+86-159 9860 6917
info@geofantex.com
geofantex@gmail.com
+86-400-8266163-44899
Retaining walls are crucial for managing slopes and hillsides, especially in areas prone to erosion or collapse. One innovative solution that has proven effective in enhancing the structural integrity of these walls is the use of geogrids. Geogrids, with their grid-like polymeric materials, reinforce soil, distributing loads evenly and increasing the overall stability of the retaining structure. This article explores the critical role of geogrids in constructing durable and reliable slope hillside retaining walls.
When to use geogrid in retaining walls?
Geogrid is typically used in retaining walls when additional reinforcement is necessary to support the wall structure and prevent it from failing due to soil pressure or external loads. Here are some specific scenarios where the use of geogrid in retaining walls is recommended:
- Tall Retaining Walls: Geogrid is often used to provide additional stability for walls taller than 3-4 feet. The taller the wall, the greater the pressure exerted by the retained soil, making reinforcement crucial.
- Sloped Backfill: When the backfill behind the retaining wall is sloped, the lateral earth pressure increases. Geogrid helps distribute this pressure more evenly, reducing the risk of wall failure.
- Poor Soil Conditions: In areas with weak or unstable soil, geogrid can improve the overall stability of the wall by reinforcing the soil and preventing movement that could lead to wall collapse.
- Heavy Loads: If the retaining wall is designed to support heavy loads, such as vehicular traffic or structures above, geogrid can provide the necessary reinforcement to handle these additional stresses.
- Segmental Retaining Walls: Geogrid is commonly used in segmental retaining walls (SRWs), where the wall is constructed from individual blocks or units. The geogrid ties these units together, improving the wall’s overall strength and stability.
In general, the decision to use geogrid in a retaining wall design should be based on an engineering assessment of the site conditions, wall height, and the expected loads on the wall.
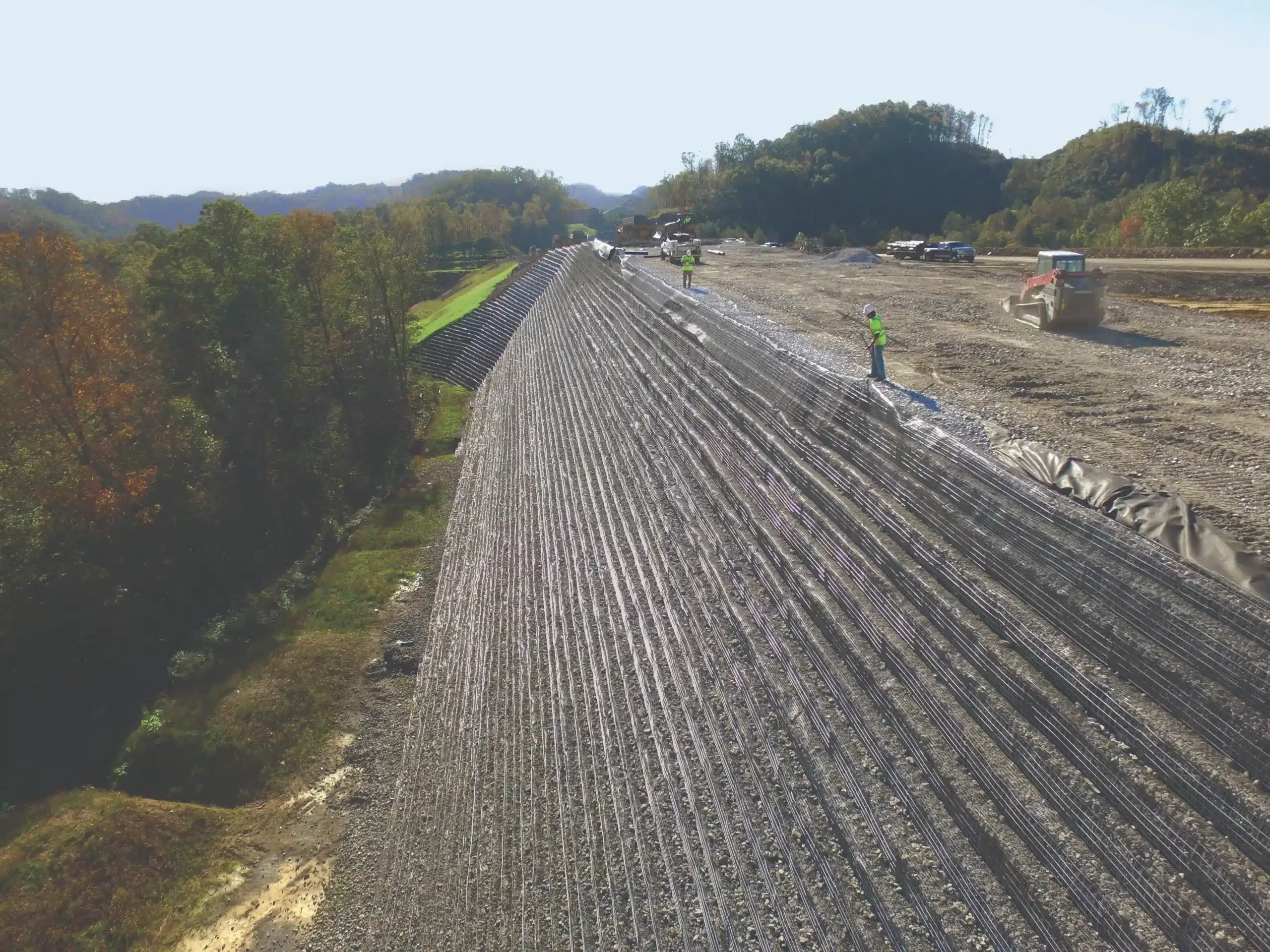

How high can a retaining wall be without geogrid?
The maximum height of a retaining wall built without geogrid reinforcement depends on wall type, soil conditions, and loading, but general engineering guidelines apply:
- Gravity retaining walls (concrete, stone, large masonry blocks) can typically reach 3–4 ft (0.9–1.2 m) without geogrid, relying on their own weight for stability.
