+86-159 9860 6917
info@geofantex.com
geofantex@gmail.com
+86-400-8266163-44899
The use of geogrid for road construction is becoming increasingly common as geosynthetics gain ground in civil engineering. These high-performance materials are critical for reinforcing soil, reducing maintenance costs, and increasing pavement lifespan.
What is a geogrid and how is it used in road construction?
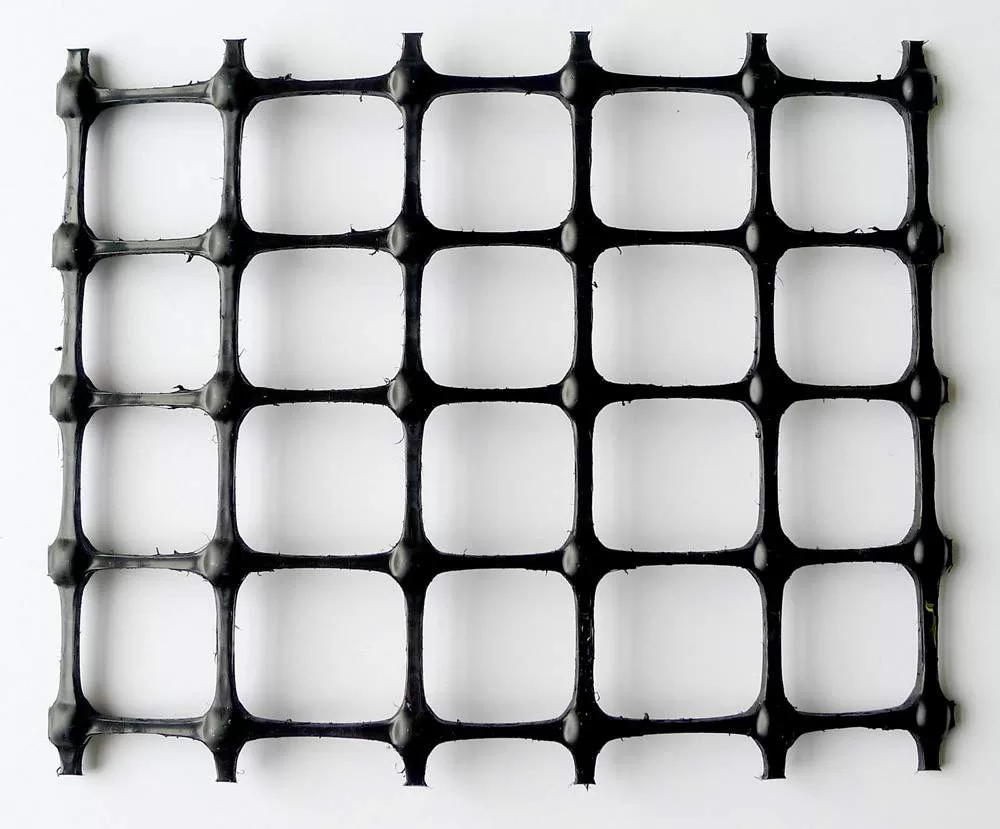
A geogrid is a high-strength geosynthetic material made from polymers such as polypropylene, polyethylene, or polyester, engineered specifically to reinforce soil and aggregate structures. In the context of road construction, geogrids serve as reinforcement layers that enhance structural integrity and prolong the life of pavements.
When used in geogrid for road construction applications, these materials are typically installed between base and subbase layers, or directly beneath asphalt surfaces. Their open-grid design allows for interlocking with aggregate materials, improving the load transfer and reducing the lateral spread of base course materials. This results in:
- Improved load distribution, especially under heavy traffic conditions.
- Reduction in pavement deformation and rutting, even in weak subgrade soils.
- Enhanced bearing capacity, allowing for reduced thickness of structural layers.
- Lower long-term maintenance costs by delaying surface cracking and deformation.
According to the Geosynthetic Research Institute, incorporating geogrids in flexible pavement systems can lead to up to 50% reduction in required base thickness without compromising performance. This not only cuts material costs but also decreases construction time and environmental impact.
Overall, the use of geogrid for road construction is a proven engineering solution that delivers long-term economic and performance benefits, especially for roads subjected to high axle loads or challenging soil conditions.
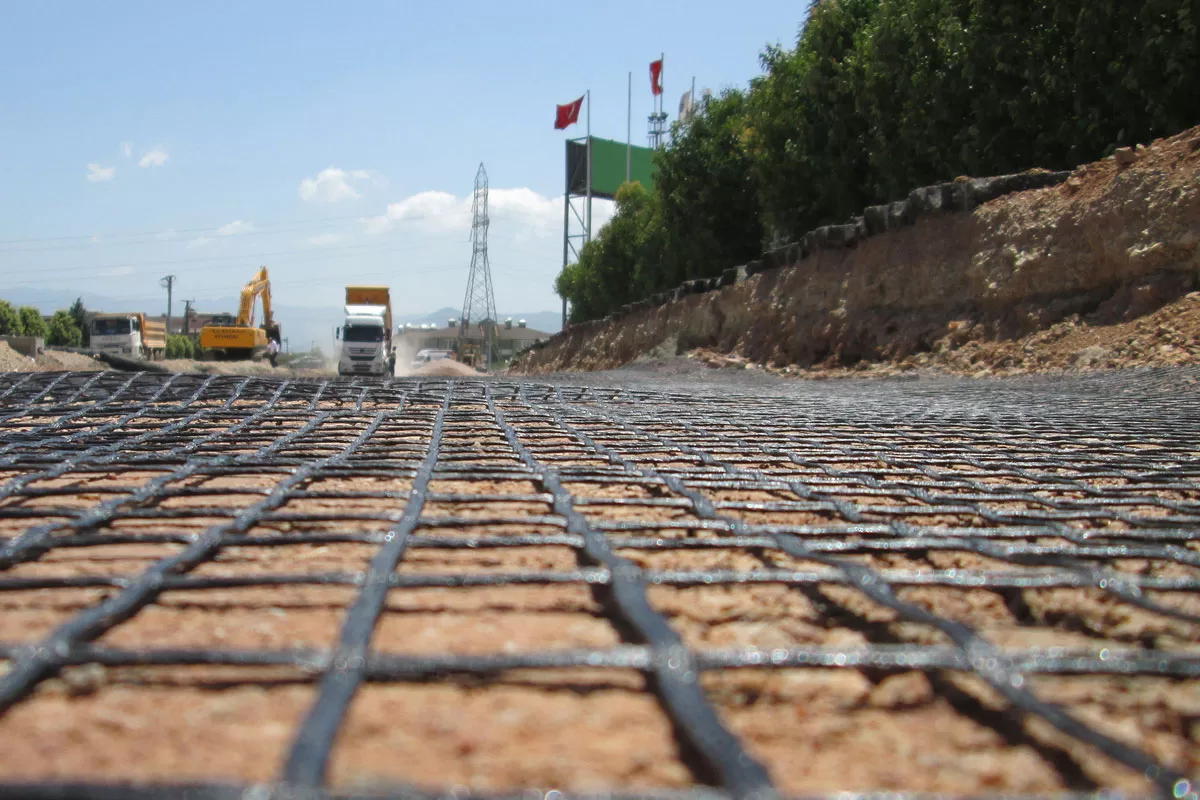

