+86-159 9860 6917
info@geofantex.com
geofantex@gmail.com
+86-400-8266163-44899
Geogrid retaining wall systems
Geogrid retaining wall systems are a type of reinforced soil structure used to retain soil and other materials in a variety of construction applications. These systems typically consist of a facing element, such as concrete blocks, masonry units, or panels, that are connected to a geogrid reinforcement.
One advantage of geogrid retaining wall systems is that they can be used in a variety of soil conditions, including soft soils and those with low shear strength. Additionally, the modular nature of many geogrid retaining wall systems allows for easy installation and customization to fit the needs of a particular project.
The geogrid reinforcement is typically made of a high-strength polymer material that is placed in layers within the soil behind the retaining wall facing. The geogrids are designed to provide additional stability and support to the retaining wall, helping to prevent soil erosion and slope failure.
Overall, geogrid retaining wall systems offer an effective and durable solution for retaining soil and other materials in a wide range of construction applications.
Is geogrid necessary for retaining wall?
Image result for geogrid retaining wall systems
Generally, most VERSA-LOK units need geogrid for walls taller than three to four feet. If there are steep slopes near the wall, loading above the wall, tiered walls or poor soils, then even shorter walls may need geogrid.
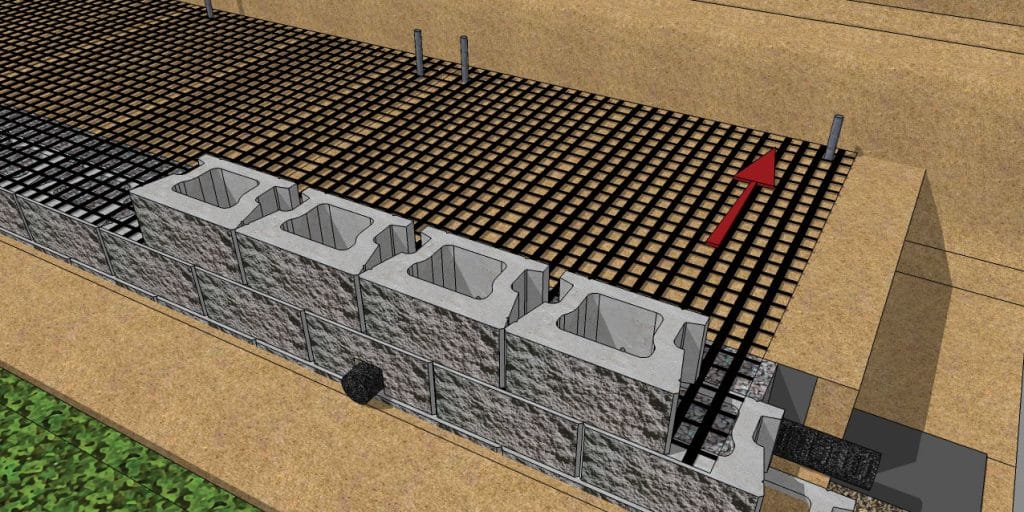
Geogrid retaining wall design example
Here’s an example of a basic geogrid retaining wall design:
Assumptions:
- The retaining wall is 12 feet high and 50 feet long
- The retained soil is level and has a unit weight of 120 pounds per cubic foot
- The geogrid reinforcement will be placed at a 3-foot spacing
Design steps:
1.Determine the required factor of safety against sliding and overturning. A typical factor of safety for retaining walls is 1.5.
2.Calculate the lateral earth pressure acting on the retaining wall. Assuming a passive earth pressure distribution, the lateral earth pressure at the base of the wall is:
Ka x H x γ x sin(φ) = 0.5 x 12 x 120 x sin(17) = 1,056 psf
Where:Ka = Active earth pressure coefficient (assumed to be 0.5)
γ = Unit weight of retained soil
H = Height of retaining wall
3.Calculate the required horizontal force capacity of the geogrid reinforcement.
φ = Angle of internal friction of retained soil (assumed to be 17 degrees)
Horizontal force per unit length of the geogrid = 52,800 lbs/ft ÷ 3 ft = 17,600 lbs/ft
Horizontal force per unit length of the wall = 1,056 psf x 50 ft = 52,800 lbs/ft
4.Select a geogrid reinforcement with sufficient strength to resist the calculated horizontal force. A common type of geogrid used in retaining wall applications is a uniaxial geogrid with a strength of at least 10,000 lbs/ft.
5.Determine the required depth of the geogrid reinforcement. A typical rule of thumb is to place the geogrid one-third of the wall height into the retained soil. Therefore, the geogrid should be placed at a depth of 4 feet.
6.Design the retaining wall facing element to resist the required vertical load and any additional loads, such as traffic loads or surcharge loads. The facing element can be made of various materials such as concrete blocks, masonry units, or panels.
7.Prepare a detailed construction plan including excavation, backfilling, and compaction procedures.
This is a simplified example of a geogrid retaining wall design. In practice, there may be additional factors to consider, such as water pressure, soil drainage, and seismic loads, that could affect the design. It’s important to consult with a qualified engineer or contractor to ensure a safe and effective geogrid retaining wall design for your specific project.

The best geogrid for a retaining wall
Uniaxial Geogrid: Geogrid for Retaining Walls
This geogrid has strength in one direction and is used predominantly in retainingwalls.