- Segmental retaining walls (SRWs) made from interlocking concrete blocks may also reach about 3–4 ft without geogrid, provided soil conditions are good and surcharge loads are minimal.
- Soil quality impact: Weak, expansive, or poorly drained soils can significantly reduce the safe unsupported height.
- Loading conditions: Sloped backfill, nearby structures, traffic, or seismic activity lower the allowable height without reinforcement.
- Code requirements: Many local building codes require engineered reinforcement, including geogrid, for walls over 4 ft, regardless of wall type.
In practice, retaining walls taller than 4 ft almost always require geogrid or another reinforcement system to control lateral earth pressure, limit deformation, and ensure long-term structural safety.
How Do You Stabilize Steep Slopes Effectively?
Stabilizing steep slopes requires a combination of soil reinforcement, drainage control, and surface protection to prevent erosion, sliding, and long-term instability. The most effective solutions are typically engineered systems rather than single methods.
Key slope stabilization approaches include:
- Geosynthetic reinforcement: Geogrids are widely used to reinforce steep slopes by increasing soil shear strength and internal stability. Installed in layers within the slope, geogrids create a reinforced soil mass that resists sliding and deformation. Geocells and geotextiles are often used alongside geogrids to improve confinement, drainage, and erosion resistance.
- Drainage management: Excess water is one of the primary causes of slope failure. Subsurface drains, drainage geocomposites, and permeable backfill materials help reduce pore water pressure and prevent soil softening.
- Terracing and benching: Cutting a steep slope into horizontal steps reduces the effective slope angle and limits downslope forces. Each bench can be reinforced with geogrid and protected with vegetation or facing systems.
In practice, steep slope stabilization is most successful when geogrid reinforcement is combined with proper drainage and surface protection. This integrated approach ensures both short-term construction stability and long-term performance under environmental and load conditions.
How do you install geogrid in retaining walls?
Installing geogrid in retaining walls involves several key steps to ensure proper reinforcement and long-term stability:
- Prepare the Base: Excavate and level the area behind the wall where the geogrid will be installed. Remove debris and compact the soil to create a stable foundation.
