+86-159 9860 6917
info@geofantex.com
geofantex@gmail.com
+86-400-8266163-44899
HDPE Geocell, a revolutionary material in civil engineering, has gained significant traction for its versatility and functionality in various construction projects. This article delves into the essence of HDPE Geocell, its applications, and requirements, and explores its pivotal role in modern infrastructure development.
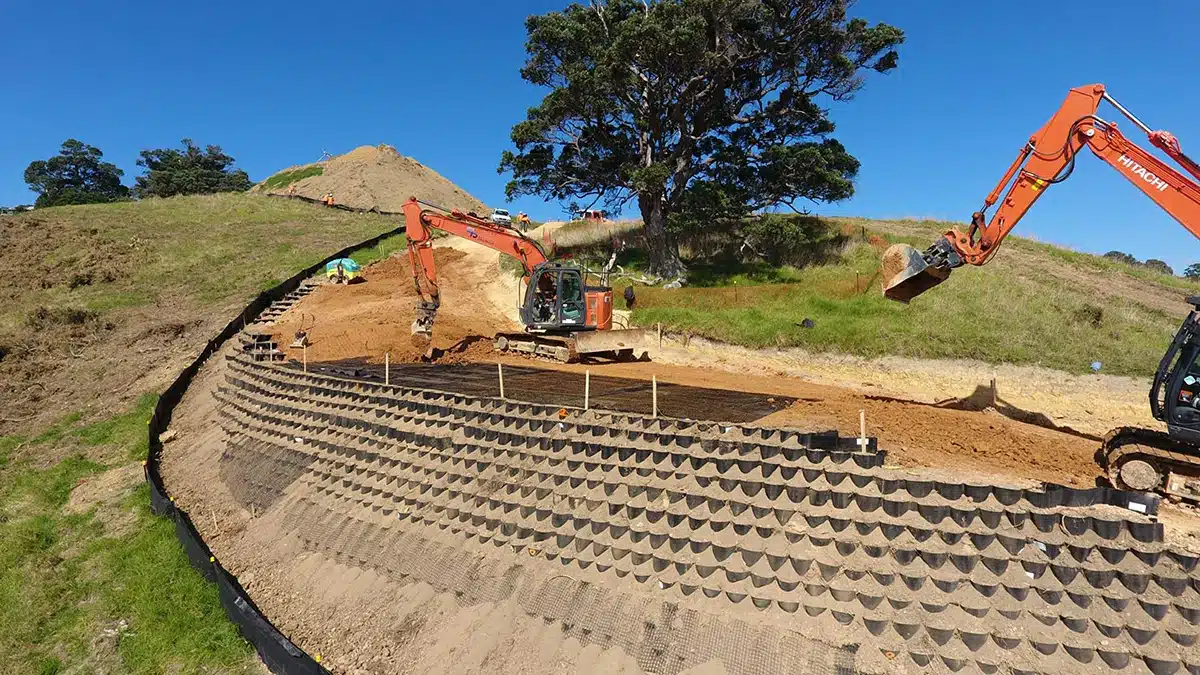

What is HDPE Geocell Material?
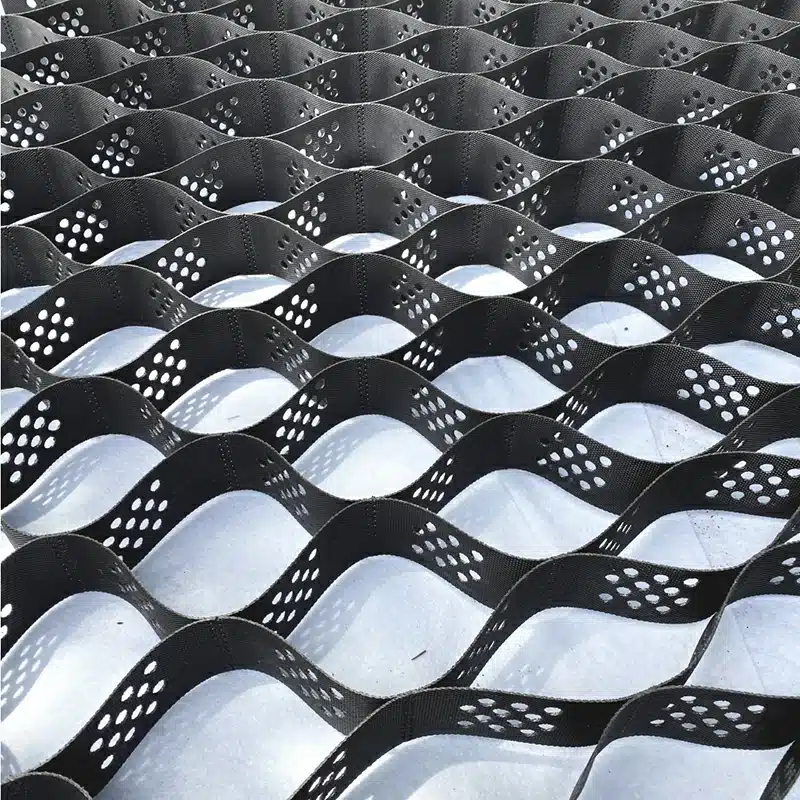
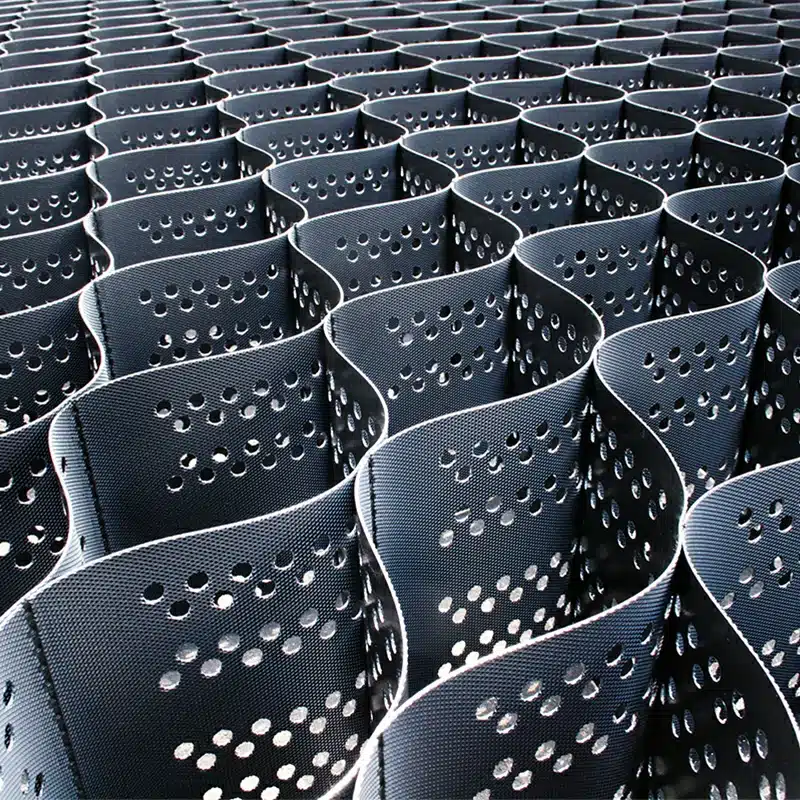
HDPE Geocell Material refers to geocells made from High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE), a strong, durable plastic polymer. HDPE is known for its high tensile strength, resistance to chemicals, UV radiation, and environmental stress.
Key Features of HDPE Geocells:
- Durability: HDPE geocells are highly resistant to environmental factors like UV exposure, chemicals, and extreme weather conditions, making them long-lasting.
- Strength: The material offers excellent strength and is used to stabilize soil, prevent erosion, and support heavy loads.
- Lightweight: Despite their strength, HDPE geocells are lightweight, which makes them easier and cheaper to transport and install.
- Flexibility: HDPE geocells can be expanded, shaped, and filled with materials like gravel, soil, or sand to reinforce weak soils or improve drainage.
HDPE geocells are commonly used in road construction, slope stabilization, erosion control, and foundation support projects.
What is the Use of HDPE Geocell?
HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene) geocells are a type of cellular confinement system used in civil engineering projects to reinforce and stabilize soils. These flexible, lightweight, and durable three-dimensional honeycomb-like structures are made from HDPE and are primarily used to enhance load distribution, improve soil strength, and control erosion.
Key Uses of HDPE Geocells
Soil Stabilization
- HDPE geocells are widely used in soil stabilization for weak or loose soils. By confining the soil within their cellular structure, they improve the shear strength of the soil and prevent lateral movement. This application is crucial in projects such as the construction of embankments, roads, and retaining walls.
Erosion Control
- Geocells are effective in preventing erosion on slopes and embankments. By securing the soil within the geocell structure, they help reduce surface runoff and the displacement of soil particles, especially in areas prone to heavy rainfall or water flow.
Load Distribution
One of the primary functions of HDPE geocells is to distribute loads over a larger area, which reduces stress on underlying soils. This makes them ideal for applications such as:
- Road construction over weak soils.
