+86-159 9860 6917
info@geofantex.com
geofantex@gmail.com
+86-400-8266163-44899
In the realm of civil engineering and construction, biaxial geogrids have gained significant recognition for their versatile applications. This article delves into the world of biaxial geogrids, explaining what they are, comparing them to uniaxial geogrids, exploring the differences between biaxial and triaxial geogrids, and discussing various types of geogrids to help you make informed decisions for your projects.
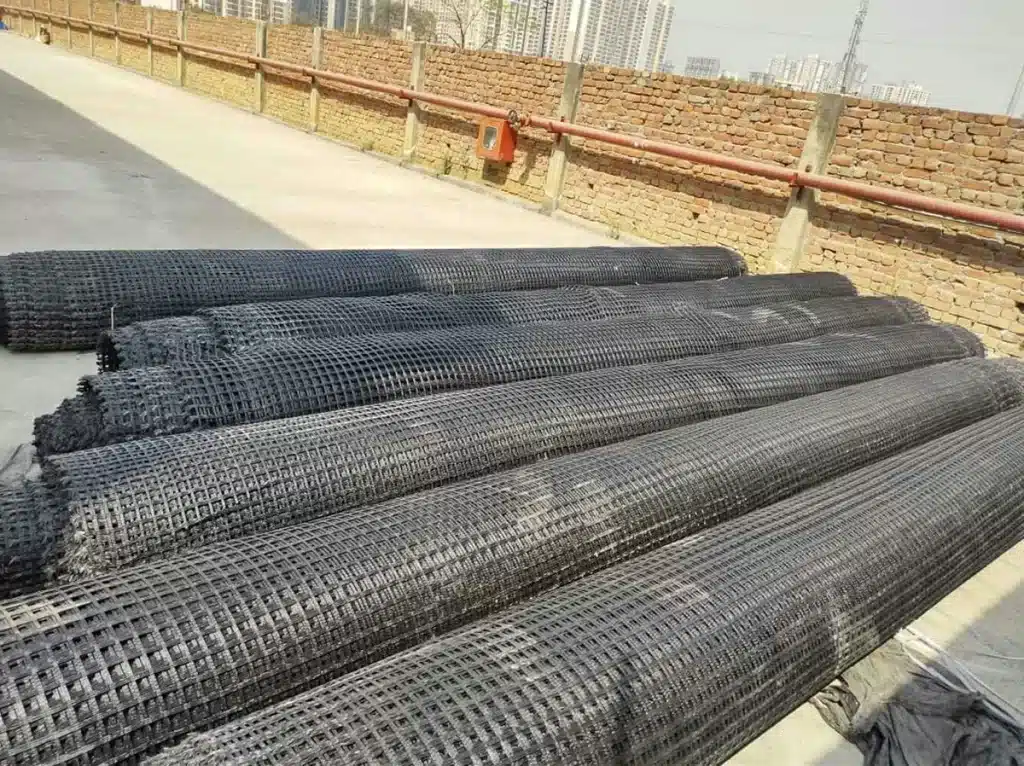

What is Biaxial Geogrid?
