+86-159 9860 6917
info@geofantex.com
geofantex@gmail.com
+86-400-8266163-44899
In the continuous battle against soil erosion and landscape degradation, innovative solutions are always in demand. Among these, geocell technology has emerged as a frontline defense, particularly in slope protection. This popular science article delves into the world of geocell technology, exploring its definition, applications, capabilities, and the different types available in the market. Through a series of questions and answers, we aim to shed light on how geocells contribute to environmental sustainability and infrastructure resilience.
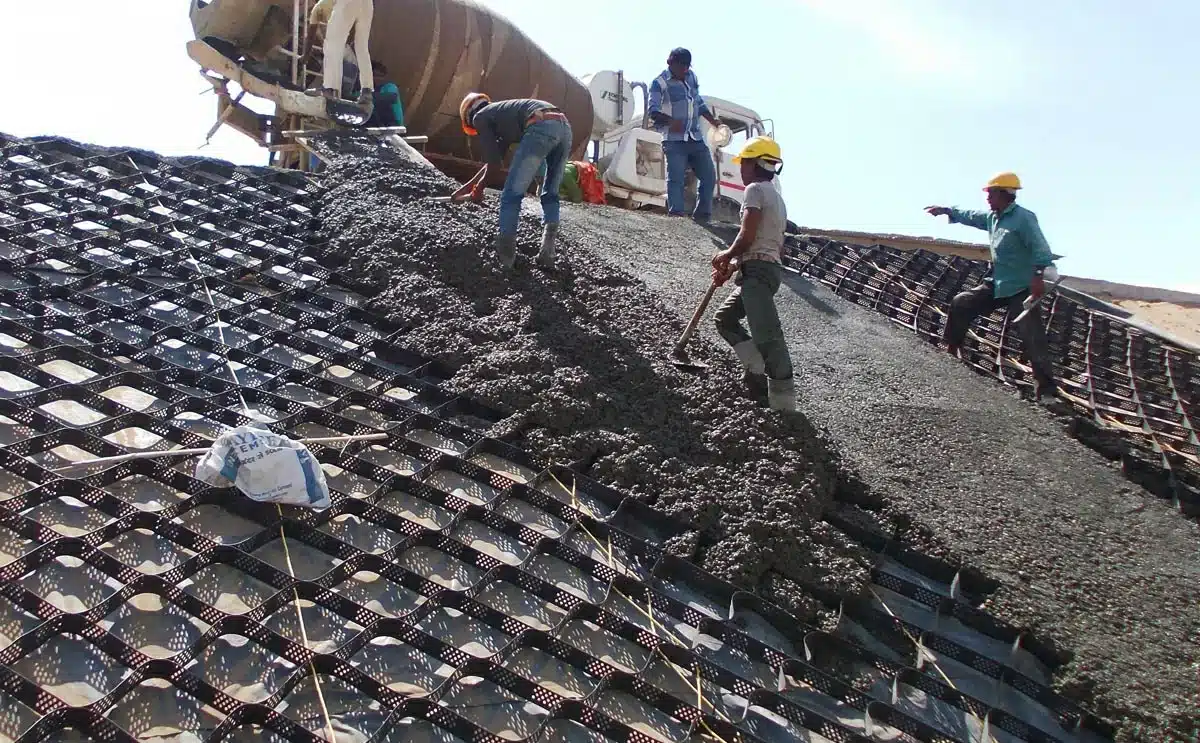

What is Slope Protection with Geocells?