- Support for railway tracks and airport runways.
- Foundation support for large structures.
Vegetation Support
- In addition to erosion control, HDPE geocells can be filled with topsoil and used to support vegetation growth, promoting green spaces and further stabilizing slopes or embankments. They can also be used in landscaping projects.
Advantages of HDPE Geocells
- High Durability and Flexibility: HDPE geocells are resistant to chemical reactions, UV degradation, and environmental stress, making them suitable for harsh environments.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Their lightweight structure reduces transportation and installation costs, and the use of local fill material makes the construction process more affordable.
- Sustainable: The use of HDPE geocells reduces the need for non-renewable construction materials such as concrete, making them an eco-friendly solution.
- Versatility: They can be used with a variety of infill materials (e.g., sand, gravel, soil), depending on the project’s requirements.
Limitations
- Limited to Certain Soil Types: HDPE geocells may not be suitable for extremely soft or organic soils without additional ground improvement techniques.
- Potential for Clogging: When used in areas prone to fine silt or clay particles, the cells may become clogged, reducing their effectiveness.
- Installation Complexity: Proper installation techniques are required to ensure optimal performance. Poor installation can lead to uneven load distribution and reduced lifespan.
Examples of Successful Implementations
- Road Construction in Soft Soils: In many road construction projects over marshy or weak ground, HDPE geocells have successfully improved load-bearing capacity, reducing road maintenance costs.
- Slope Reinforcement in Mountainous Areas: HDPE geocells have been used to stabilize slopes in hilly and mountainous regions, preventing landslides and erosion.
- Erosion Control in Coastal Areas: Along coastlines, HDPE geocells have been employed to reinforce embankments and prevent erosion caused by waves and tidal action.
HDPE geocells are a versatile and effective tool in civil engineering for soil stabilization, erosion control, and load distribution. Their advantages, such as durability, cost-effectiveness, and environmental benefits, make them a preferred choice over traditional materials in many projects. However, careful consideration of soil types and proper installation techniques is essential to ensure their long-term performance.
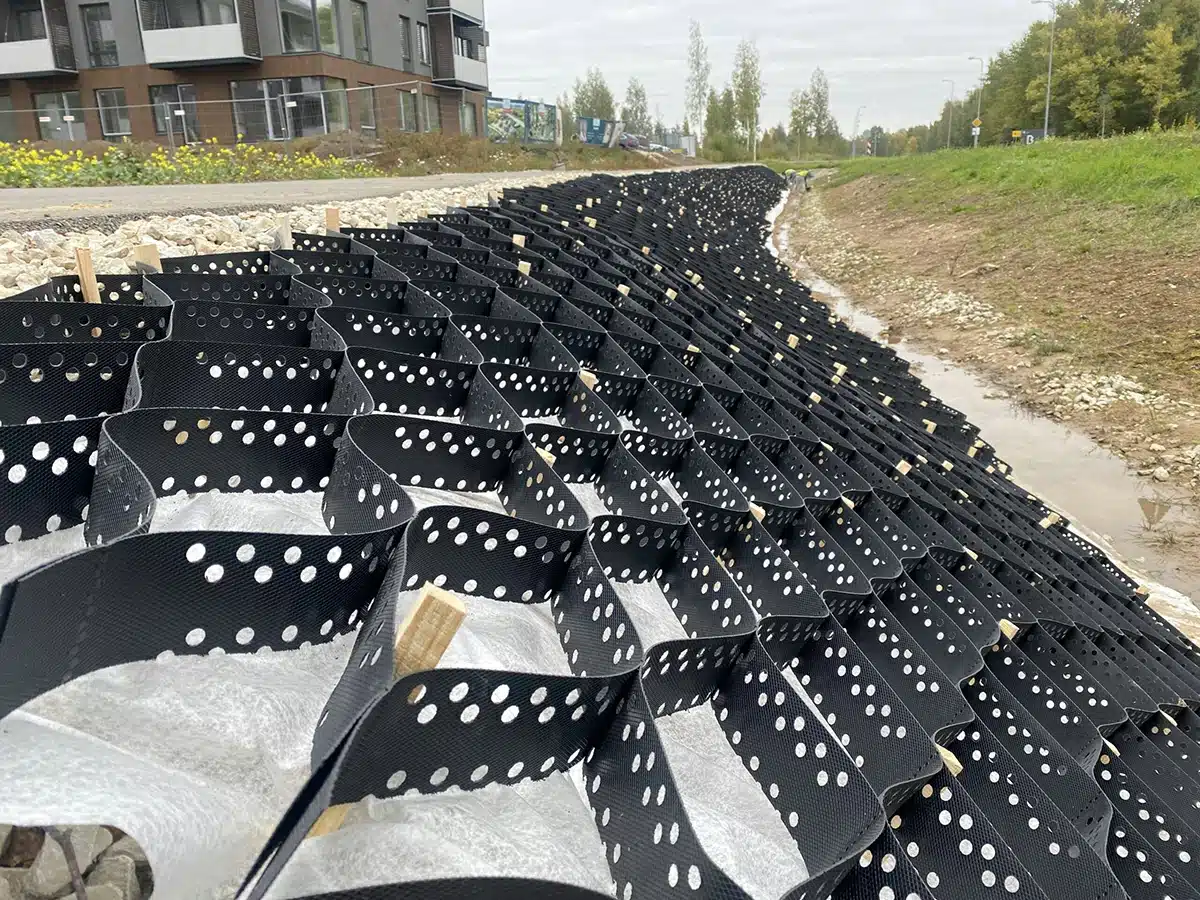

What distinguishes HDPE Geocell from other soil stabilization methods or materials?
