+86-159 9860 6917
info@geofantex.com
geofantex@gmail.com
+86-400-8266163-44899
In the continuous battle against soil erosion and landscape degradation, innovative solutions are always in demand. Among these, geocell technology has emerged as a frontline defense, particularly in slope protection. This popular science article delves into the world of geocell technology, exploring its definition, applications, capabilities, and the different types available in the market. Through a series of questions and answers, we aim to shed light on how geocells contribute to environmental sustainability and infrastructure resilience.
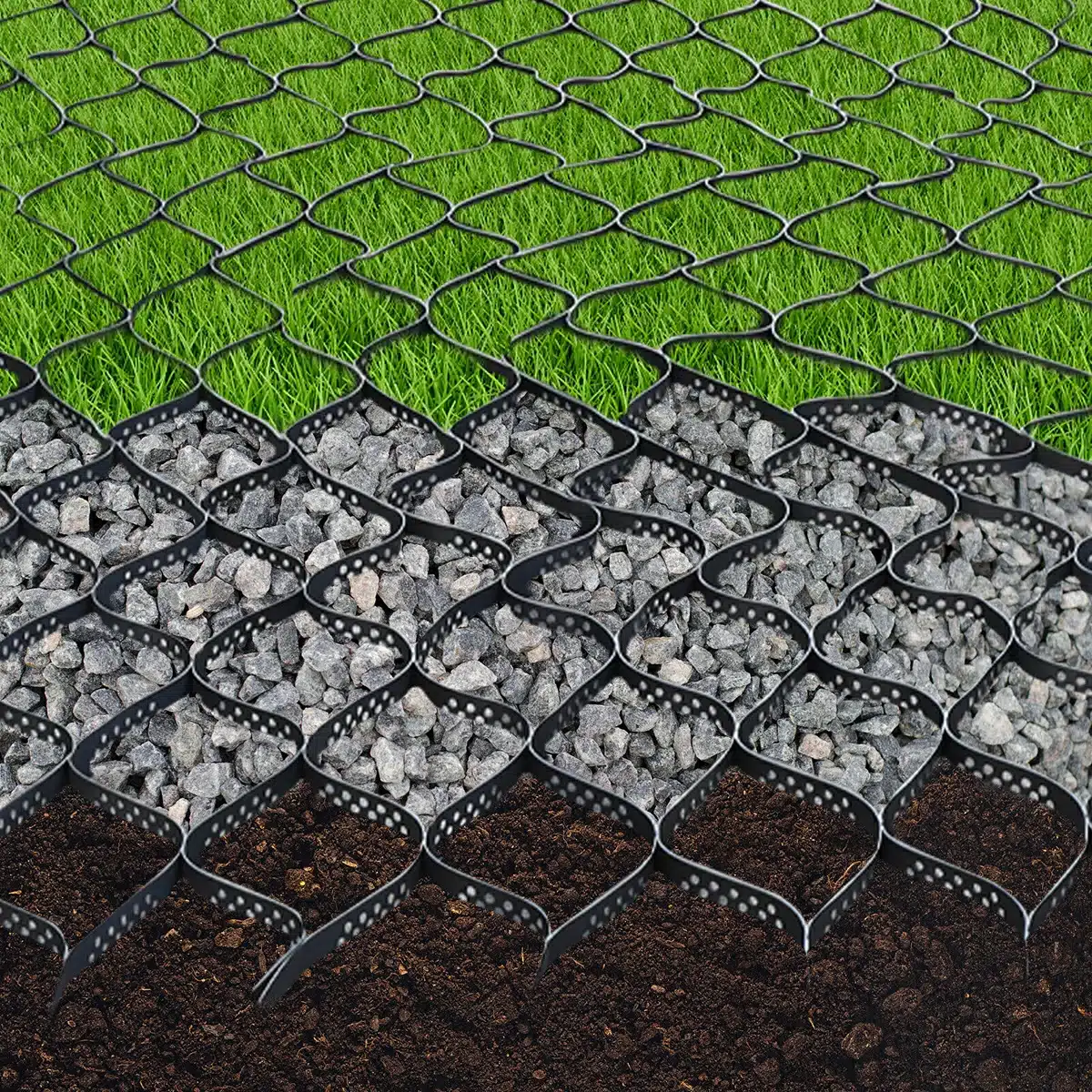

What is Slope Protection with Geocells?
