+86-159 9860 6917
info@geofantex.com
geofantex@gmail.com
+86-400-8266163-44899
Drainage composites are essential materials designed to manage and direct the flow of water in various construction, engineering, and landscaping projects. These versatile products help prevent water accumulation and damage, promoting better water flow and reducing the risk of soil erosion. This article will explore the importance of drainage composites, focusing on their structure, functions, and differences from similar materials.
What is composite drainage?
Composite drainage refers to an innovative system designed to manage and direct water flow by combining multiple materials, such as geotextiles, drainage membranes, and sometimes geocomposites. These materials work synergistically to filter water, prevent clogging, and support soil stability. For added performance, composite drainage often includes an all-in-one system that combines a dimple core and a nonwoven geotextile fabric, which enhances the flow of water while maintaining the integrity of the surrounding soil. Such a system is particularly valuable in environments where proper drainage is essential for structural stability, such as in roadways, retaining walls, and landfills.
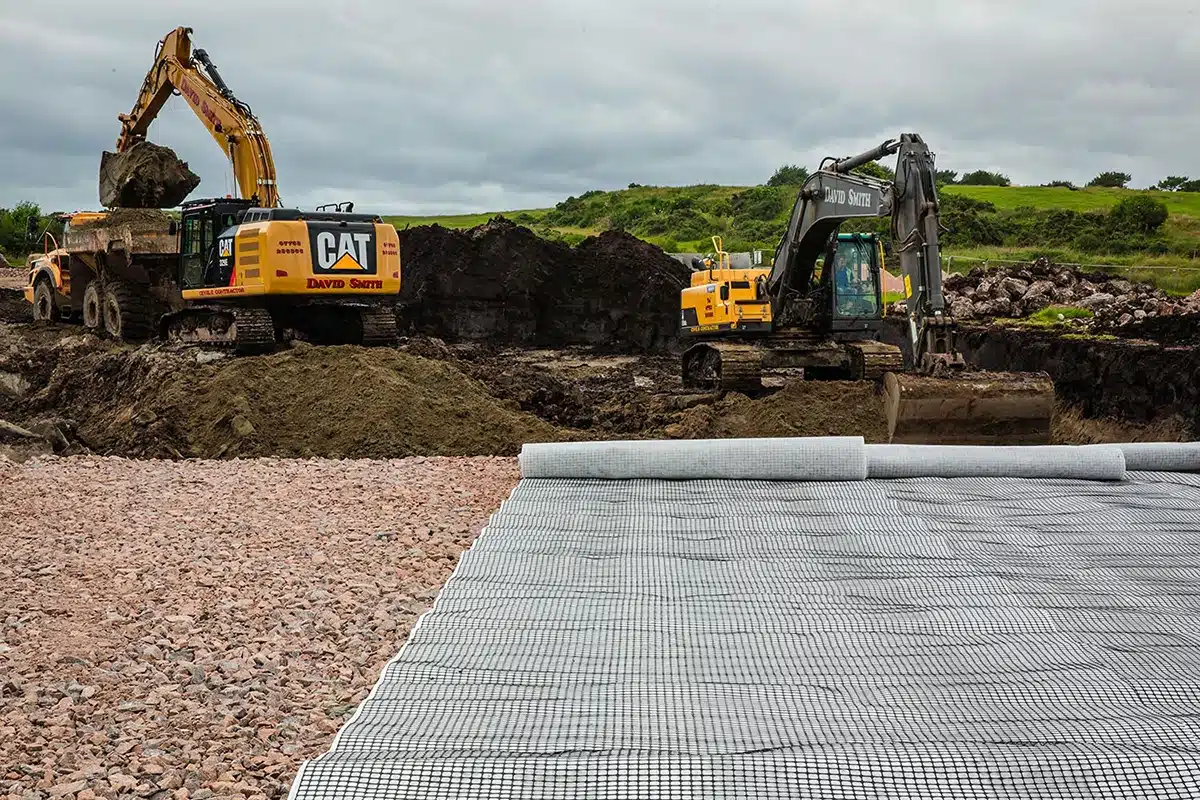

What is drainage geocomposite?