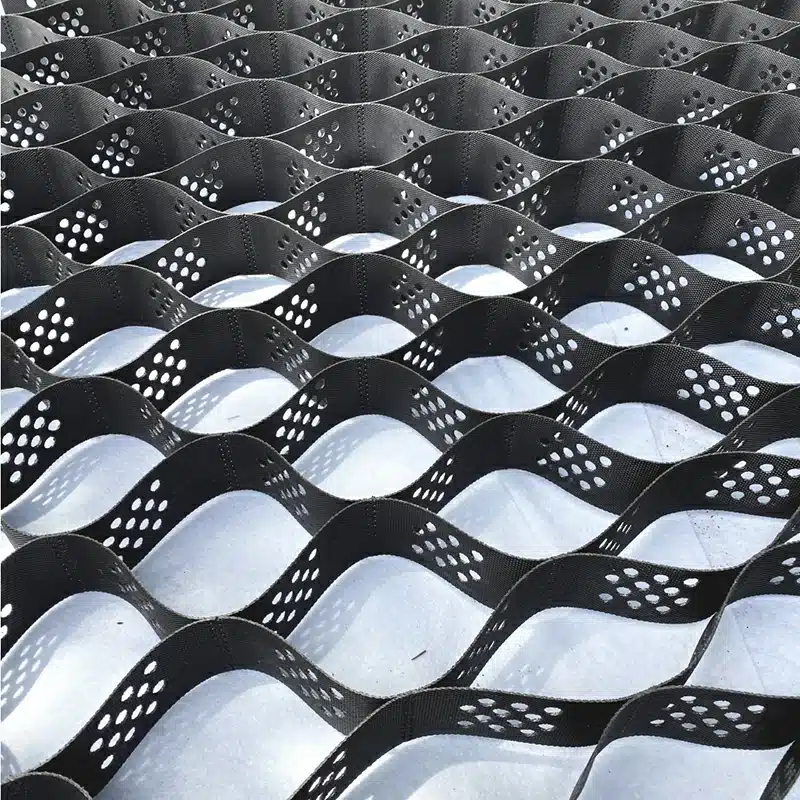
Slope protection with geocells involves using cellular confinement systems, typically made of high-density polyethylene (HDPE) material, to reinforce and stabilize slopes. Geocells are three-dimensional, honeycomb-like structures that can be filled with soil, aggregate, or other materials.
Here’s how slope protection with geocells typically works:
- Site Assessment: Engineers assess the slope’s stability, soil conditions, and other factors to determine the appropriate solution.
- Design: Based on the site assessment, engineers design a slope protection system using geocells. This includes determining the spacing and height of the geocells, as well as the appropriate infill material.
- Installation: Geocells are laid out on the slope and secured in place. They can be interconnected to form a continuous reinforcement system.
- Filling: The geocells are filled with soil, aggregate, or other materials. This infill material provides additional stability to the slope.
- Vegetation: In some cases, vegetation may be planted within the geocells to further enhance slope stability and aesthetics.
Slope protection with geocells offers several benefits, including erosion control, increased slope stability, and reduced maintenance requirements. The confined infill material prevents erosion by locking it in place, while the geocells themselves distribute forces and reduce soil movement. This can be particularly useful in areas prone to erosion, such as steep slopes, riverbanks, or coastal areas
What is the Maximum Slope for Geocell?
Geocells can typically be used on slopes up to 45 degrees (1:1 slope), though this depends on soil type, geocell material, and reinforcement methods.
Factors Affecting Maximum Slope:
- Soil Type: Cohesive soils allow steeper slopes.
- Geocell Size and Material: Larger or stronger cells support more load.
- Anchorage & Reinforcement: Proper fixing can increase stability.
- Drainage Conditions: Good drainage reduces erosion and slippage risk.
Risks of Exceeding Maximum Slope:
Steeper slopes may become unstable, require more maintenance, and pose safety hazards.
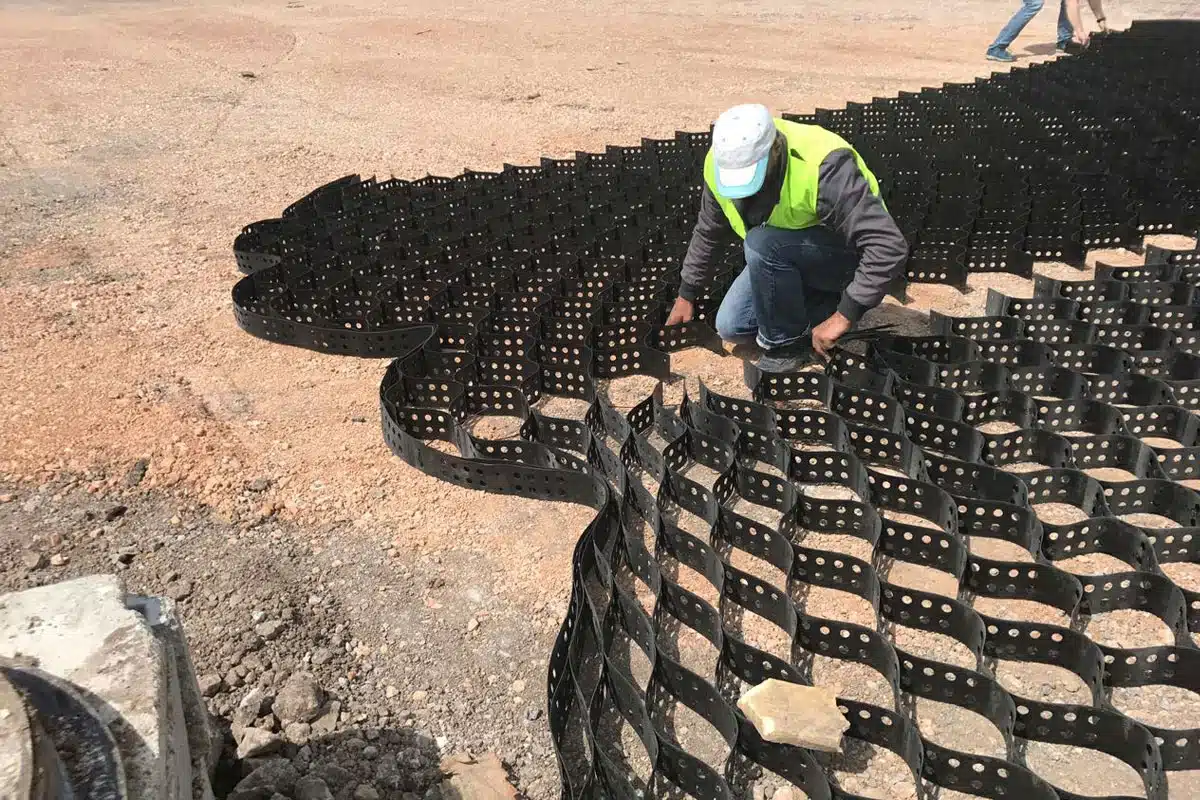

What are the Different Types of Geocells?
Geocells, also known as cellular confinement systems, are three-dimensional geosynthetic materials used in various civil engineering applications. They are typically made from polyethylene, polypropylene, or other polymers. Here are some different types of geocells based on their structure and material:
- Perforated Geocells: These geocells have small perforations or holes in the cell walls, allowing water to flow through easily. They are suitable for applications where drainage is critical, such as slope stabilization and channel protection.
- Textured Geocells: Textured geocells have a roughened surface inside the cells, which enhances soil or aggregate interlock. This type is often used in load support applications such as road construction and reinforcement of weak soils.
