+86-159 9860 6917
info@geofantex.com
geofantex@gmail.com
+86-400-8266163-44899
Geogrid fabrics help prevent structural failure through their ability to withstand forces in a variety of applications. One common application is in driveway construction, where utilizing a biaxial driveway geogrid can help retain the structural integrity and long-term stability of the surface. One way to evaluate a geogrid’s reliability is through its junction integrity, defined by its ultimate junction strength.
Ultimate Junction Strength
Ultimate Junction Strength refers to the maximum tensile strength at the junction of a material, particularly relevant in geosynthetic materials such as geogrids. This concept is critical in applications where geosynthetics are subjected to forces that stress their interconnection points or junctions, such as in soil reinforcement or retaining walls.
In the context of geogrids, the junction strength determines how well the material can transfer loads between the grid structure and the surrounding soil or aggregate. The ultimate junction strength ensures that the geogrid’s nodes—where the ribs intersect—maintain their integrity under pressure and do not separate or fail under the applied load. It is tested to ensure the grid can withstand the maximum design stresses in the field.
Do you need more detailed information on how ultimate junction strength is tested or applied in geosynthetics?
Triaxial Geogrids
Triaxial geogrids have great junction integrity for two main reasons:
- Ribs cross in three directions, making for thicker junctions.
- Dense polymeric material: Each rib is made from a very dense polymeric material.
These features help triaxial geogrid junctions remain intact over time.
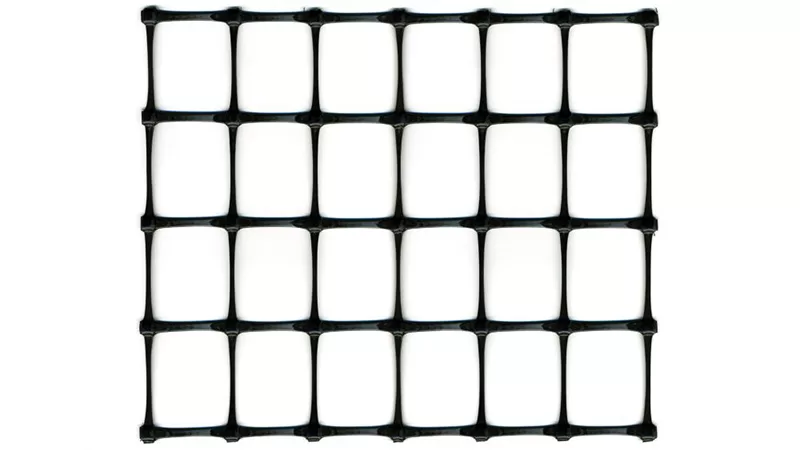
Biaxial Geogrids
Biaxial geogrids are geosynthetic materials formed into a grid of integrally connected tensile elements with apertures large enough to allow “strike-through” and interlocking with surrounding aggregate base materials, commonly rock. Biaxial geogrid increases the stiffness of unbound aggregate base layers and confines the aggregate particles under repetitive loading.
Specifications and Placement
Biaxial geogrids must be punched and drawn with polypropylene material and comply with Caltrans’ Standard Specifications for Biaxial Geogrids. The Biaxial geogrid is placed either below or within the aggregate base layer of a pavement structure. This composite section of geogrid and aggregate base is known as a mechanically stabilized layer (MSL).
Benefits of Biaxial Geogrids
- Reduced aggregate base thickness: Provides immediate cost savings.
- Increased performance life and reliability of the pavement.
- Improved compaction and uniformity over soft or variable soils.
- Reduced hauling and heavy construction traffic on local roads.
- Versatility in installation: Can be installed in a wide range of weather conditions.
- Improved safety: Reduced construction time due to less hauling and processing of subgrade or backfill materials.
- Compatibility: Can be used with reclaimed asphalt concrete aggregate base.
Appropriate Application Use
Biaxial geogrids are intended for asphalt or gravel (flexible) surfaces. There is no known benefit to using biaxial geogrids under concrete pavement. Biaxial geogrids are most cost-effective in areas where pavement surface grade and drainage control the pavement structural section.
Appropriate Applications Include:
- Restricted pavement surface grades due to local drainage or vertical clearance. A biaxial geogrid can provide a thinner section with equivalent performance.
- Expedited construction: The thinner biaxial geogrid section results in less construction time.
- Increased pavement structural capacity and performance life for the same thick pavement section without biaxial geogrid.
- Soft or weak subgrades: Biaxial geogrids can reduce or eliminate the need for material removal.
Overall, biaxial geogrids offer significant advantages in terms of structural support, cost savings, and construction efficiency in appropriate driveway and roadway applications.


Get Free Sample
We’ll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)






















