+86-159 9860 6917
info@geofantex.com
geofantex@gmail.com
+86-400-8266163-44899
In the realm of road construction and maintenance, the integration of innovative materials is pivotal for enhancing durability and performance. Among these, using a geocomposite for paved roads has emerged as a game-changer. This article delves into the specifics of geocomposite materials, examining their role, benefits, and application in road construction. We will explore the various geosynthetic materials used in roads, address common questions, and provide insights into why geocomposites are becoming an indispensable part of modern road infrastructure.
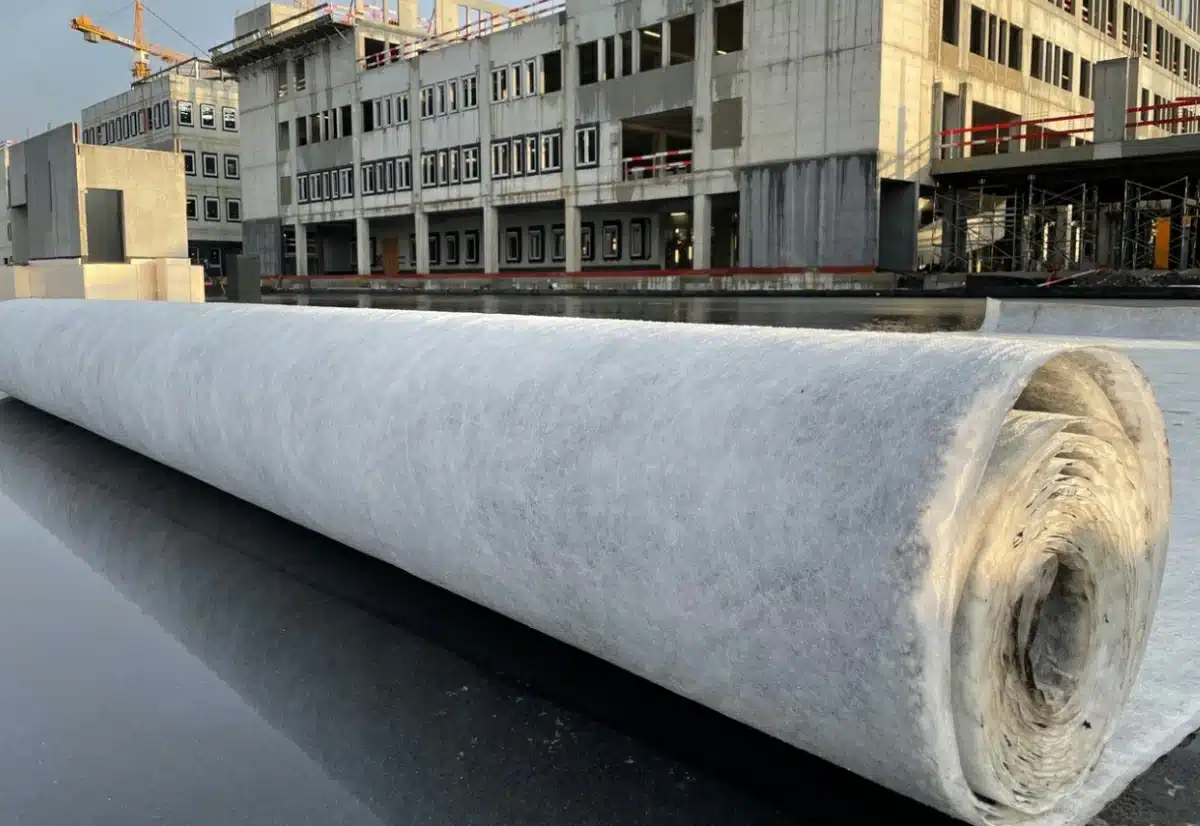

