+86-159 9860 6917
info@geofantex.com
geofantex@gmail.com
+86-400-8266163-44899
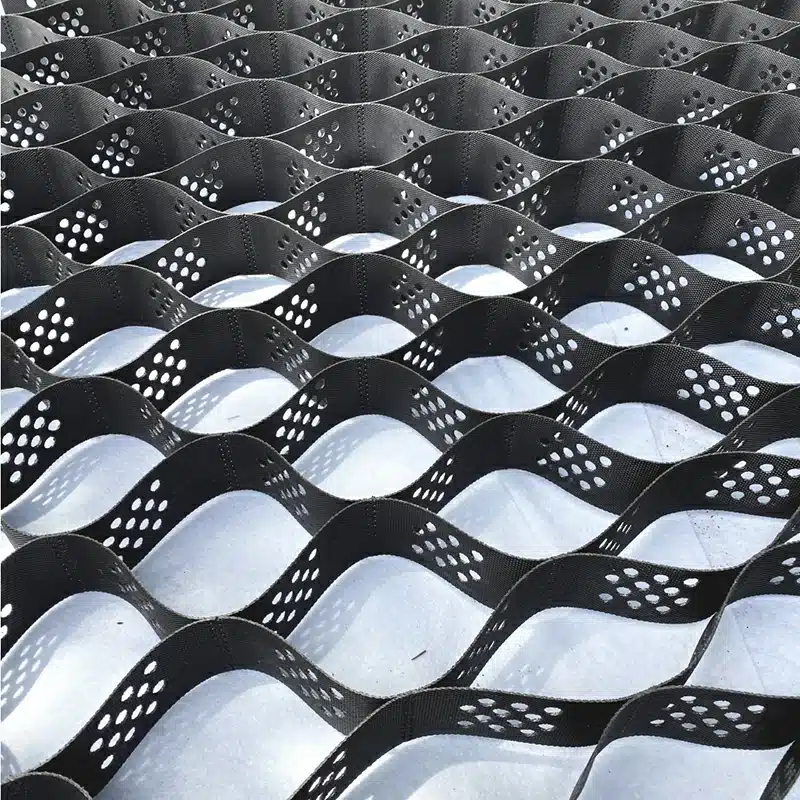
Geocell erosion control is an innovative solution for managing steep slopes. Geocells are cellular confinement systems that stabilize soil and prevent erosion by creating a flexible and durable structure. These honeycomb-like cells efficiently distribute loads, reducing soil or aggregate movement on slopes. This article explores the key aspects of geocells for erosion control and answers common questions about their application and effectiveness.
What Is the Maximum Slope for Safe and Effective Geocell Erosion Control?
- Typical Limit: Most commercial HDPE geocell systems can safely stabilize slopes up to 1:1 under standard geocell erosion control conditions.
- Condition: Appropriate infill materials—such as well-graded soil, gravel, or concrete—must be selected and placed in accordance with project design requirements.
- Installation Standards: Geocells should be installed strictly following manufacturer guidelines and accepted geotechnical engineering practices to ensure structural integrity.
- Drainage: Proper surface and subsurface drainage is critical to prevent hydrostatic pressure buildup behind or within the geocell system.
- Steeper Slopes: Slopes steeper than 1:1 may require additional stabilization measures, including geogrids, mechanical anchors, soil nails, or retaining structures.
When installed with suitable infill, adequate compaction, reliable anchoring, and effective drainage control, geocell slope stabilization solutions can provide long-term, erosion-resistant performance for slopes up to 1:1. Consultation with a qualified geotechnical engineer is recommended for site-specific design and performance verification.
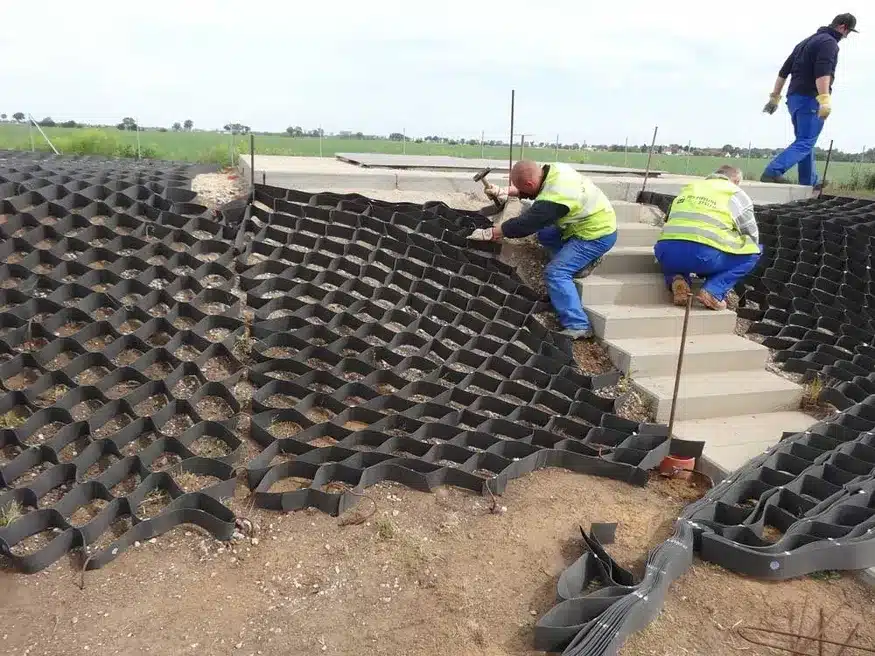

