+86-159 9860 6917
info@geofantex.com
geofantex@gmail.com
+86-400-8266163-44899
In the realm of civil engineering, particularly in road construction, the integration of geosynthetics has been a game-changer, offering reinforcement, stabilization, and filtration benefits. Among these, geonets have become increasingly popular due to their unique properties and functionalities in these areas. This article aims to shed light on the use of geonets in road construction, exploring their functions in reinforcement, stabilization, and filtration, their materials, design aspects, and how they differ from similar materials like geogrids in providing these crucial benefits.

What is the function of the Geonet?
A geonet is a geosynthetic material primarily used for drainage applications. It consists of a series of ribs or strands that are typically made from polymeric materials, and they form a network that allows fluids to flow through the structure. The main functions of a geonet are:
- Drainage: Geonets are designed to facilitate the movement of water or other fluids, especially in applications where efficient drainage is required, such as landfills, roadways, and foundations. They help prevent water accumulation and reduce the risk of soil erosion.
- Separation: Geonets can act as a separator between different soil layers. For example, in landfill applications, they prevent the mixing of drainage layers with the surrounding soil or waste material.
- Filtration: While not as effective as a geotextile, geonets can provide some filtration properties by allowing water to flow through while blocking the migration of fine particles.
- Reinforcement: In certain applications, such as in road construction or retaining walls, geonets can provide additional strength and stability to the structure.
Overall, geonets are used to improve the efficiency of drainage systems, reduce the risk of soil instability, and enhance the long-term performance of infrastructure projects.
What is a geonet made of?
Geonets are constructed from durable polymeric materials designed to provide strength, flexibility, and long-term performance in drainage and stabilization applications. Key components include:
- High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE):
- Properties: Strong, chemically resistant, UV-stable, and durable.
- Role: Forms the primary rib structure of the geonet, ensuring long-term stability and load-bearing capacity.
- Polypropylene (PP):
- Properties: Excellent stress resistance and chemical stability.
- Role: Sometimes combined with HDPE to enhance flexibility and durability under varying environmental conditions.
- Reinforcement Layers:
- Materials: Additional polymers or geotextiles.
- Role: Provide extra strength and support, improving the geonet’s structural integrity and load distribution.
- Additives:
- Types: UV stabilizers, antioxidants, and colorants.
- Role: Enhance resistance to environmental degradation, prolong lifespan, and improve visibility during installation.
In summary, geonets are engineered with a combination of robust polymers and additives to withstand mechanical stress, environmental exposure, and long-term use, making them ideal for drainage, filtration, and soil stabilization in road construction.
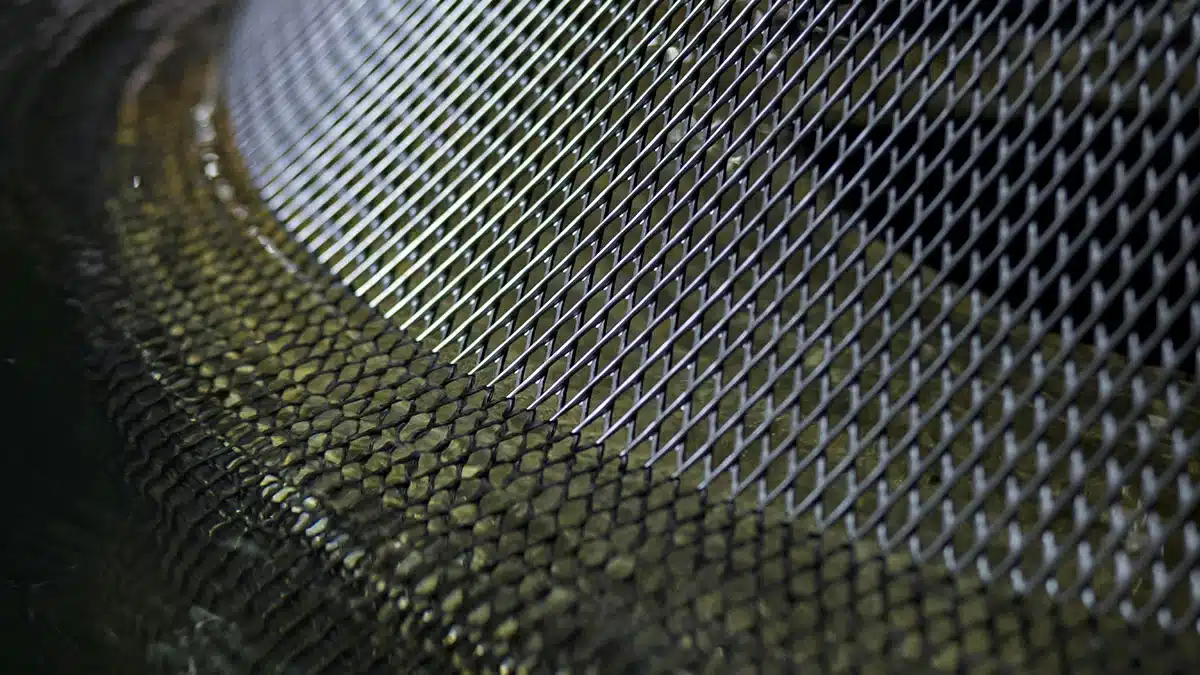
What is the shape of apertures in geonets?
- Shape: The apertures in geonets typically have a diamond or rectangular shape. The exact shape can vary depending on the specific type and application of the geonet.
- Size: The size of the apertures varies widely and is often specified by the manufacturer. Commonly, the apertures range from a few millimeters to several centimeters in width and length.
- Structure: Geonets are composed of intersecting ribs or strands that create a net-like structure. These intersecting strands form the apertures, providing both drainage and support functions.
- Arrangement: The apertures are arranged in a regular, repeating pattern across the geonet. This consistent arrangement ensures uniform performance in terms of drainage and filtration.
The Geonet as a Key Element in Road Construction
The geonet plays an essential role in road construction, enhancing drainage performance, soil stability, and the longevity of the pavement system. Its main functions include:
- Efficient Drainage: Facilitates the rapid flow of water through its three-dimensional structure, preventing accumulation and reducing hydrostatic pressure beneath the pavement.
- Soil Separation: Prevents the intermixing of different soil layers, maintaining the integrity of the subgrade and improving the stability of the road base.
- Erosion Control: Protects the subgrade and embankments by preventing soil displacement caused by rainwater or surface runoff.
- Structural Reinforcement: Provides additional support and load distribution, increasing the bearing capacity of the pavement structure.
- Environmental Protection: Reduces the risk of soil contamination and water infiltration in sensitive areas such as landfills or drainage channels.
- Key Benefit: Using geonets in road construction ensures effective drainage, prolonged pavement durability, and enhanced road performance, contributing to sustainable and cost-efficient infrastructure.
Geonets have become an indispensable tool in modern road construction, offering vital solutions for drainage and soil stabilization. Made from robust materials like HDPE, their unique aperture designs facilitate efficient water management, crucial for maintaining road integrity. While sharing some similarities with geogrids, geonets stand out in their primary function of drainage, as opposed to the reinforcement role of geogrids. The use of geonets in road construction not only enhances the durability and lifespan of roads but also contributes to safer and more reliable infrastructure development. As the industry continues to evolve, the role of geonets is likely to expand, further underlining their importance in contemporary road construction techniques.

Get Free Sample
We’ll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)






















