+86-159 9860 6917
info@geofantex.com
geofantex@gmail.com
+86-400-8266163-44899
Geogrid for soil stabilization is a powerful tool in civil engineering, ensuring the stability of various structures. This article delves into the concept of geogrid stabilization, its applications, and requirements, and answers key questions related to this innovative technology.
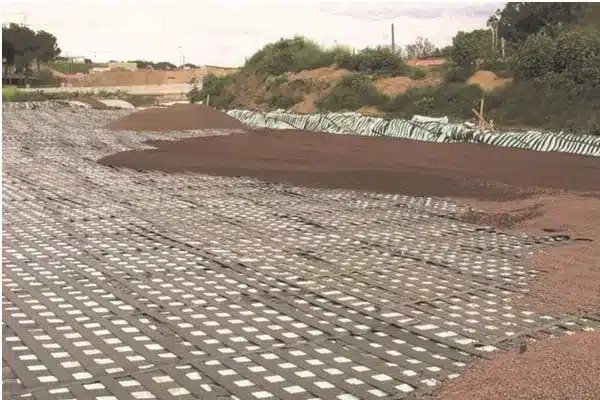

What Is Geogrid Stabilization in Soil Engineering?
Geogrid stabilization in soil engineering is a ground improvement technique that uses geogrid reinforcement to enhance the mechanical behavior and load-bearing capacity of soil and aggregate layers. Geogrids are polymer-based, grid-like geosynthetic materials designed to work through mechanical interlock with surrounding soil or aggregate.
When embedded within soil layers, geogrids perform several critical functions:
- Soil reinforcement: The geogrid provides tensile strength that soil alone lacks, reducing lateral movement and increasing overall stability.
- Load distribution: Applied loads are spread over a wider area, decreasing stress concentrations and minimizing settlement and deformation.
- Soil confinement: Interlocking between the geogrid apertures and aggregate restricts particle movement, improving stiffness and shear resistance.
- Structural support: Geogrid stabilization enables weak or unstable soils to safely support roads, pavements, embankments, retaining walls, and slopes.
- Long-term performance: Properly designed geogrid systems reduce rutting, cracking, and maintenance requirements, significantly extending the service life of infrastructure.
Geogrid stabilization is widely adopted in modern civil engineering because it offers a reliable, cost-effective alternative to traditional soil replacement methods while improving structural performance and durability.
How is geogrid used in soil stabilization?
Geogrids serve various purposes in soil stabilization:
- Soil Reinforcement: Geogrids are laid horizontally in the soil to bolster it. They consolidate aggregate, carry variable loads, and ensure the dispersal of tensile forces, reducing the formation of ruts and deformation from frictional forces, thus enhancing their capacity to support structures like roads, embankments, and retaining walls.
- Retaining Walls: Geogrids can be incorporated to stabilize the soil and boost the wall’s structural integrity in the construction of retaining walls.
- Slope Stability: Geogrids are applied on steep slopes to prevent erosion and landslides, effectively securing the soil in place.
- Pavement Construction: Geogrids play a key role in pavement construction by minimizing cracking and prolonging the lifespan of roads and parking lots.
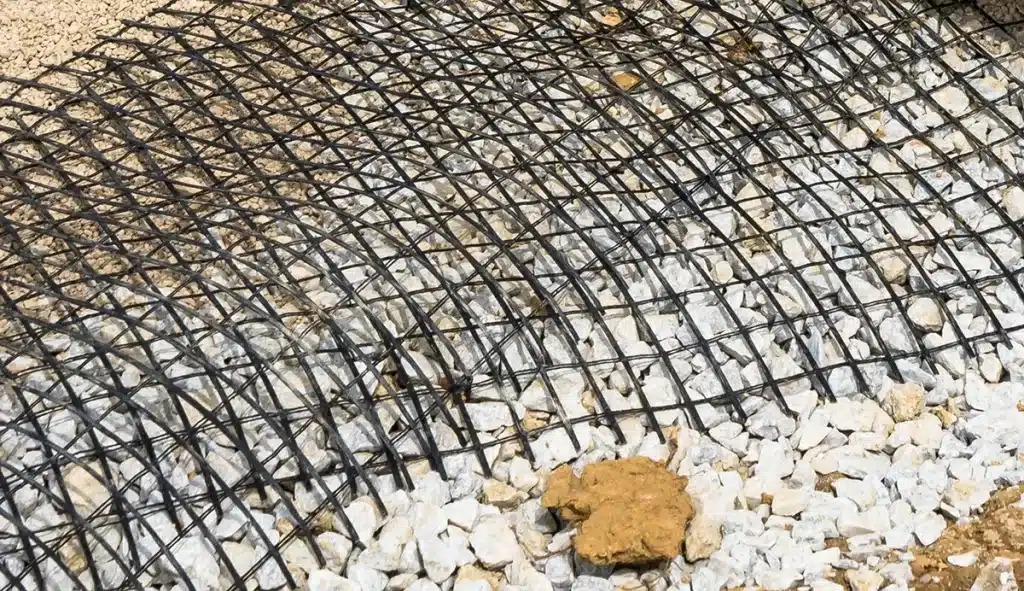

What are the benefits of using geogrid for soil stabilization?
Using geogrid for soil stabilization offers several advantages. Some key benefits include:
- Increased Load-Bearing Capacity: Geogrids improve the soil’s load-bearing capacity, allowing it to support heavier structures and traffic loads.
- Preventing Soil Erosion: Geogrids help stabilize slopes and prevent soil erosion, preserving the integrity of infrastructure.
- Extended Lifespan: Geogrids contribute to the longevity of construction projects by reducing the risk of settlement and shifting.
- Cost-Efficiency: Geogrid stabilization can be a cost-effective solution when compared to traditional methods that may require more excavation and backfill.
Are There Specific Considerations for Using Geogrid in Different Soil Types?
Yes. Geogrid performance depends on soil conditions and project requirements:
- Soil type: Granular soils provide strong interlock, while cohesive and organic soils may require drainage measures or layered reinforcement.
- Load conditions: Higher traffic or structural loads require geogrids with greater tensile strength.
- Environmental factors: Moisture, chemicals, and temperature changes affect material selection.
- Installation quality: Proper compaction and correct layer placement are essential.
- Geogrid selection: Uniaxial, biaxial, or triaxial geogrids should match stress direction and application needs.
Correct selection and installation ensure effective stabilization and long-term performance.
In conclusion, geogrids are a versatile and effective solution for soil stabilization in civil engineering and construction projects. When used correctly and in line with specific project requirements, geogrids provide enhanced stability, increased load-bearing capacity, and reduced maintenance costs, making them a valuable tool in modern infrastructure development.


Get Free Sample
We’ll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)






















