+86-159 9860 6917
info@geofantex.com
geofantex@gmail.com
+86-400-8266163-44899
Geonet landscape, a term often associated with geotextiles and geosynthetics, plays a crucial role in modern engineering and environmental projects. In this article, we will delve into the world of geonet and answer essential questions, such as what it is, what it’s made of, its applications, and its relationship with geotextile geomembranes.
What is geonet in geotextile?
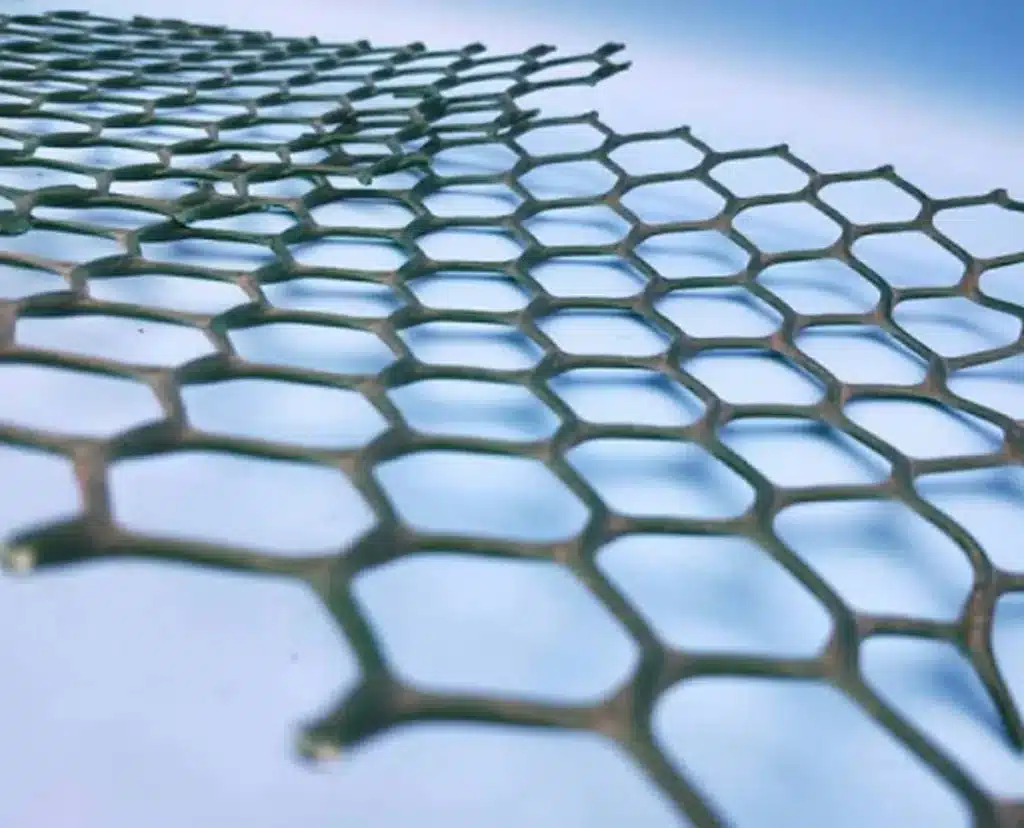
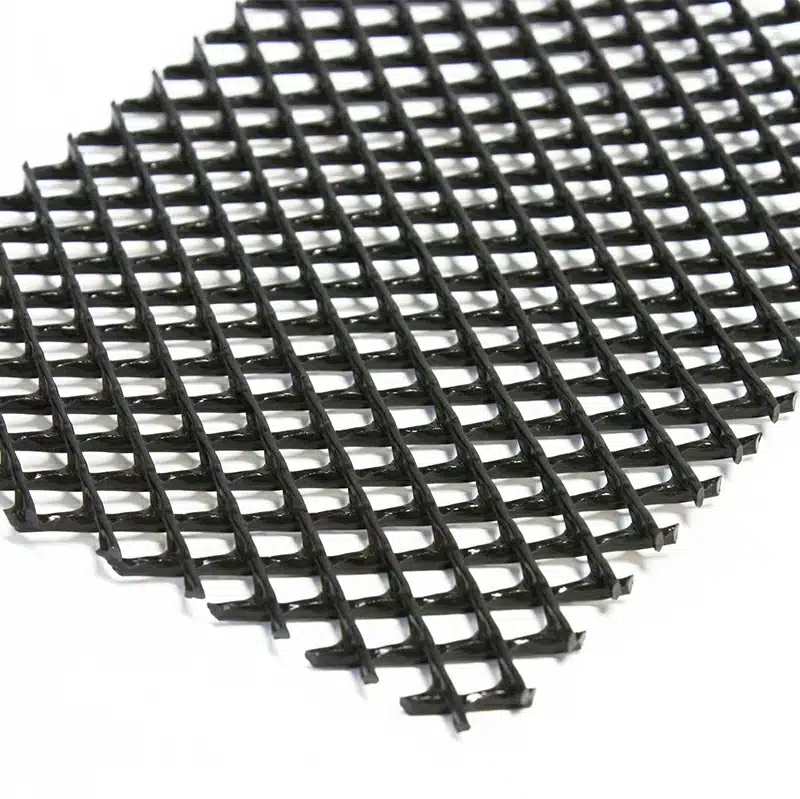
A geonet in geotextiles is a three-dimensional, synthetic drainage material made from high-density polyethylene (HDPE) or other polymers. It is designed to provide high flow capacity for drainage applications, typically placed between geotextiles or geomembranes in civil engineering projects.