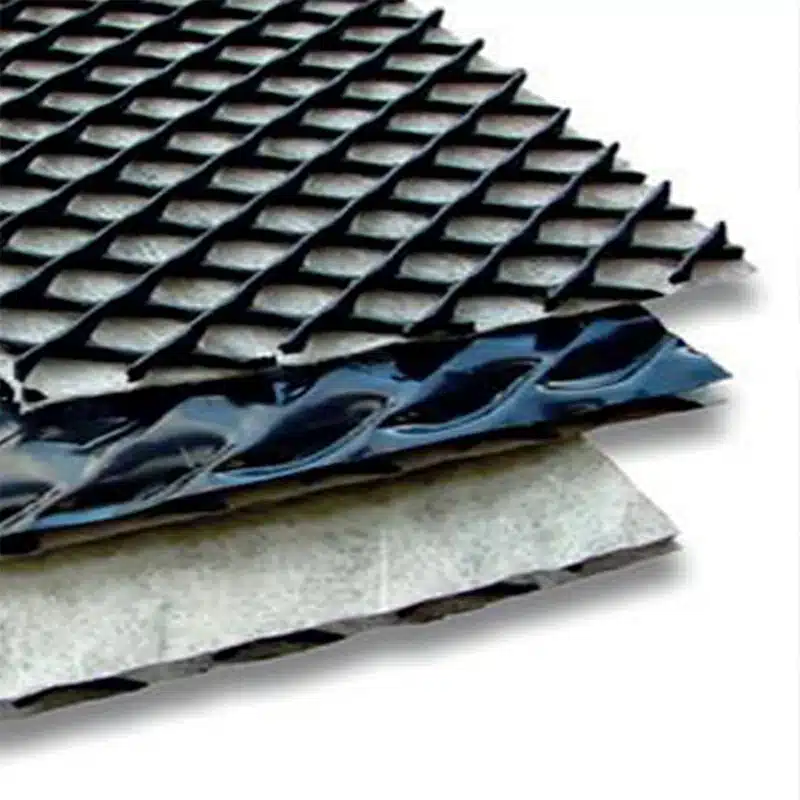
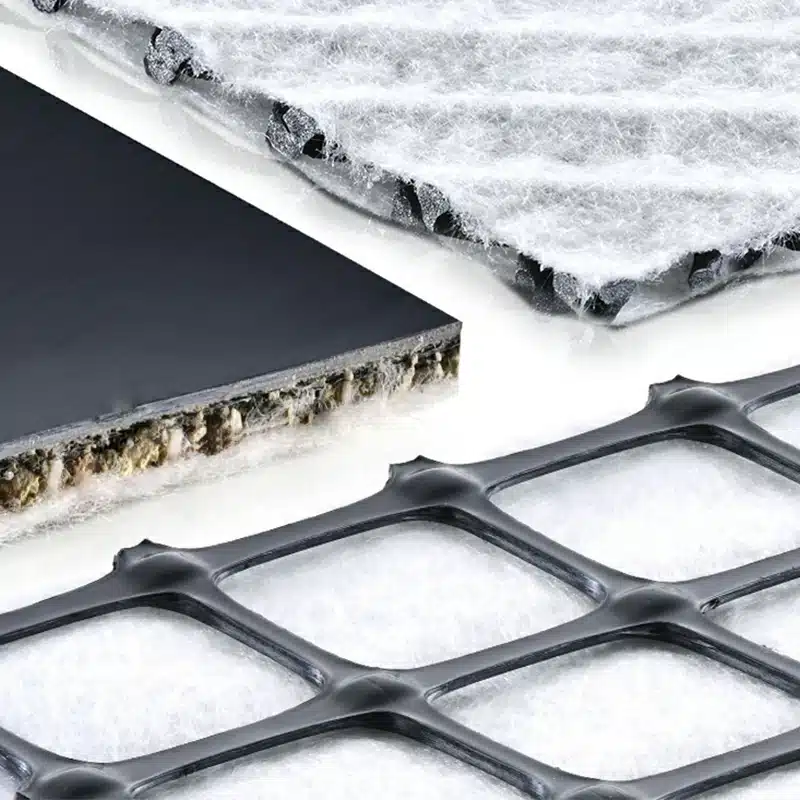
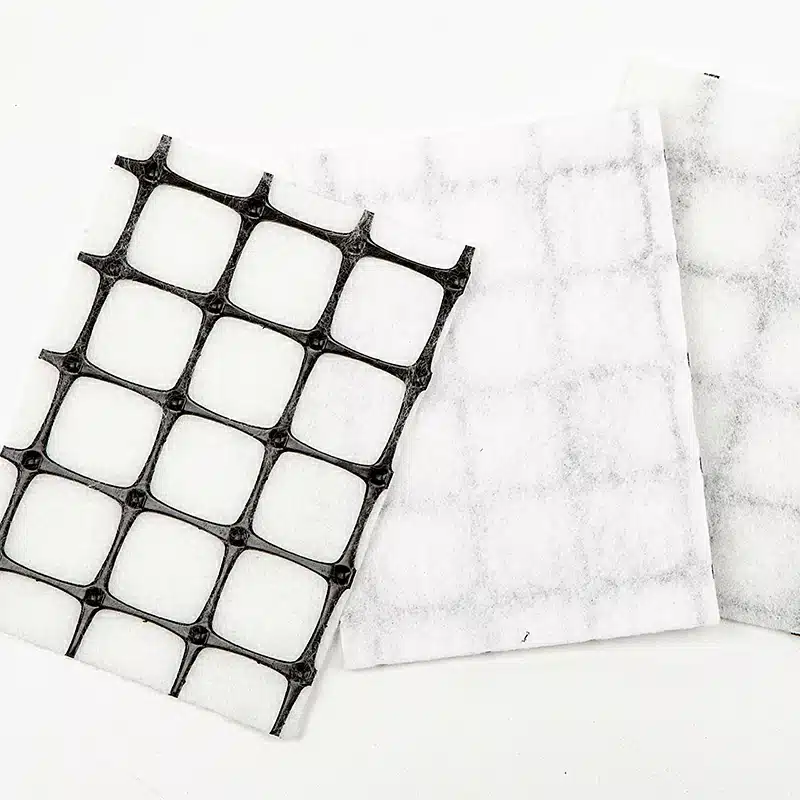
A drainage geocomposite is an engineered composite material that combines a geotextile with a drainage core. The geotextile serves primarily to provide filtration and separation, ensuring that only clean water flows through while preventing soil and debris from clogging the system. The drainage core, often made of materials such as plastic or polypropylene, acts as a conduit to direct water flow efficiently.
These geocomposites are structured to complement or replace sand, stone, and gravel to act as drainage, filtration, separation, and barrier protection. This makes them a versatile solution in civil engineering and construction projects, particularly when managing water flow, preventing soil erosion, and safeguarding against groundwater contamination.
In practice, drainage geocomposites are widely used in various applications, including landfill drainage systems, highway construction, and green roof designs. Their ability to replace traditional materials like gravel allows for more cost-effective, efficient, and long-lasting solutions. The integrated design reduces the need for bulky stone or sand layers, while still offering high performance in water management and structural protection.
In conclusion, drainage geocomposites provide a robust and efficient solution for water management in a variety of civil engineering and construction contexts, offering benefits in filtration, separation, and protection without the need for traditional aggregate materials.
What is the drainage layer made of?
The drainage layer in a composite system plays a critical role in managing water flow while preventing soil and particles from clogging the system. When designing an effective drainage layer, a combination of materials such as **gravel, sand, or geocomposites** is commonly used to ensure both water movement and structural stability.
Key Components of the Drainage Layer:
Geotextiles:
- Role: Geotextiles filter water, allowing it to pass through while blocking larger particles like soil or sediment. They are crucial for maintaining the integrity of the system and preventing clogging.
- Materials: Nonwoven fabrics are often used for their excellent filtration properties.
- Benefits: They prevent soil erosion, improve drainage efficiency, and enhance the longevity of the system.
Perforated Pipes:
- Role: Perforated pipes are strategically placed within the drainage layer to collect and transport water from one area to another. These pipes help direct water flow efficiently.
