+86-159 9860 6917
info@geofantex.com
geofantex@gmail.com
+86-400-8266163-44899
Laying geocomposite correctly is essential for efficient drainage and soil stabilization. In this article, we’ll guide you through the process step by step. We’ll also answer key questions about geocomposite, including its composition, thickness, and its differences from geotextile. Let’s dive in!
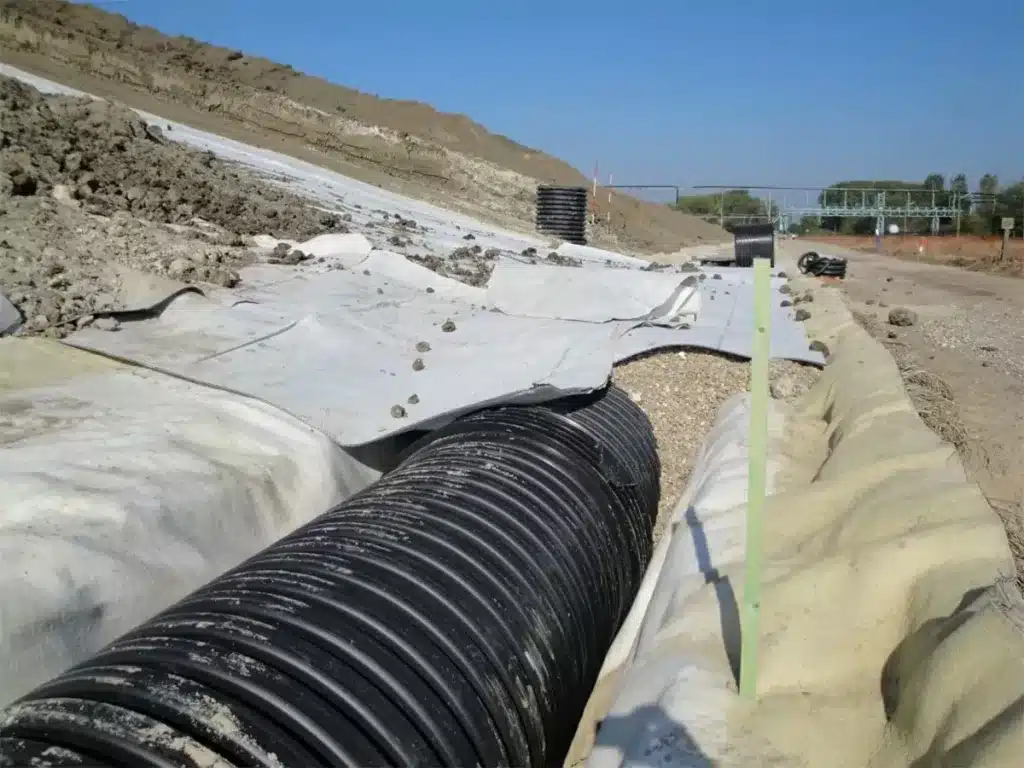