- Smooth Geocells: Smooth-walled geocells have a smooth surface inside the cells, providing uniform support and confinement. They are versatile and used in various applications like load support, erosion control, and retaining wall construction.
- High-Strength Geocells: These geocells are designed to withstand heavy loads and provide robust confinement. They are used in applications requiring high load-bearing capacity, such as parking lots, railway ballast stabilization, and heavy-duty pavements.
- Lightweight Geocells: Lightweight geocells are made from materials that are specifically chosen for their low weight and high strength. They are suitable for applications where minimizing overall structure weight is crucial, such as green roofs and slope protection on weak foundations.
- Composite Geocells: Composite geocells combine different materials or features to enhance their performance in specific applications. For example, a composite geocell may combine the benefits of perforations for drainage with the strength of high-density polyethylene for load support.
Each type of geocell offers unique advantages depending on the project requirements, such as soil type, load conditions, drainage needs, and environmental considerations.
Where is Geocell Used?
- Site Assessment: Engineers evaluate slope stability, soil conditions, gradient, and environmental factors to determine the most suitable protection solution.
- Design: Based on the site assessment, engineers design a geocell slope protection system, including geocell height, spacing, anchorage method, and appropriate infill material.
- Installation: Geocells are expanded on the slope surface and securely anchored. Individual panels are interconnected to form a continuous reinforcement system.
- Filling: The geocells are filled with soil, aggregate, or other suitable materials. The confined infill enhances structural stability and load distribution.
- Vegetation: When required, vegetation can be planted within the geocells to further improve slope stability and visual appearance.
- Benefits: Geocell slope protection provides effective erosion control, improved slope stability, and reduced maintenance requirements. The three-dimensional confinement locks infill materials in place, distributes applied forces, and limits soil movement, making it especially suitable for steep slopes, riverbanks, and coastal areas.
Geocell technology offers an effective and environmentally friendly solution for slope protection and soil stabilization. By understanding the fundamental aspects of geocells, including their applications, limitations, and types, stakeholders can make informed decisions about their use in combating erosion and enhancing infrastructure resilience. As the technology evolves, the potential for geocells in new applications will undoubtedly expand, further solidifying their role in sustainable construction and environmental conservation.


Get Free Sample
We’ll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)






















