+86-159 9860 6917
info@geofantex.com
geofantex@gmail.com
+86-400-8266163-44899
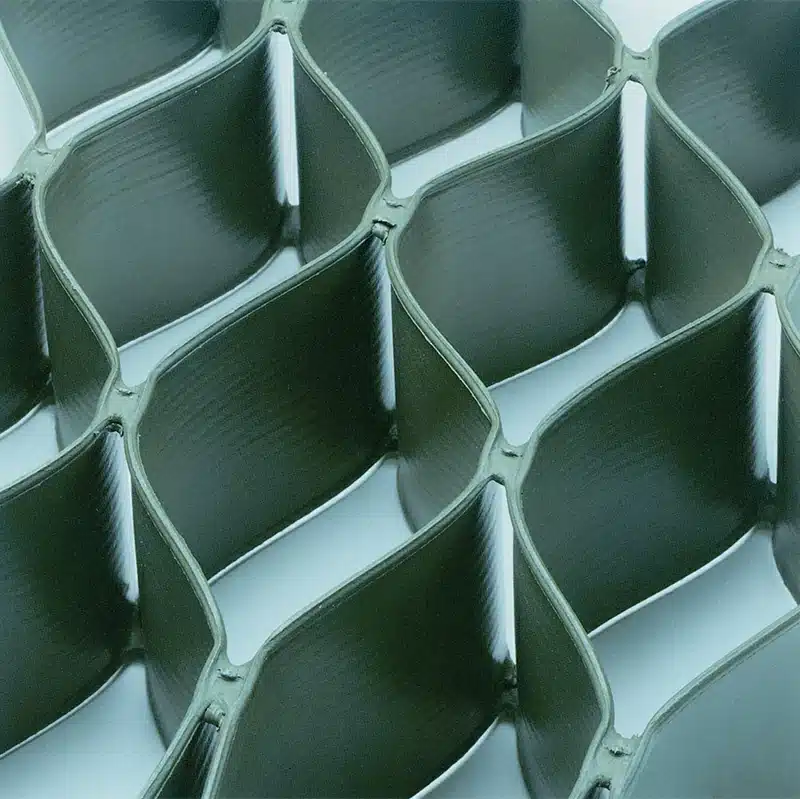
Geocells are three-dimensional, honeycomb-like structures made of polymeric materials used for soil stabilization, erosion control, and load support in construction projects. Their ability to confine soil or aggregate within their cells provides improved strength and durability to the surface. Proper installation of geocells is crucial to maximize their benefits. This essay explores the key steps involved in installing geocells effectively by answering four important questions.

What Site Preparations Are Necessary Before Installing Geocells?
Before installing geocells, proper site preparation is essential to ensure stability and performance. Key steps include:
- Clearing the site: Remove vegetation, roots, debris, rocks, and topsoil to create a clean working surface.
- Grading and compacting: Level the ground according to design requirements and compact the subgrade to provide a stable base.
- Subgrade assessment: Evaluate soil strength and add a stabilization layer or geotextile if needed to improve load-bearing capacity.
- Drainage planning: Install necessary drainage systems like trenches or pipes to prevent water accumulation under the geocells.
- Geotextile placement: Where required, lay a geotextile layer to separate subgrade and infill material, enhancing stability and filtration.
- Anchoring preparation: Mark positions for stakes or tendons, especially on slopes or in high-load applications.
- Material staging: Ensure infill materials are delivered and accessible without disturbing the prepared area.
Proper execution of these steps helps ensure a durable and effective geocell installation.
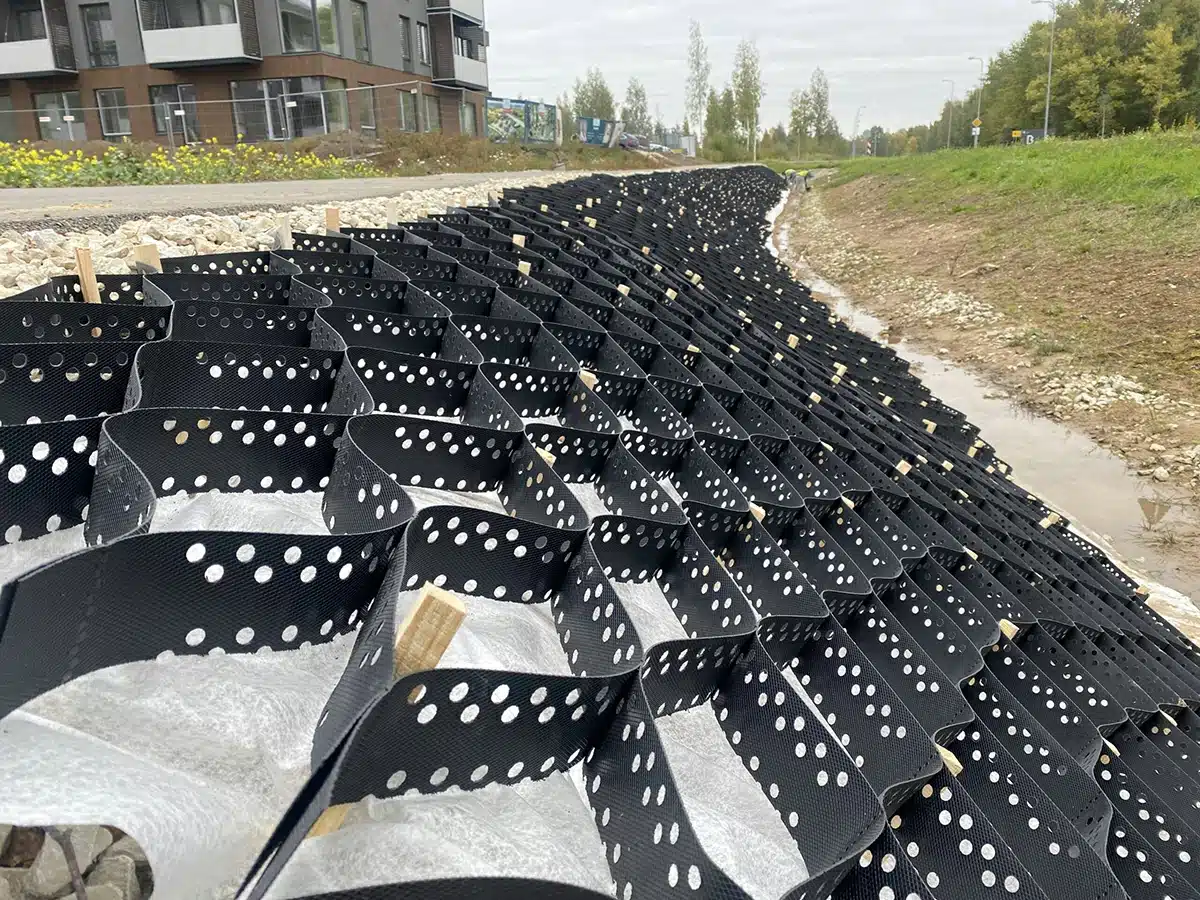