High-density polyethylene (HDPE) geocells are a unique form of soil stabilization that stands out for several reasons:
- Structure: Geocells are three-dimensional cellular structures made from interconnected panels or cells that confine and stabilize soil. HDPE geocells have a strong, rigid structure that can withstand heavy loads and distribute weight more evenly compared to traditional stabilization methods like gravel, sand, or geotextiles.
- Versatility: They can be used in various applications such as erosion control, slope protection, retaining walls, and load support for roads and railways. Their versatility allows engineers to use them in different soil conditions and terrains.
- Increased Load-Bearing Capacity: Geocells improve load-bearing capacity by spreading the load over a larger area. When filled with materials like soil, aggregate, or concrete, they create a stable foundation that can support heavy loads.
- Erosion Control: Geocells help prevent soil erosion by confining soil particles within the cells. This prevents them from being washed away by water runoff or wind.
- Ease of Installation: They are relatively easy to install and require minimal specialized equipment. This can reduce construction time and costs compared to other conventional stabilization methods.
- Environmental Benefits: HDPE geocells are often made from recycled materials, making them environmentally friendly. Additionally, their use can reduce the need for excavation and disposal of soil, minimizing environmental impact.
How Does HDPE Geocell Benefit Construction Projects?
High-density polyethylene (HDPE) geocells are widely used in construction projects due to their unique properties and the benefits they bring. Here are some of the key ways in which HDPE geocells benefit construction:
- Soil Stabilization: Geocells are used to stabilize soils in various applications, such as roads, railways, and embankments. The cellular confinement system effectively holds the soil in place, preventing erosion and improving the load-bearing capacity of the soil.
- Increased Load Distribution: The 3D honeycomb structure of geocells distributes loads over a broader area, reducing pressure on the underlying soil. This helps prevent soil deformation and increases the lifespan of the structure, particularly useful in areas with soft ground or where heavy loads are expected.
- Cost Efficiency: By improving the structural integrity of weaker soils, geocells can reduce the need for expensive traditional construction materials like concrete and large quantities of compacted base layers. This results in significant cost savings in material transport, handling, and installation.
- Environmentally Friendly: HDPE geocells are often manufactured from recycled materials, which helps reduce the environmental impact. Additionally, the use of geocells can minimize the disturbance to the existing landscape and reduce the need for additional quarried materials.
- Versatility: Geocells can be used in a variety of construction scenarios including slope protection, channel protection, retaining walls, and erosion control. Their flexibility allows them to be installed in diverse environments ranging from deserts to wetlands.
- Speed of Construction: The installation of geocells is relatively quick and easy, requiring less specialized equipment and labor than many traditional construction methods. This speeds up project timelines significantly.
- Durability: HDPE is resistant to chemicals, ultraviolet degradation, and extreme weather conditions, which makes geocells particularly durable and suitable for long-term applications in challenging environments.
By incorporating HDPE geocells into construction projects, engineers and contractors can achieve more durable, cost-effective, and environmentally sustainable results. This technology continues to evolve and find new applications in the field of civil engineering.
In conclusion, HDPE Geocell stands as a transformative material in the realm of civil engineering, offering innovative solutions for soil stabilization, erosion control, and structural reinforcement. Its durability, and versatility benefits position it as a crucial component in modern construction practices.

Get Free Sample
We’ll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)






