Why Is Geogrid for Road Construction Gaining Popularity in the Geosynthetics Industry?
Geogrid for road construction is gaining widespread adoption due to its ability to address key challenges in modern infrastructure development—namely weak subgrades, rising construction costs, sustainability requirements, and long-term performance demands.
- Cost efficiency and material reduction: One of the primary drivers is the significant reduction in aggregate and base course thickness. By improving load distribution and confinement, geogrids can reduce base layer thickness by up to 50%, lowering material consumption, transportation costs, and construction time.
- Improved pavement performance and lifespan: Geogrid-reinforced roads exhibit reduced rutting, cracking, and deformation under repeated traffic loads. Industry studies show that pavements incorporating geogrids can achieve up to 30% longer service life, decreasing maintenance frequency and lifecycle costs.
- Adaptability to poor soil conditions: As infrastructure expands into areas with weak or variable subgrade soils, geogrids provide a reliable solution for soil stabilization without extensive excavation or soil replacement, making them ideal for rehabilitation and new construction alike.
- Sustainability and environmental benefits: Reducing aggregate usage and construction thickness directly lowers carbon emissions associated with quarrying, hauling, and placement. This aligns geogrid for road construction with global sustainability and low-carbon infrastructure goals.
- Market growth and standardization: According to industry forecasts, the global geogrid market continues to expand steadily, driven by highway expansion, urbanization, and road rehabilitation projects. Increased standardization in design guidelines and specifications has further accelerated adoption.
In summary, geogrid for road construction is gaining popularity because it delivers a rare combination of engineering performance, economic savings, and environmental responsibility, making it a preferred solution for modern, resilient road infrastructure.
How does geogrid performance compare with traditional construction methods?

- Improved load distribution: Geogrids enhance the transfer of wheel loads across a wider area, significantly reducing stress concentrations in the base and subgrade layers, particularly under heavy and repetitive traffic conditions.
- Reduction in pavement deformation and rutting: By restricting lateral movement of aggregates, geogrids minimize rut formation and surface deformation, even when roads are constructed over weak or variable subgrade soils.
- Enhanced bearing capacity: The interlocking mechanism between geogrids and aggregate increases overall structural stiffness, allowing engineers to reduce the thickness of base and subbase layers without sacrificing performance or safety.
- Lower long-term maintenance costs: Geogrid-reinforced pavements experience delayed crack initiation and slower structural degradation, resulting in fewer repairs, extended maintenance intervals, and reduced lifecycle costs.
According to the Geosynthetic Research Institute, incorporating geogrids in flexible pavement systems can achieve up to a 50% reduction in required base thickness without compromising structural performance. This reduction directly lowers material consumption, shortens construction timelines, and decreases the environmental footprint of road projects.
What are the challenges and innovations in geogrid development?
While geogrids offer significant advantages, they require careful design and proper installation to achieve optimal results. Innovations such as biaxial and triaxial geogrids have improved performance by enhancing load distribution in multiple directions. A 2023 report from ResearchAndMarkets indicates that North America accounted for over 35% of global geogrid demand due to highway expansion and road rehabilitation projects.
The integration of geogrid for road construction represents a forward-thinking solution in geosynthetics, combining strength, cost-efficiency, and sustainability. As demand for long-lasting infrastructure grows, geogrids are set to play an increasingly vital role in modern road engineering.


Get Free Sample
We’ll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)






















