of issues allows for timely repairs and prevents further damage.
- Drainage Inspection: Proper drainage is essential for retaining wall stability. Ensure the drainage system, including weep holes and drainage pipes, is functioning correctly and is free of blockages. Address any drainage issues immediately.
- Control Vegetation: Monitor and control vegetation growth near the retaining wall. Remove any plants or trees that could exert pressure on the wall or disrupt the backfill material.
- Make Repairs: If you notice any damage, such as displaced wall units or geogrid damage, repair it promptly and ensure the repairs are effective.
Case Studies
- Residential Retaining Wall: A homeowner facing soil erosion on a sloped property installed a retaining wall reinforced with uniaxial geogrids. The geogrids provided the necessary reinforcement, allowing for a stable and visually appealing wall that reduced the amount of required backfill material.
- Commercial Development Project: In a commercial development, a large retaining wall was needed to create level building pads on a sloped site. Geogrids were used to construct a tall and stable wall capable of supporting heavy loads and reducing long-term maintenance costs.
- Infrastructure Project: Geogrids were employed to reinforce a retaining wall along road embankments. The geogrid-reinforced walls offered excellent stability and load distribution, reducing the risk of wall movement and erosion. This approach also facilitated faster construction and reduced material costs, enhancing project efficiency.
Geogrids are a versatile and effective solution for enhancing the stability and longevity of retaining walls. By reinforcing the soil and evenly distributing loads, geogrids help prevent wall failure and minimize the need for extensive maintenance and repairs. When selecting geogrids, consider the type, material, opening size, and tensile strength to ensure the best fit for your project.


Get Free Sample
We’ll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)






