Key Features of Geonets:
- Structure: Composed of parallel or crisscrossing polymeric ribs, forming a net-like configuration that enhances drainage.
- Function: Acts as a drainage layer, facilitating the lateral flow of liquids or gases in landfills, retaining walls, and roadbeds.
- Types:
- Biplanar: Two layers of intersecting ribs.
- Triplanar: Three layers with a central rib for higher compressive strength.
- Quadriplanar: Four-layered structure for extreme drainage efficiency.
Applications:
- Landfill drainage: Prevents leachate buildup.
- Road and railway subgrade: Reduces water accumulation.
- Retaining walls: Enhances stability by draining excess water.
- Green roofs: Manages water flow efficiently.
By combining geonets with geotextiles, engineers can create geocomposites for enhanced filtration, separation, and reinforcement in soil stabilization projects.
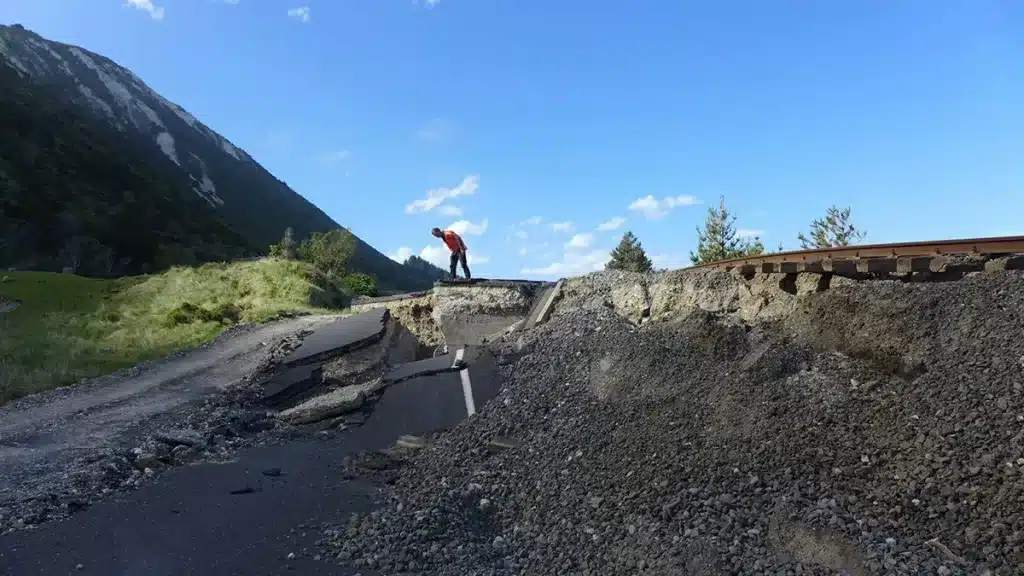

What is a geonet made of?
A geonet is typically made from high-density polyethylene (HDPE) or polypropylene (PP). These materials are chosen for their durability, chemical resistance, and long-term stability. Geonets are designed to provide efficient drainage and are often used in conjunction with other geosynthetics, such as geotextiles, to enhance their performance in various civil engineering and environmental applications. The HDPE or PP composition ensures that the geonet can withstand environmental stresses and maintain its structural integrity over time.
What is geonet used for?
Geonet, also known as geosynthetic net, is a geosynthetic material designed for various applications in civil engineering, environmental protection, and construction industries.
Primary Functions:
- Drainage: Geonets provide an efficient method for fluid drainage by allowing water or other liquids to pass through while preventing soil or debris from clogging the drainage system.
- Erosion Control: They help stabilize soil and prevent erosion on slopes, embankments, and riverbanks by providing structural support.
- Reinforcement: Geonets enhance the strength and stability of soil structures, making them suitable for applications such as retaining walls and road foundations.
Industry Utilization:
- Civil Engineering: Used in road construction, retaining walls, and bridge abutments to improve structural integrity and longevity.
- Environmental Protection: Applied in landfills and waste management facilities to control leachate and gas emissions, and prevent contamination.
- Agriculture: Employed for soil stabilization in agricultural fields and to prevent erosion in irrigation channels.
- Mining: Utilized in mining operations for drainage, soil stabilization, and erosion control.
Specific Benefits:
- Durability: Made from high-density polyethylene (HDPE) or polypropylene, geonets are resistant to chemicals, UV radiation, and environmental degradation.
- Cost-Effectiveness: They reduce the need for traditional drainage systems and soil reinforcement methods, leading to lower construction and maintenance costs.
- Environmental Protection: By providing effective erosion control and drainage, geonets help protect natural habitats and prevent soil and water contamination.
In conclusion, understanding the world of geonet landscape is essential for those involved in civil engineering and environmental projects. Geonets, with their drainage and filtration properties, play a pivotal role in enhancing the performance and longevity of various geosynthetic applications. Whether you’re working on drainage systems, erosion control, or waste management, geonets are a valuable tool in your toolkit.

Get Free Sample
We’ll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)






















