+86-159 9860 6917
info@geofantex.com
geofantex@gmail.com
+86-400-8266163-44899
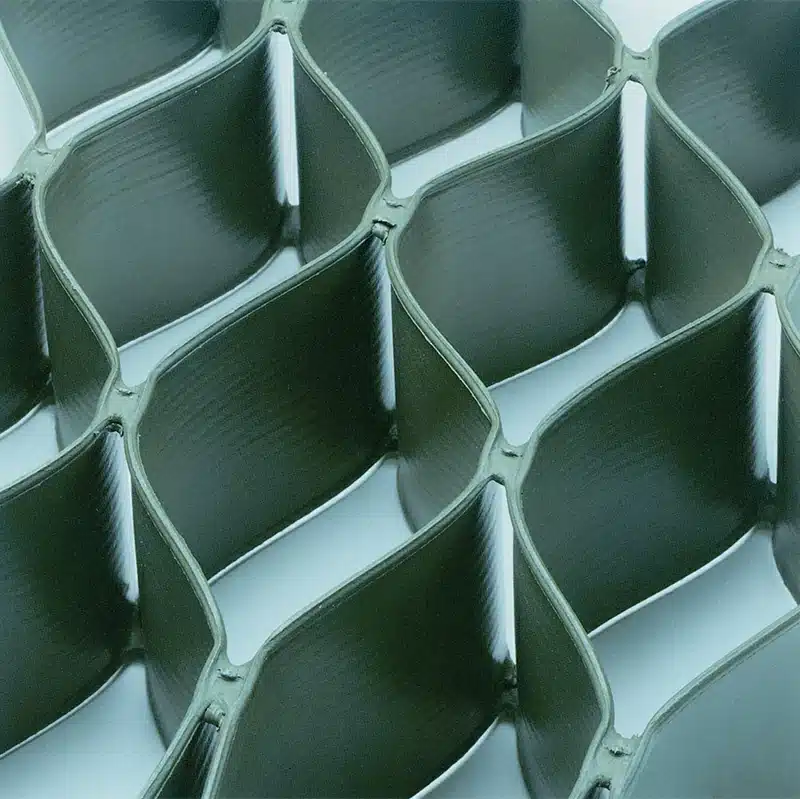
Geocell slope reinforcement is an innovative solution in civil engineering, designed to stabilize slopes and prevent soil erosion. This cellular confinement system, made from high-density polyethylene (HDPE) or similar materials, forms a flexible honeycomb structure when deployed. It is widely used in various construction projects, including highways, railways, and embankments, to provide structural integrity and erosion control. In this article, we will explore the maximum slope for geocell use, its role in slope protection, the differences between geocell and geogrid, and the different types of geocells available.
What is the maximum slope for GeoCell?
The maximum slope that can be effectively reinforced using geocells typically ranges from 45 degrees to 60 degrees, depending on the soil type, load conditions, and specific geocell product used. In some cases, with additional engineering support, slopes up to 70 degrees can be stabilized. Geocells work by confining soil within their cellular structure, thereby enhancing the shear strength of the soil and preventing erosion or landslides on steep slopes. However, it’s crucial to conduct a thorough site analysis to determine the appropriate slope angle for geocell application.

What is GeoCell in slope protection?
Geocells in slope protection serve as a three-dimensional reinforcement system, employed to protect slopes from erosion and assist in stabilizing the surface by strengthening the soil on slopes. By confining the fill material within its honeycomb-like structure, geocells distribute loads evenly, reduce soil displacement, and minimize erosion. This is particularly important in areas prone to heavy rainfall, where soil erosion can be a significant issue. Geocells can be filled with various materials, such as soil, gravel, or concrete, depending on the project requirements. Their flexibility allows them to adapt to the natural contours of the slope, providing effective and long-lasting protection.
What is the difference between Geogrid and Geocell?
Geogrid and geocell are geosynthetic materials used in soil reinforcement but differ in structure and application. In summary, geogrids primarily provide tensile reinforcement to soils, enhancing their stability, while geocells confine and stabilize granular materials within their cells, creating a rigid structure. Geogrid is a planar, grid-like material made from polymers, primarily used to reinforce soil by increasing its tensile strength. It is often employed in retaining walls, roads, and dams. In contrast, a geocell is a three-dimensional structure that confines the fill material within its cells, providing both lateral and vertical support. While geogrid is more suitable for applications requiring tensile reinforcement, geocell excels in scenarios requiring soil confinement and erosion control on slopes. Geogrids are grid-like and focus on reinforcement, while geocells are cellular structures that confine fill material.
What are the different types of geocells?