How Are Geocells Expanded and Positioned on the Site?
Expanding and positioning geocells correctly is crucial to ensure stability, load distribution, and long-term performance. The installation follows a systematic process:
- Prepare the Ground: Level and compact the subgrade, removing rocks, debris, or vegetation that could damage the geocells.
- Expand the Panels: Lay out the geocell panels and expand them to form a honeycomb-like structure. Ensure the cells are fully opened and evenly spread across the designated area.
- Anchor the Geocells: Secure the panels to the ground using stakes, steel rods, or specialized anchors, particularly on slopes or high-load areas, to prevent movement during filling.
- Connect Adjacent Panels: Join neighboring panels using clips, staples, or integrated fastening systems to create a continuous, stable grid.
- Check Alignment and Coverage: Ensure panels cover the intended area with proper overlap at edges, minimizing gaps and maintaining consistent cell structure.
Proper expansion and positioning create a durable base that maximizes the geocell system’s ability to stabilize soil, control erosion, and support loads.
What Material Should Be Used to Fill the Geocells?
Selecting the correct infill material is a critical factor that determines the structural performance, durability, and functionality of a geocell system. The choice should be based on load conditions, drainage requirements, slope angle, and intended application.
- Topsoil with Vegetation:
Best suited for landscaping, green slopes, and erosion control projects. When combined with grass or ground cover, it provides natural reinforcement and long-term surface stability. - Crushed Stone or Gravel:
Ideal for roads, access tracks, parking areas, and heavy-load zones. This infill delivers high bearing capacity, excellent drainage, and strong resistance to rutting and deformation. - Granular Soil (Sand or Sandy Gravel):
Commonly used for embankments and moderate-load erosion control. It compacts easily within the cells and offers a balance between stability and permeability. - Aggregate (Crushed Rock or Limestone):
Recommended for industrial platforms or traffic-bearing slopes where durability and load distribution are critical. - Concrete or Cement-Treated Fill:
Used in high-performance applications such as highways, ports, retaining structures, or steep slopes requiring maximum structural strength. The geocell confinement significantly reduces cracking and displacement.
The infill must be well-graded, evenly placed, and properly compacted inside each cell. Matching infill properties with geocell height and design loads ensures optimal confinement, minimizes settlement, and extends service life.
What Are the Essential Finishing Steps After Filling Geocells?
Proper finishing after geocell infill is critical to lock the system in place, ensure load transfer, and achieve long-term stability. The following steps complete a successful geocell installation:
- Leveling and compaction: Evenly level the infill material across the geocell surface. Compact it using a plate compactor or roller to ensure uniform load distribution and minimize future settlement.
- Capping or surface layer placement (if required): Install a protective or functional surface layer such as gravel, asphalt, concrete, or topsoil, depending on the application. This layer enhances durability, usability, and surface performance.
- Edge restraint and anchoring: Secure edges with curbs, anchors, stakes, or structural borders to prevent lateral movement, particularly in sloped areas or under traffic loads.
- Surface finishing and protection: Apply finishing treatments based on project needs, such as turf seeding for erosion control, paving for traffic areas, or decorative aggregates for landscaping applications.
- Drainage verification: Inspect surface and subsurface drainage systems to confirm proper water flow and prevent ponding or erosion that could undermine the geocell system.
- Final inspection and quality check: Conduct a final inspection to verify alignment, compaction quality, edge security, and compliance with design specifications and engineering requirements.
Completing these finishing steps ensures that the geocell system performs as designed, delivering long-term soil stabilization, erosion resistance, and structural reliability across a wide range of applications.
Installing geocells correctly is essential for achieving their full potential in soil stabilization and erosion control. Careful site preparation, precise expansion and positioning, proper fill material selection, and finishing work all contribute to a successful installation. By understanding these critical steps and addressing the key questions involved, construction professionals can optimize the use of geocells to create stronger, more durable infrastructure with environmental benefits.


Get Free Sample
We’ll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)






