What are the geosynthetic materials used in roads?
Types of Geosynthetic Materials Used in Roads:
Geotextiles:
- Properties: Made from synthetic fibers (polypropylene, polyester), can be woven or non-woven.
- Functions: Separation, filtration, reinforcement, and drainage.
- Advantages: Prevents mixing of different soil layers, improves drainage, enhances soil stability, and increases road durability.
Geomembranes:
- Properties: Impermeable synthetic membranes, typically made from high-density polyethylene (HDPE) or polyvinyl chloride (PVC).
- Functions: Barrier for water and other fluids, prevents contamination.
- Advantages: Effective in preventing soil and groundwater contamination, long-lasting and durable.
Geogrids:
- Properties: Grid-like structure made from polymers (polypropylene, polyester).
- Functions: Soil reinforcement, load distribution, and subgrade stabilization.
- Advantages: Enhances the load-bearing capacity of the soil, reduces road maintenance costs, and improves road lifespan.
- Properties: Net-like structure made from polymeric materials.
- Functions: Drainage and reinforcement.
- Advantages: Facilitates water flow, reduces hydrostatic pressure, and provides structural support.
Geocells:
- Properties: Three-dimensional honeycomb-like structures made from high-density polyethylene (HDPE).
- Functions: Soil confinement, load support, and erosion control.
- Advantages: Increases load-bearing capacity, prevents soil erosion, and enhances slope stability.
Geocomposites:
- Properties: Combination of two or more geosynthetic materials (e.g., geotextile-geonet, geomembrane-geotextile).
- Functions: Multiple functions such as drainage, reinforcement, and barrier.
- Advantages: Combines the benefits of different geosynthetics, versatile, and cost-effective.
What are the Requirements for Using Geocomposite on Paved Roads?
- Quality Standards: Geocomposites used in road construction must meet specific industry standards for durability, strength, and environmental resistance.
- Proper Installation: Skilled labor and adherence to manufacturer guidelines are crucial for the effective installation of geocomposites.
- Site Assessment: A thorough evaluation of the site, including soil type, drainage conditions, and traffic load, is essential to determine the appropriate type of geocomposite.
- Maintenance Plan: Regular maintenance schedules should be established to ensure the longevity and performance of the geocomposite material.
- Environmental Considerations: The selection of geocomposites should also consider environmental impact, ensuring materials are eco-friendly and sustainable.
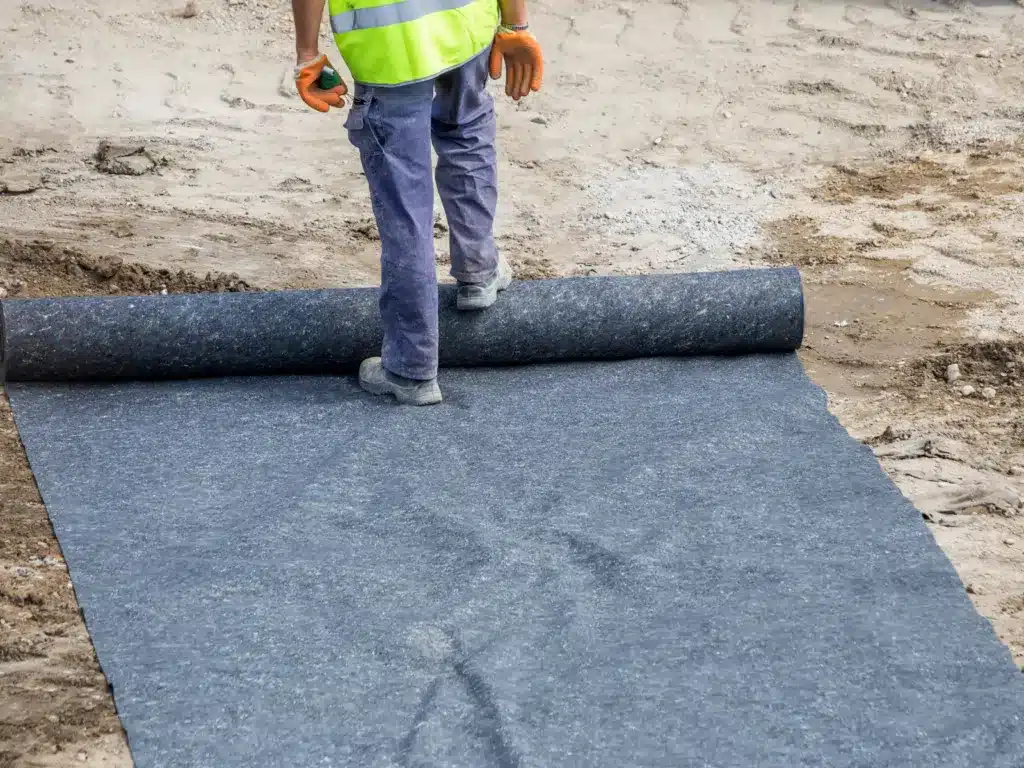

How does a geocomposite enhance the durability of paved roads?
Improved Drainage:
- Function: Geocomposites often incorporate drainage layers that help manage water flow within the pavement structure.
- Benefit: Reducing water accumulation prevents damage such as cracking and pothole formation, extending pavement life.
Enhanced Reinforcement:
- Function: Geocomposites can include reinforcement materials like geogrids.
- Benefit: These materials distribute loads more evenly and increase the structural integrity of the pavement, making it more resistant to deformation and stress.
Separation of Layers:
- Function: Geocomposites act as separators between different pavement layers.
- Benefit: This prevents the mixing of materials, maintaining the distinct properties and performance of each layer, which is crucial for durability.
Mitigation of Reflective Cracking:
- Function: When placed between old and new pavement layers, geocomposites can reduce the propagation of cracks from the old layer to the new one.
- Benefit: This leads to a smoother and longer-lasting pavement surface.
Erosion Control:
- Function: Geocomposites can stabilize soil and subgrade materials.
- Benefit: Preventing erosion under the pavement helps maintain its structural integrity over time.
Can geocomposites be used in all types of road construction?
Geocomposites are versatile and can be used in various types of road construction, including highways, urban roads, and access roads. However, their application depends on the specific requirements of the project, such as load-bearing capacity, soil type, and environmental conditions. It’s essential to consult with a civil engineer or a geotechnical expert to determine the suitability of geocomposites for a particular project.
In conclusion, the use of a geocomposite for paved roads offers a multifaceted solution to common road construction challenges. By enhancing durability, ensuring sustainability, and adapting to various project needs, geocomposites represent a significant advancement in modern road construction and maintenance practices.


Get Free Sample
We’ll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)






















