+86-159 9860 6917
info@geofantex.com
geofantex@gmail.com
+86-400-8266163-44899
As road infrastructure continues to evolve, engineers and construction professionals are constantly seeking innovative solutions to enhance road durability and performance. One such advancement is the use of geocells in road reinforcement. This article explores the concept of geocells, and their application in road construction, and addresses common questions regarding their usage, gravel size, weld spacing, and installation process.
What is Geocell in Road Construction?
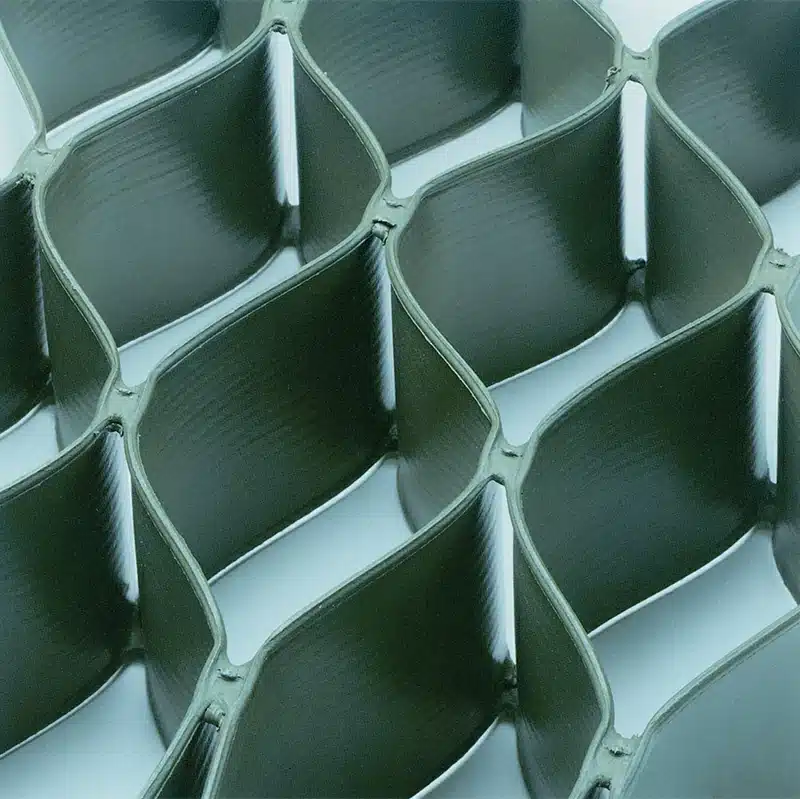
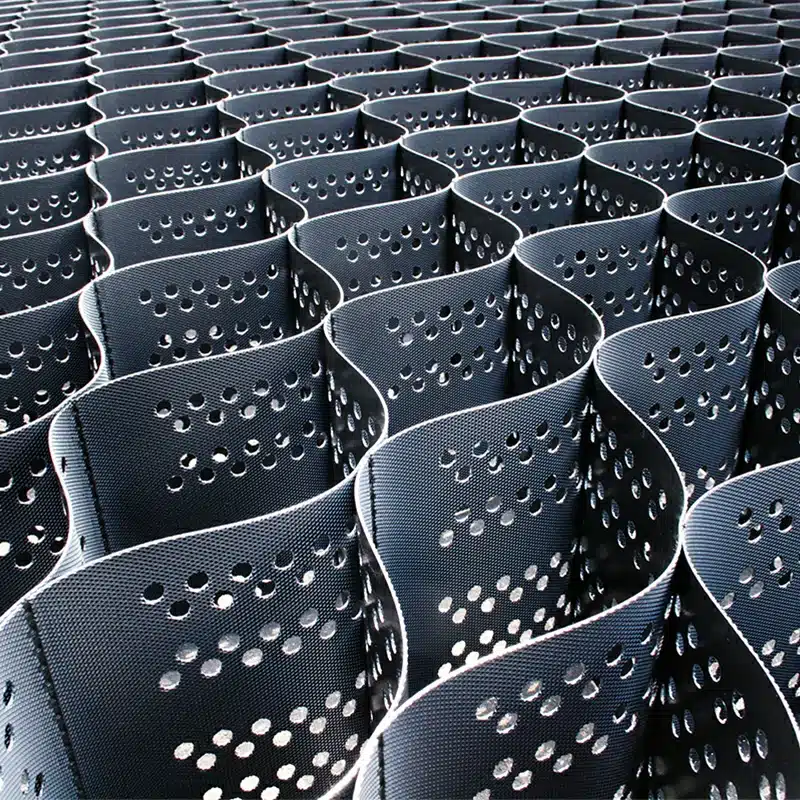
Geocells are three-dimensional, honeycomb-like cellular confinement systems made from high-density polyethylene (HDPE) or other polymeric materials. In road construction, they are used to stabilize soils and provide a solid foundation for roads, highways, and pavements.