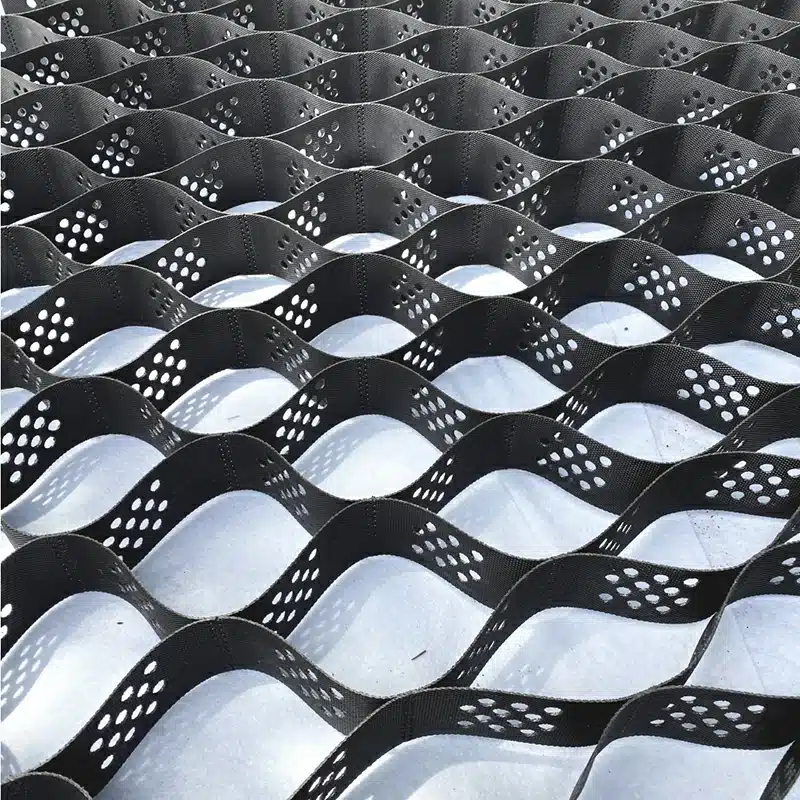
Slope protection is a crucial aspect of civil engineering and environmental management, particularly in areas prone to soil erosion, landslides, or degradation. One modern solution for stabilizing slopes and preventing erosion is the use of geocells. These are three-dimensional, honeycomb-like structures made of high-density polyethylene or other durable materials, which are used to reinforce and protect slopes. The geocells are filled with soil or other materials to provide structural support, enhancing slope stability.
Benefits
- Enhanced Slope Stability: Geocells distribute the weight of the soil more evenly, reducing the likelihood of slope failure.
- Erosion Control: By confining soil within the cells, geocells prevent soil movement and surface erosion due to water runoff.
- Vegetation Support: Geocells create a stable environment for vegetation to take root, promoting natural habitat restoration and environmental benefits.
- Cost-Effective: Geocells are relatively affordable compared to traditional slope stabilization methods, requiring less maintenance over time.
- Quick Installation: The modular nature of geocells allows for fast deployment, making them suitable for projects with tight timelines.
Applications
Geocells are widely used in various civil engineering and environmental protection projects, such as:
- Road Construction: Stabilizing embankments and slopes along highways or railways to prevent soil erosion and landslides.
- Stormwater Management: Installing geocells in drainage ditches or retention ponds to control erosion while allowing vegetation to flourish.
- Coastal and Riverbank Protection: Using geocells to reinforce shores or riverbanks, preventing erosion and stabilizing the land.
- Slope Reinforcement in Mining Areas: Securing slopes in open-pit mines or quarries to reduce the risk of landslides.
