+86-159 9860 6917
info@geofantex.com
geofantex@gmail.com
+86-400-8266163-44899
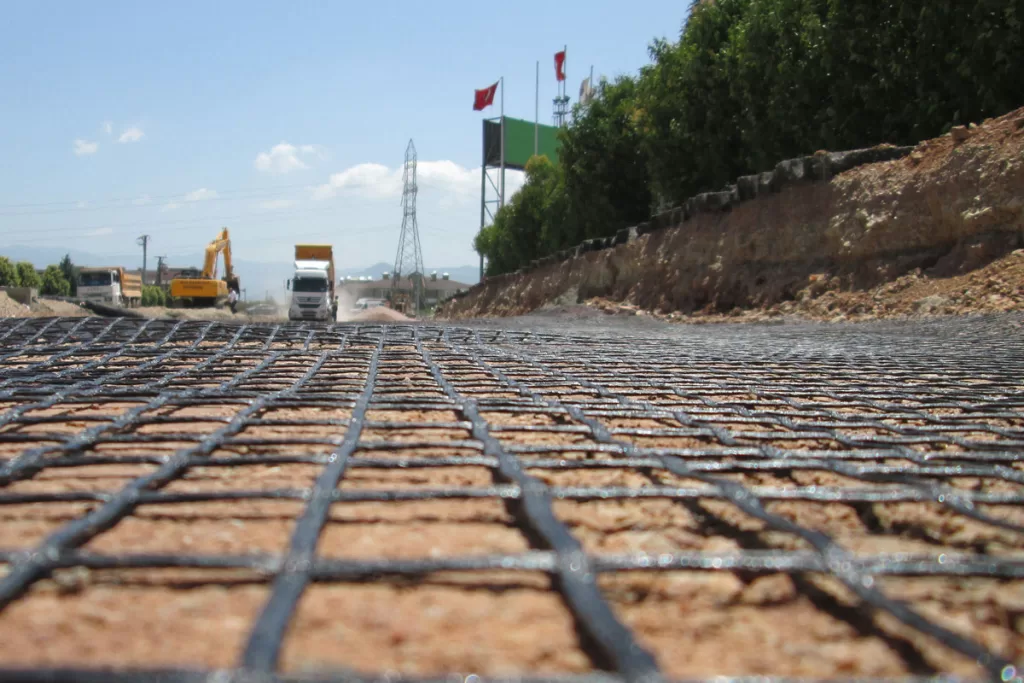
Geogrid road reinforcement is a crucial application in modern civil engineering, providing enhanced strength and longevity to road structures. Geogrids are a type of geosynthetic material designed to stabilize soil and distribute loads evenly across road surfaces, effectively reducing rutting, cracking, and overall deterioration. They are widely used in constructing and reinforcing roads, railways, embankments, and other load-bearing surfaces. This article explores the role of geogrids in road reinforcement, their unique characteristics compared to other geosynthetics, and their broader applications in pavement engineering.
What is Geogrid Used for in Roads?
Geogrid is a geosynthetic material widely used in road construction to improve performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Its main functions in road applications include:
- Soil Stabilization: Geogrids reinforce weak subgrades by distributing loads more evenly, reducing rutting and deformation.
- Base Reinforcement: Placed between soil layers or within the base course, geogrids enhance the load-bearing capacity, allowing for thinner pavement structures without sacrificing strength.
- Improved Load Distribution: They spread vehicle loads over a broader area, minimizing stress on underlying layers.
- Reduced Maintenance: Roads with geogrid reinforcement experience fewer cracks and failures over time, lowering long-term repair costs.
- Separation and Filtration (in composite forms): When combined with geotextiles, geogrids can also help separate soil layers and maintain drainage.
Overall, geogrids are essential for building longer-lasting, more efficient roads, especially in areas with poor soil conditions.

What is Geogrid Reinforcement?
Geogrid reinforcement is a type of geosynthetic material used in civil engineering to reinforce soil or improve the stability of a structure. It’s typically made from polymer materials such as polyester, polypropylene, or fiberglass and is designed with an open grid structure that allows it to interlock with surrounding soil, aggregate, or other materials.
Geogrids are often used in applications like:
- Reinforced soil structures: They help improve the strength of soil, allowing for the construction of retaining walls, embankments, and other structures on weak or unstable ground.
- Pavement reinforcement: Used in road construction to improve the stability and lifespan of pavements by reducing rutting and cracking.
- Slope stabilization: Geogrids help prevent erosion and provide stability for steep slopes and embankments.
The primary benefit of geogrid reinforcement is that it allows for better load distribution and prevents lateral movement of the soil, which can enhance the performance of structures built on or with it.
What Are Geogrids?
Geogrids offer critical support in various infrastructure applications:
- Soil reinforcement: Their open-grid design allows for interlocking with soil or gravel, increasing load-bearing capacity and reducing settlement.
- Slope and embankment stabilization: Geogrids help retain soil on steep slopes or embankments, preventing erosion or collapse.
- Retaining wall support: They provide structural integrity behind retaining walls by distributing loads evenly.
- Road and pavement support: Used under roads and highways to stabilize weak subgrades and extend pavement life.
- Long-term durability: Geogrids are resistant to UV, chemicals, and biological degradation, making them ideal for long-term buried applications.
In short, geogrids are essential in any project that requires improved ground stability, load distribution, and soil confinement.

What is the Difference Between Geogrids and Geotextiles?
The difference between geogrids and geotextiles lies in their structure, function, and application in civil engineering and geosynthetic projects:
| Feature | Geogrids | Geotextiles |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Grid-like, rigid/flexible | Fabric-like, woven/non-woven |
| Key Function | Reinforcement | Separation, filtration, drainage |
| Soil Interaction | Interlock with aggregates | Filter or separate fine materials |
What are Geosynthetics in Pavement Reinforcement Applications?
Here’s the information rewritten in a clear table format:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition | Synthetic materials used to improve the performance and durability of pavements. |
| Common Types | – Geotextiles: Separation, filtration, minor reinforcement- Geogrids: Soil stabilization and load distribution- Geocells: 3D confinement for load support- Geomembranes: Impermeable barriers to block water- Geocomposites: Combined materials for multi-functionality |
| Key Functions | – Separation: Prevents mixing of soil layers- Reinforcement: Enhances structural strength- Filtration/Drainage: Manages water flow- Load Distribution: Reduces stress and deformation |
| Benefits | – Longer pavement life- Reduced maintenance- Cost-effective construction- Improved resistance to rutting and cracking- Sustainable and efficient resource use |
| Applications | Synthetic materials are used to improve the performance and durability of pavements. |
Geogrid road reinforcement is a critical technique in road construction, designed to increase durability and load-bearing capacity. Geogrids enhance pavement stability by reinforcing the underlying soil layers and ensuring that roads withstand heavy traffic without significant deformation. Although distinct from geotextiles, geogrids work in tandem with other geosynthetics to provide comprehensive support for road structures. By leveraging geosynthetics, engineers can build more resilient, sustainable, and cost-effective roads, contributing to the longevity of infrastructure in challenging environments.


Get Free Sample
We’ll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)






