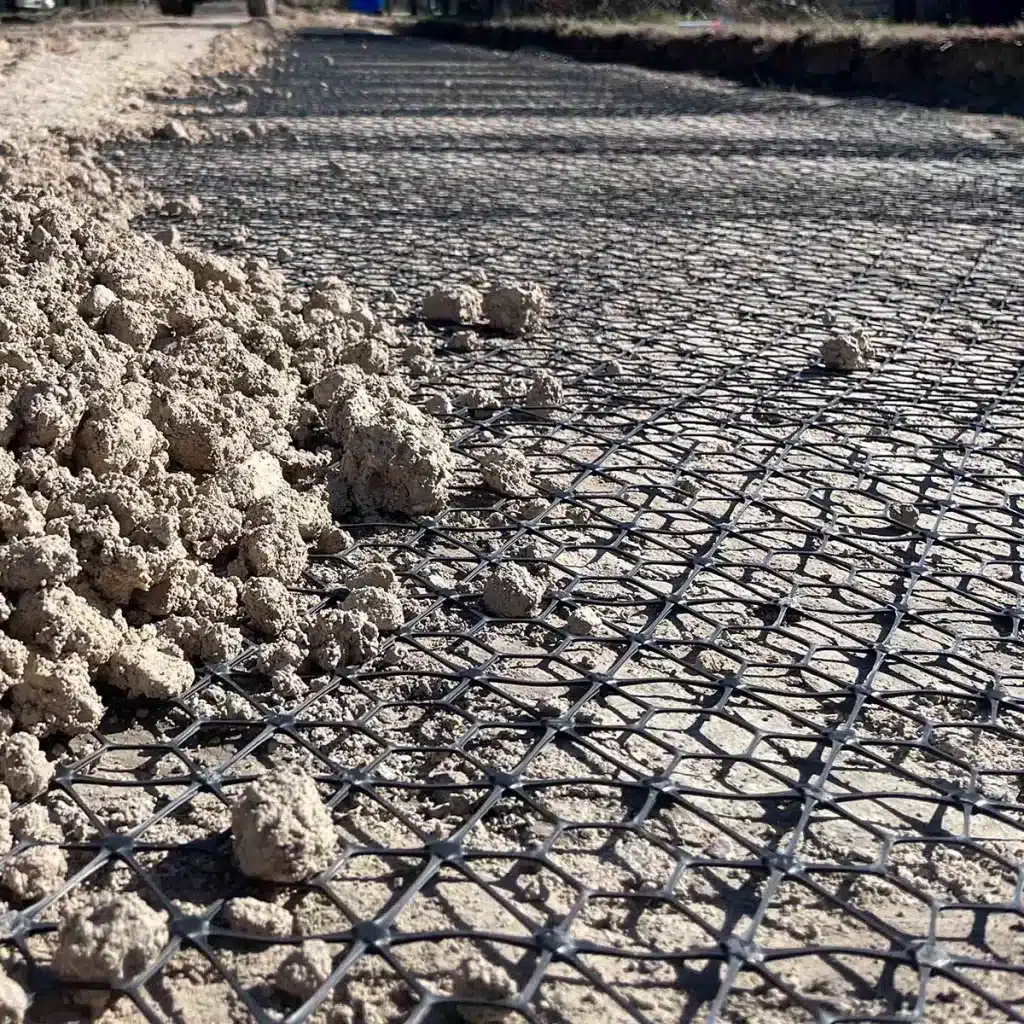
- Place the Geogrid: Roll out the geogrid horizontally behind the wall face, extending it into the backfill area. Ensure the grid is flat and free of wrinkles.
- Anchor the Grid: Secure the geogrid to the wall face using pins, stakes, or block faces, depending on the wall type. Proper anchoring prevents movement during backfilling.
- Backfill in Layers: Add soil or aggregate in layers over the geogrid, compacting each layer carefully. Ensure the geogrid remains flat and properly tensioned.
- Overlap Seams: If multiple geogrid sheets are needed, overlap them according to manufacturer guidelines, usually 12–24 inches (30–60 cm).
- Repeat for Multiple Layers: For taller walls, install additional layers of geogrid at specified vertical intervals (typically every 30–60 cm), following engineering recommendations.
- Final Compaction: Once all layers are installed, finish backfilling and compact the soil to complete the wall construction.
Proper installation of geogrid ensures that retaining walls achieve maximum load distribution, improved slope stability, and resistance to soil movement, ultimately extending the structure’s lifespan.
Geogrids are a powerful tool in the construction of slope hillside retaining walls, providing essential reinforcement that ensures the longevity and safety of these structures. By understanding when and how to effectively use geogrids, you can enhance the stability of slopes and hillsides in a cost-effective and environmentally friendly way. Whether you are dealing with high walls or steep slopes, geogrids offer a proven solution for challenging terrain.


Get Free Sample
We’ll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)






