Examples and Case Studies
- Case Study: Highway Slope Protection in California, USA: In California, geocells were used to stabilize steep highway embankments vulnerable to erosion. The geocells not only prevented soil washout but also helped in establishing vegetation on the slopes, reducing long-term maintenance costs.
- Case Study: Riverbank Stabilization in South Africa: In South Africa, geocells were deployed along the banks of a river where erosion was threatening the surrounding ecosystem. The geocells helped control soil erosion while supporting vegetation growth, and restoring natural habitats along the river.
- Case Study: Coastal Erosion Control in Japan: In Japan, geocells were used to protect coastal slopes from erosion due to typhoons. The geocell system enhanced the structural integrity of the coast while minimizing the environmental impact of traditional erosion control methods.
Geocells offer an innovative and effective solution for slope protection, providing enhanced stability, erosion control, and vegetation support. Their application is diverse, spanning road construction, water management, and environmental restoration. Through case studies, it’s clear that geocells are an essential tool for sustainable engineering practices, offering cost-effective and environmentally friendly outcomes.
What is the Maximum Slope for Geocell?
Geocell systems are versatile solutions used in a variety of civil engineering applications, especially for erosion control, slope stabilization, and foundation reinforcement. The maximum slope that geocells can effectively manage depends on several key factors, including the type of soil, the design of the geocell, and the installation techniques used
Key Influencing Factors:
Soil Type:
- Cohesive Soils (e.g., clay): These soils are typically less prone to slippage, and geocells can often support steeper slopes—around 30 to 45 degrees, depending on soil cohesion and other conditions.
- Non-Cohesive Soils (e.g., sandy or gravelly soils): Geocell systems are less effective in non-cohesive soils for very steep slopes, where erosion and soil instability are more significant concerns. In such cases, slope angles are typically limited to around 20 to 30 degrees unless additional reinforcement is provided.
Geocell Design:
- The thickness of the cells and the type of material used (typically HDPE, geotextile, or aluminum) influence the system’s ability to withstand forces from erosion, sliding, and shear stress. Thicker, high-strength geocells can tolerate steeper slopes. For instance, high-density polyethylene (HDPE) geocells with reinforced designs can handle slopes exceeding 40 degrees in some cases.
- Cell Size: Larger cells may be suitable for stabilizing larger volumes of soil but may not work as effectively on steep, fine-grained slopes.
Installation Methods:
- The way geocells are installed plays a critical role. Proper anchoring at the base and ensuring that the cells are filled with the right type of material (e.g., gravel, soil, or concrete) can greatly improve the system’s ability to handle steeper slopes.
- Additional stabilization methods like terracing or vegetation (e.g., planting grass within the geocell structure) can enhance geocell performance on steep slopes.
The maximum slope a geocell system can effectively handle is generally between 20 and 45 degrees, depending on several factors such as soil type, the specific design of the geocell, and installation techniques. Geocells made of high-density polyethylene (HDPE) and similar strong materials, when combined with proper installation methods, can support steeper slopes. Always consider product recommendations, the soil type, and additional stabilization techniques to ensure optimal performance in slope stabilization and erosion control applications.