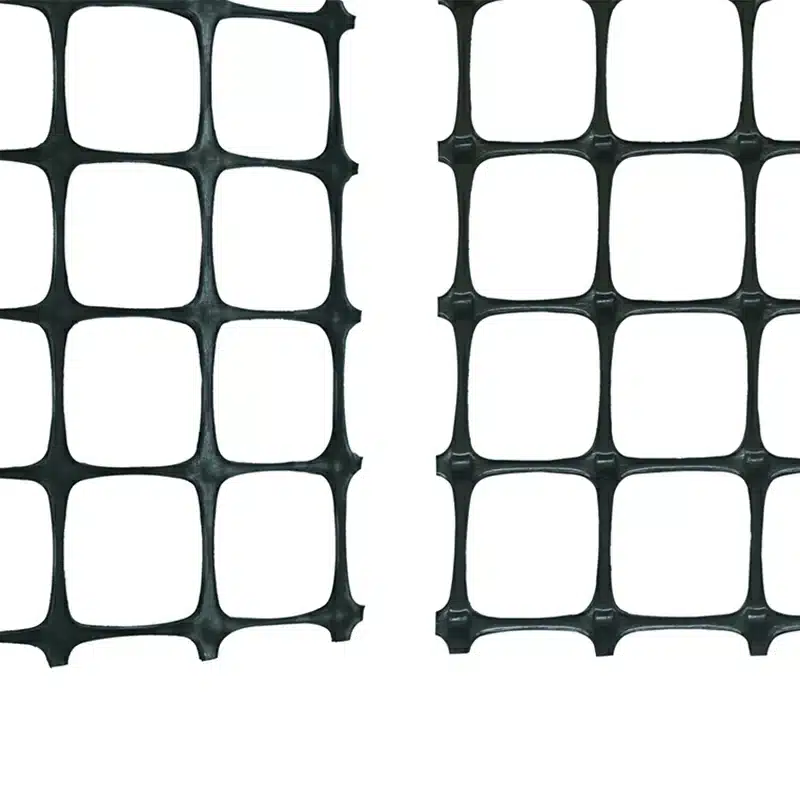
A type of geogrids, biaxial geogrids are strong synthetic materials commonly employed in civil engineering and construction. They are made by creating intersecting ribs that shape a grid-like structure, using durable materials like polyethylene or polyester that withstand environmental factors. Biaxial geogrids are designed to enhance soil performance, improve load distribution, and prevent soil erosion. Their primary purpose is to strengthen and stabilize weak soil, boosting the structural integrity of various projects like retaining walls, roadways, and embankments.
What is Biaxial Geogrid vs. Uniaxial Geogrid?
The fundamental difference between biaxial and uniaxial geogrids lies in their reinforcement directions. Biaxial geogrids have ribs intersecting in both the longitudinal and transverse directions, providing equal reinforcement in two dimensions. On the other hand, uniaxial geogrids have ribs running in a single direction, offering reinforcement only along the length or width of the grid. While biaxial geogrids are suitable for applications requiring multidirectional support, uniaxial geogrids are typically used for projects where reinforcement is needed in only one direction.
What is the Difference Between Biaxial and Triaxial Geogrid?
Biaxial and triaxial geogrids differ primarily in the number of reinforcement directions. As mentioned earlier, biaxial geogrids provide reinforcement in two directions, making them ideal for projects with moderate soil stabilization needs. On the other hand, triaxial geogrids excel because they feature the presence of ribs in three directions, rather than two—longitudinal, transverse, and vertical. This additional vertical reinforcement gives triaxial geogrids an edge in demanding applications, such as steep slopes and retaining walls subjected to heavy loads. Choosing between biaxial and triaxial geogrids hinges on the specific requirements of your project.
What are the Different Types of Geogrids?
There are several types of geogrids available, each tailored to specific engineering challenges. These include Uniaxial, Biaxial, Triaxial, and Geogrid-Geotextile Composites. Here’s a brief overview of each:
- Uniaxial Geogrids: These geogrids provide reinforcement in one direction, making them suitable for applications requiring support in a single dimension.
- Biaxial Geogrids: With reinforcement in two directions, biaxial geogrids are versatile and used for various projects, enhancing stability in two dimensions.
- Triaxial Geogrids: As previously mentioned, triaxial geogrids offer reinforcement in three directions, making them ideal for high-stress applications.
- Knitted Geogrids: These geogrids are created by knitting or weaving strong fibers, providing excellent reinforcement and flexibility.
- Woven Geogrids: Manufactured by weaving polyester or polypropylene tapes, woven geogrids are known for their high tensile strength and stability.
- Composite Geogrids: Combining different materials, composite geogrids strike a balance between strength, flexibility, and durability, making them suitable for a wide range of projects.
In conclusion, biaxial geogrids are indispensable tools in modern civil engineering and construction. Understanding their characteristics, differences from other geogrid types, and various applications is crucial for successful project planning and execution. By choosing the right geogrid for your specific needs, you can enhance the stability and longevity of your construction projects.


Get Free Sample
We’ll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)






