- Materials: Typically made from plastic or PVC, perforated pipes are durable and resistant to corrosion.
- Benefits: They facilitate water movement and reduce the risk of waterlogging by quickly draining excess moisture.
Synthetic Drainage Cores:
- Role: Synthetic drainage cores, often made of materials like plastic or polypropylene, act as a conduit for water, channeling it effectively to its designated path.
- Materials: These cores are often structured in a way that mimics the role of gravel, sand, or geocomposites, acting as a replacement for traditional materials like gravel while maintaining high drainage efficiency.
- Benefits: They are lightweight, easy to install, and help maintain water flow without the compaction issues associated with stone-based drainage systems.
Best Practices:
- Material Selection: Choose materials based on the specific needs of the drainage system, such as the level of filtration or the type of soil.
- Installation: Ensure proper placement of geotextiles to prevent soil contact with the drainage core and avoid clogging.
- Maintenance: Regular inspections and cleaning of perforated pipes help maintain water flow and prevent blockages.
By combining these components, the drainage layer becomes a highly effective system for managing water, improving soil stability, and preventing waterlogging, with materials like **gravel, sand, or geocomposites** offering alternative solutions for various construction needs.
What is the difference between geotextile and geocomposite?
Geotextiles and geocomposites are both essential components in modern drainage systems, each serving distinct but complementary functions. Below is a detailed comparison of these materials, exploring their roles infiltration, drainage, reinforcement, and more.
Geotextiles
Geotextiles are permeable fabrics, typically made from synthetic fibers, used primarily for soil filtration, separation, and reinforcement.
Primary Functions:
- Isolation: Geotextiles mainly play the role of isolation, preventing the mixing of soil layers while allowing water to flow freely.
- Filtration: They act as a filtration medium, permitting the passage of water while blocking the movement of soil particles, and preventing clogging of the drainage system.
- Drainage: By facilitating water flow through their porous structure, geotextiles ensure that moisture is efficiently removed from the soil.
- Applications: Commonly used in road construction, landfills, and drainage systems where basic soil reinforcement and filtration are required.
Geocomposites
Geocomposites combine geotextiles with additional materials like drainage cores or membranes to offer more complex functions in drainage systems.
Primary Functions:
- Isolation and Filtration: Like geotextiles, geocomposites serve isolation and filtration roles but with enhanced capabilities due to their integrated design.
- Drainage: Geocomposites provide superior drainage performance because the drainage core within the composite helps channel water more efficiently.
- Reinforcement: Some geocomposites also offer reinforcement, enhancing soil stability, especially in high-stress environments.
- Applications: Preferred in more demanding applications such as high-capacity drainage systems, landfills, and large-scale construction projects where advanced drainage, filtration, and reinforcement are necessary.
Key Differences and Performance Advantages:
- Complexity: Geotextiles are simpler in design, focusing primarily on filtration, separation, and drainage. Geocomposites, however, combine geotextiles with other components, enabling additional functions like reinforcement and enhanced water flow.
- Efficiency in Drainage: Geocomposites excel in applications where advanced drainage solutions are required, due to the inclusion of drainage cores which improve water management.
- Reinforcement: While geotextiles can provide some reinforcement, geocomposites are more effective in this regard, offering greater support for soil and structures.
In summary, geotextiles mainly play the role of isolation, filtration, drainage, etc, providing essential functions in simpler drainage applications. Geocomposites, on the other hand, offer a broader range of functions, such as isolation, filtration, drainage, and reinforcement, making them more suitable for demanding applications that require high performance and enhanced efficiency.
Drainage composites play a crucial role in modern construction, agriculture, and environmental management by providing effective water management solutions. From composite drainage systems to advanced geocomposites, these materials ensure that water is efficiently directed away from sensitive areas, preventing soil erosion and damage to structures. Understanding the differences between geotextiles and geocomposites helps in selecting the right material for the job, ultimately contributing to safer and more sustainable infrastructure.


Get Free Sample
We’ll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)






