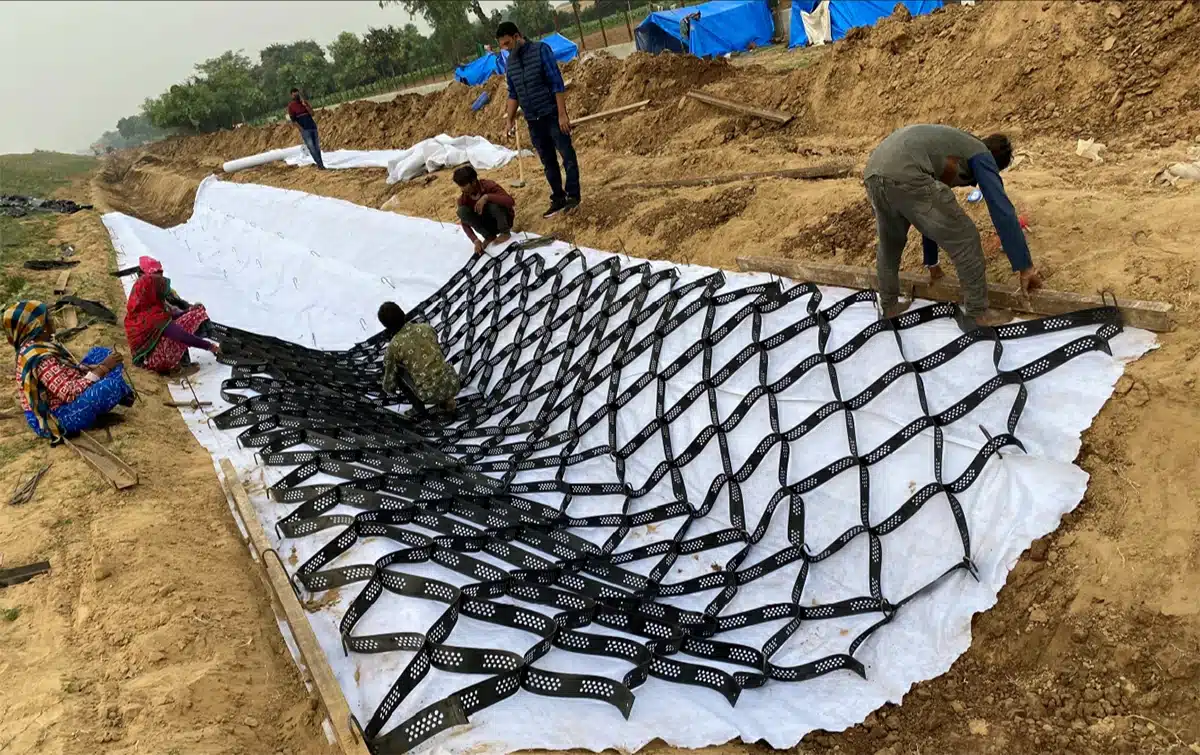

What are the Different Types of Geocells?
Geocells come in various types, primarily distinguished by their material, cell size, depth, and whether they are non-perforated or perforated. The most common material is high-density polyethylene (HDPE), known for its durability and environmental resistance. Other materials include polyester and novel biodegradable options for temporary applications. Cell sizes can range from small for pedestrian loads to large for heavy vehicular loads. The depth of the geocell also varies, with deeper cells providing greater stability for more challenging applications. Among the variations, non-perforated geocell and perforated geocell options stand out; the latter features perforations to facilitate water drainage and promote vegetation growth within the cells, while the former offers a solid structure for specific environmental conditions.
Where is Geocell Used?
Geocell technology has a wide range of applications beyond slope protection, encompassing construction for erosion control, soil stabilization on flat ground and steep slopes, channel protection, and structural reinforcement for load support and earth retention. It is instrumental in road construction to stabilize the base and subbase layers, effectively reducing the need for traditional aggregate materials. In landscaping, geocells help create green retaining walls and embankments, showcasing their utility in soil stabilization on both flat ground and steep inclines. Moreover, their application extends to channel protection to prevent erosion in waterways and the construction of robust load support platforms for heavy equipment in industries such as oil and gas, and military operations, serving as a testament to their effectiveness in structural reinforcement for load support and earth retention. The versatility of geocells makes them a popular choice for a myriad of civil engineering and environmental protection projects.
Geocell technology offers an effective and environmentally friendly solution for slope protection and soil stabilization. By understanding the fundamental aspects of geocells, including their applications, limitations, and types, stakeholders can make informed decisions about their use in combating erosion and enhancing infrastructure resilience. As the technology evolves, the potential for geocells in new applications will undoubtedly expand, further solidifying their role in sustainable construction and environmental conservation.


Get Free Sample
We’ll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)






