Geocells are classified based on their material composition and intended application. The most common types are:
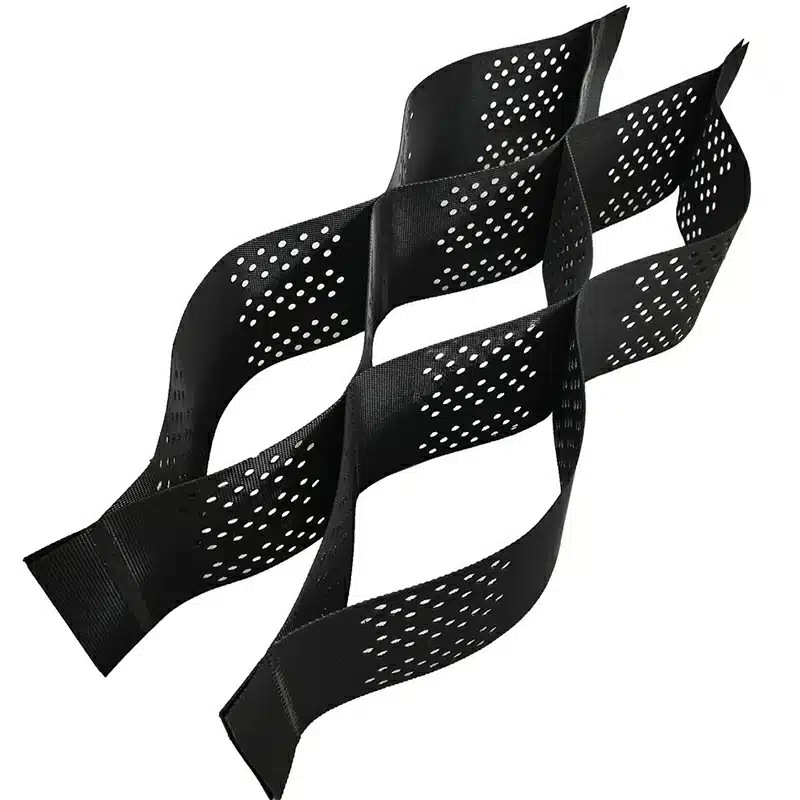
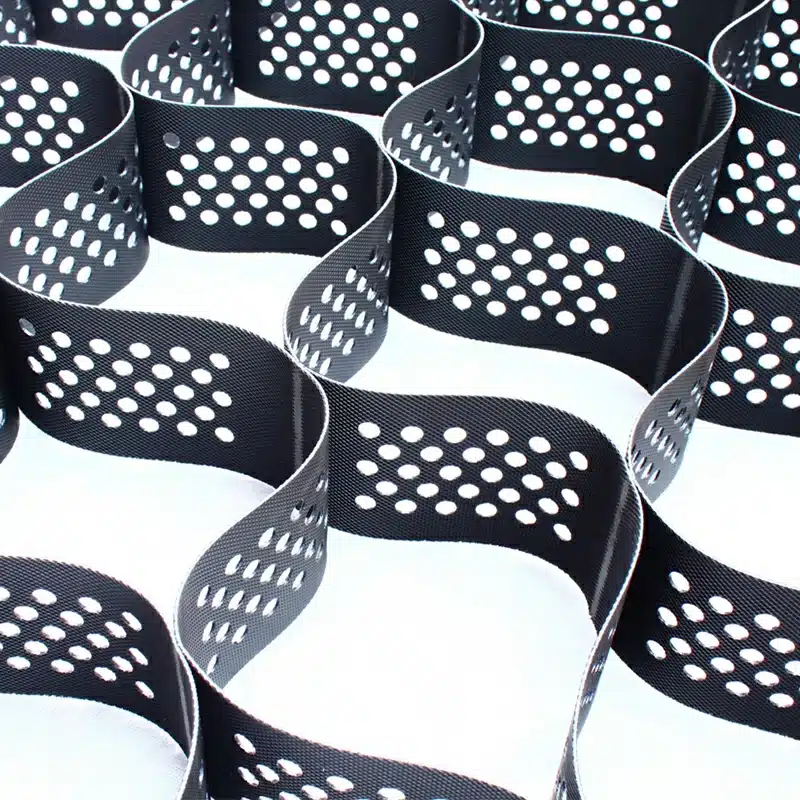
- HDPE Geocells: Made from high-density polyethylene, these are widely used for slope reinforcement, load support, and erosion control due to their durability and flexibility.
- Perforated Geocells: These geocells have small holes in their walls to allow water drainage, making them ideal for applications in areas with high water flow or where drainage is a concern.
- Non-perforated Geocells: Used in scenarios where water drainage is not required, these geocells provide a solid barrier for soil and fill material.
- Textured Geocells: These have a textured surface to enhance friction between the cell walls and the fill material, improving stability in slope reinforcement applications.
Both non-perforated geocell and perforated geocell types serve distinct purposes, depending on whether drainage or a solid barrier is needed.
Geocell slope reinforcement is a versatile and effective solution for stabilizing slopes and preventing soil erosion. By understanding the maximum slope angles for geocell use, its role in slope protection, and the differences between geocell and geogrid, engineers can make informed decisions in their construction projects. With various types of geocells available, each suited to specific applications, geocell technology continues to be a critical tool in modern civil engineering, ensuring the safety and longevity of infrastructure in challenging terrains.


Get Free Sample
We’ll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)






