What is the difference between geotextile and geocomposite?
- Standard applications: Most drainage geocomposites used in road construction, retaining walls, and landfill drainage systems typically fall within the 5–7 mm thickness range. This specification provides sufficient in-plane flow capacity while minimizing material consumption, making it suitable for conventional drainage requirements under moderate loads.
- High-flow or heavy-load conditions: For applications that demand rapid water evacuation or must withstand higher compressive stresses—such as tunnel linings, bridge abutments, deep foundations, or steep slope drainage—thicker drainage cores (8–10 mm or greater) are often specified. Increased thickness enhances flow capacity, structural stability, and long-term performance under sustained loads.
- Selection factors: Key parameters influencing geocomposite thickness selection include soil permeability, hydraulic gradient, confining pressure, and expected service loads. As hydraulic demand and vertical stress increase, a thicker drainage core is generally required to maintain adequate transmissivity and prevent long-term deformation.
The thickness of a geocomposite drainage layer is application-specific rather than standardized. Proper engineering design should balance drainage performance, ground conditions, and structural loading to ensure reliable and durable drainage over the project’s service life.
How Thick Is the Geocomposite Drainage Layer?
The thickness of a geocomposite drainage layer typically ranges from 4 mm to 10 mm, depending on hydraulic performance requirements and applied loads. There is no universal standard thickness—selection must be based on project-specific conditions.
Typical thickness ranges and applications include:
- Standard drainage applications (5–7 mm)
Commonly used in road construction, retaining walls, green roofs, and landfill drainage systems. This range provides adequate in-plane water flow while maintaining a slim profile and efficient material use. - High-flow or high-load conditions (8–10 mm or greater)
Specified for projects requiring rapid water evacuation or higher compressive strength, such as tunnel linings, bridge abutments, deep foundations, and steep slope drainage. Increased thickness improves transmissivity and long-term deformation resistance.
Key factors influencing thickness selection:
- Soil permeability and gradation
- Hydraulic gradient and expected water volume
- Confining pressure and overburden load
- Long-term service life and creep resistance requirements
As hydraulic demand and vertical stress increase, a thicker drainage core is generally required to maintain flow capacity and structural integrity. Proper geocomposite thickness selection should always be verified through engineering design to ensure reliable and durable drainage performance throughout the project lifecycle.
What is the geocomposite drainage layer?
A geocomposite drainage layer is a modern substitute for traditional stone and gravel drainage layers. It provides drainage, filtration, separation, and barrier functions in a compact, engineered system. Key aspects include:
- Functionality: the geocomposite replaces thick gravel/sand layers while providing equivalent or better water flow and filtration performance
- Core Material: constructed from HDPE, PP, or natural fibers, the core transports water efficiently
- Geotextile Layer: bonded to the core, it prevents soil particles from clogging the drainage system
- Applications: widely used in landfills, roadways, retaining walls, tunnels, and slope drainage
- Advantages: reduces excavation depth, transportation cost, and installation time compared with traditional drainage layers
Geocomposite drainage layers offer a cost-effective, high-performance alternative to bulky aggregate drains, improving construction efficiency and long-term drainage performance.
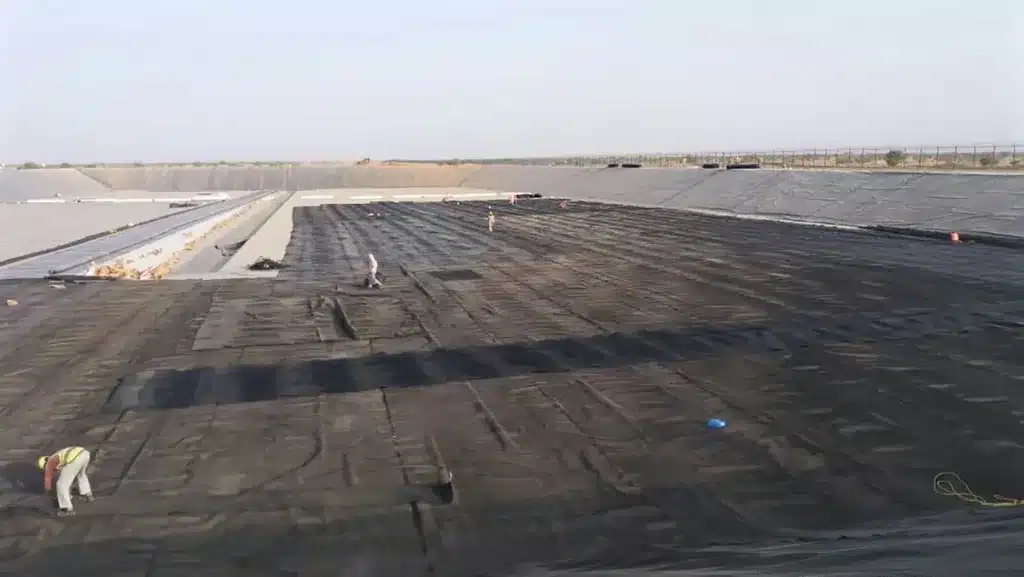

What Is a Geocomposite Made Of?
- Geotextile layers form the outer components of most geocomposites and are typically made from polypropylene (PP) or polyester (PET). These layers provide filtration, separation, and protection by allowing water to pass through while preventing soil particles from clogging the system.
- Drainage core is the central functional element, designed to transport water efficiently. It is commonly manufactured from HDPE or PP and may take the form of a geonet, cuspated sheet, or structured drainage core.
- Additional geosynthetic elements, depending on application requirements, may include geogrids for reinforcement, geomembranes for containment and impermeability, or bonded multi-layer systems that combine several functions in one product.
- Bonding method (thermal bonding, adhesive bonding, or mechanical attachment) ensures that all layers act as a single integrated unit, maintaining performance under load and during installation.
- Material selection is based on site conditions such as soil type, hydraulic requirements, chemical exposure, and long-term load expectations.
By combining multiple geosynthetic materials into one engineered system, geocomposites deliver filtration, drainage, reinforcement, and protection in a compact, efficient, and durable solution for modern civil engineering projects.
By following these steps and understanding the key characteristics of geocomposite, you can successfully lay geocomposite for various construction and civil engineering applications. It’s important to tailor the process to your specific project requirements for the best results.


Get Free Sample
We’ll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)






















