+86-159 9860 6917
info@geofantex.com
geofantex@gmail.com
+86-400-8266163-44899
Geosynthetic reinforcement has become a cornerstone in modern soil bridge design, offering enhanced stability, longevity, and cost-effectiveness. By integrating geosynthetics into the construction of bridges, engineers can create robust structures that efficiently distribute loads and resist environmental stresses. This article explores the concept of geosynthetic reinforcement in soil bridge design, addressing its applications, benefits, and the specific technologies that make it a vital tool in contemporary civil engineering.
What is Geosynthetic Reinforced Soil Integrated Bridge System?
The Geosynthetic Reinforced Soil Integrated Bridge System (GRS-IBS) is an innovative method of bridge construction that uses geosynthetics to reinforce the soil, providing a stable foundation for bridge abutments and approach roads. The technology consists of three main components: the reinforced soil foundation, the abutment, and the integrated approach. This system involves the layering of geosynthetic materials with compacted soil, creating a reinforced mass that can support the weight of the bridge and distribute loads more evenly. GRS-IBS is known for its simplicity, cost-effectiveness, and durability, making it a popular choice for both new bridge construction and the rehabilitation of existing structures.
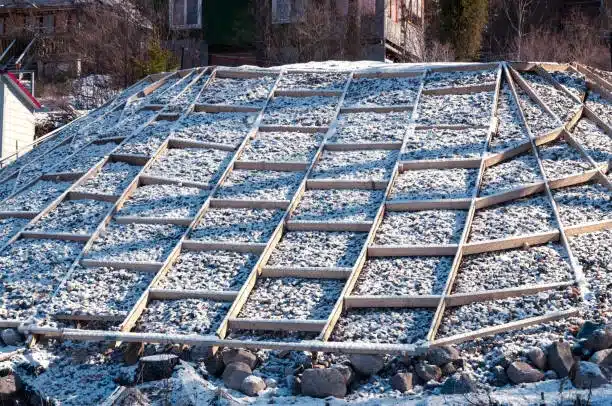

Can Geosynthetics Be Used as Soil Reinforcement?
Yes, geosynthetics can be used as soil reinforcement. Geosynthetics, which include materials like geogrids, geotextiles, and geomembranes, are specifically designed to enhance the mechanical properties of soil. Sometimes required to provide additional stability in the construction of embankments on soft soil, these materials increase the soil’s tensile strength, improve load distribution, and reduce deformation under stress. This makes geosynthetics particularly effective in applications such as retaining walls, embankments, and bridge foundations, where soil stability is critical.
What is Geosynthetic Reinforced Soil?
Geosynthetic reinforced soil (GRS) refers to soil that has been strengthened by the incorporation of geosynthetic materials. GRS typically consists of closely-spaced layers of geosynthetic reinforcement and compacted granular fill material, providing additional support and stability. This reinforcement method enhances the soil’s ability to bear loads, resist erosion, and maintain its shape under varying environmental conditions. GRS is commonly used in the construction of retaining walls, embankments, and other structures where traditional soil alone would not provide sufficient strength.
In Which Areas Are Geosynthetic Materials Used as Soil Reinforcement?
Geosynthetic materials are used as soil reinforcement in a variety of areas, particularly in civil engineering and construction projects. These areas include:
- Bridge Abutments: Geosynthetics are used to reinforce the soil beneath bridge abutments, improving load distribution and stability.
- Retaining Walls: Geosynthetic materials help reinforce the retaining wall structure, retain soil, prevent erosion, and provide essential structural support.
- Road Embankments: Geosynthetics reinforce the soil in road embankments, ensuring stability and preventing settlement.
- Slope Stabilization: Geosynthetics are used to stabilize slopes, reducing the risk of landslides and erosion.
- Foundations: In areas with poor soil conditions, geosynthetics are used to reinforce foundations, providing additional strength and durability.
Geosynthetic reinforcement in soil bridge design is a cutting-edge approach that significantly enhances the stability and durability of bridges. Through systems like the Geosynthetic Reinforced Soil Integrated Bridge System, engineers can construct more resilient structures that effectively manage load distribution and resist environmental stresses. The use of geosynthetics as soil reinforcement is not limited to bridges; it extends to a wide range of civil engineering applications, making it an indispensable tool in modern construction. Understanding the role of geosynthetics in these contexts is crucial for developing sustainable and long-lasting infrastructure.


Get Free Sample
We’ll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)






