What Is Slope Protection with Geocells?
Slope protection with geocells is an engineered erosion-control method that uses three-dimensional HDPE cellular confinement systems to stabilize soil and protect slopes from erosion, sliding, and surface failure.
- Erosion Control: The interconnected cells confine soil or aggregate, significantly reducing surface runoff velocity and preventing soil washout.
- Soil Stabilization: Geocells distribute loads laterally and vertically, increasing shear resistance and minimizing slope deformation or slippage.
- Vegetation Reinforcement: Confined topsoil promotes root development, allowing vegetation to act as a natural reinforcement layer over time.
- Drainage Performance: Open cell geometry enables controlled water flow, reducing hydrostatic pressure and improving slope drainage behavior.
- Structural Flexibility: The system adapts to ground movement without cracking, making it suitable for steep or irregular terrain.
- Long-Term Durability: UV-stabilized HDPE geocells resist weathering, chemical exposure, and temperature variation, ensuring extended service life.
Geocell slope protection combines mechanical confinement with environmental compatibility, delivering a cost-effective and sustainable alternative to rigid retaining systems.
What Is the Best Fill Material for Geocells in Geocell Erosion Control?
Selecting the right fill material for Geocell erosion control depends on slope gradient, load demands, drainage conditions, and the project’s functional goals. Proper infill directly affects slope stability, erosion resistance, and service life.
- Soil (Native Soil)
- Cost-effective and widely available
- Suitable for landscaping, embankments, and moderate slopes
- Sandy, clay, or loamy soils can be improved through grading and compaction
- Best for vegetation-based geocell erosion control applications
- Gravel or Crushed Stone
- High load-bearing capacity and excellent drainage
- Ideal for roads, access paths, and high-traffic slopes
- Enhances shear strength and long-term slope stability
- Sand
- Easy to place and compact
- Commonly used for shoreline protection and surface erosion control
- Works well in low-load geocell erosion control systems
- Aggregate (Crushed Rock, Limestone)
- Recommended for industrial areas and vehicle-loaded zones
- Provides superior load distribution and durability
- Minimizes deformation under repeated stress
Matching the geocell infill material to slope angle, hydraulic conditions, and load requirements is essential for effective Geocell erosion control, ensuring long-term stability, reduced maintenance, and improved environmental performance.

How to Cut Geocells?
Properly cutting geocells ensures precise installation and long-term performance. Follow these steps for accuracy and safety:
- Required Tools: Utility knife or heavy-duty scissors, measuring tape, chalk or marker, cutting mat, safety gloves, and protective goggles.
- Measure and Mark: Lay the geocell flat. Measure dimensions carefully and mark cut lines clearly.
- Cutting Technique:
- For thick geocells: make shallow cuts with a utility knife first, then deepen gradually to avoid tearing.
- For thinner geocells: heavy-duty scissors work effectively.
- Stabilize While Cutting: Hold the geocell firmly without stretching to maintain its shape.
- Edge Finishing: Trim any uneven or rough edges for a neat, professional finish.
- Safety Tips: Always cut on a stable surface, wear protective gear, and keep blades sharp.
Cutting geocells to fit slope contours and corners accurately reduces installation errors and ensures optimal erosion control performance. For full guidance, refer to detailed geocell installation tips.
Geocell erosion control is highly effective for stabilizing steep slopes and preventing erosion. Supporting slopes up to 1:1, geocells provide reliable slope protection. By filling them with suitable materials like gravel or soil, you can create a stable, erosion-resistant surface. The ease of cutting and customization enhances their versatility, making geocells ideal for commercial and residential applications.


Get Free Sample
We’ll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)






