Mechanism:
Geocells work by confining soil or other materials within their cellular structure. This confinement increases the load-bearing capacity of the underlying soil, reduces erosion, and distributes loads more evenly across a wider area. By preventing lateral movement, they enhance the strength and stability of road surfaces, making them ideal for use in areas with soft or unstable soils.
Benefits:
- Load distribution: Geocells help distribute the load across a broader surface area, reducing stress on the subgrade.
- Soil stabilization: They improve soil stability, making them particularly useful in challenging terrains like wetlands or slopes.
- Reduction in material use: Geocells often reduce the need for thicker layers of aggregates, which can lower material and transportation costs.
- Erosion control: Their use in sloped terrains helps prevent soil erosion and surface runoff.
Examples of successful implementation:
- Highway in India: Geocells were used to stabilize weak soil for a section of highway, reducing construction time and material costs.
- Alaska’s Dalton Highway: Geocells were applied to strengthen the road over permafrost, providing long-term durability in extreme conditions.
- Mining access roads in Australia: Geocells enabled the creation of durable, low-maintenance access roads in remote areas with soft soils.
These projects highlight the versatility and effectiveness of Geocells in improving road performance and longevity.
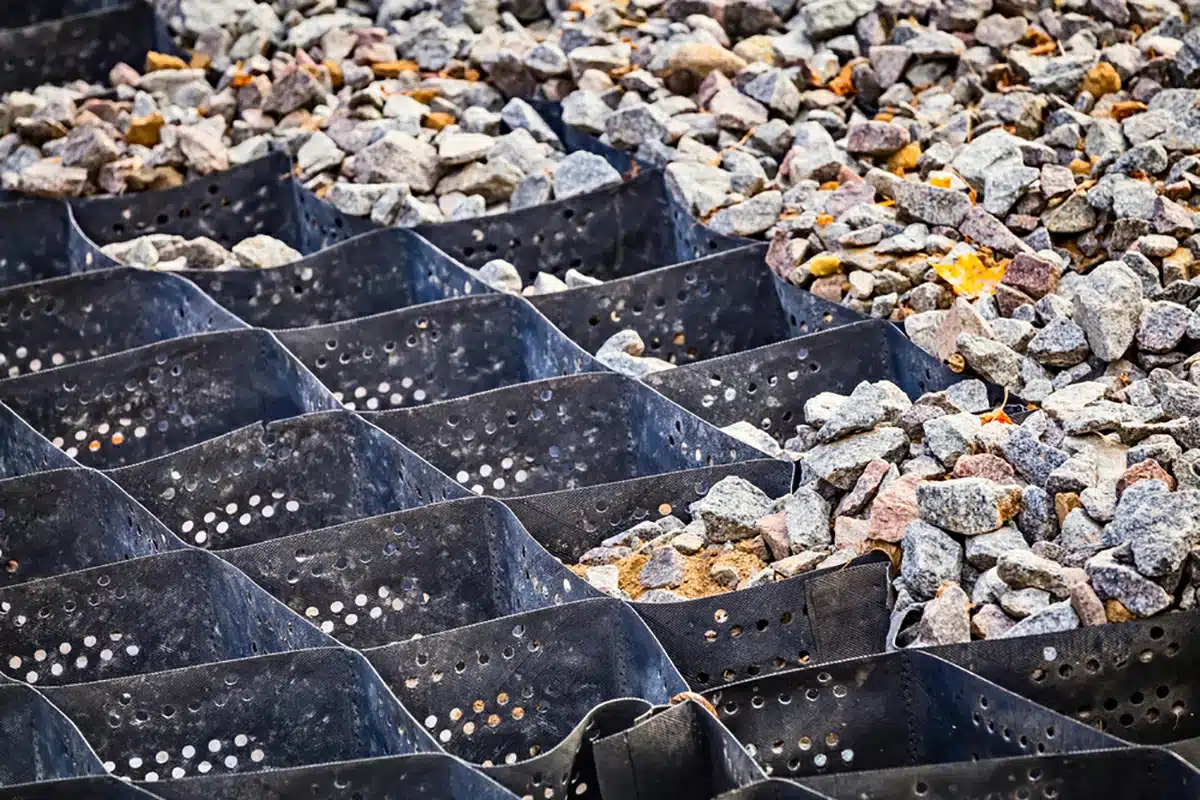

What Size Gravel for Geocell?
When choosing gravel size for geocell applications, it is important to select the right aggregate to ensure effective stabilization and support for your project. Here are specific recommendations:
Common Gravel Size Ranges:
- Driveways/Pathways: 20-40mm gravel, typically crushed stone, is ideal for vehicle and pedestrian traffic. This size ensures good interlocking, which increases stability.
- Erosion Control: Larger gravel, around 40-75mm, can be used in erosion control applications as it provides more resistance to water flow and helps prevent soil washout.
- Load-Bearing Surfaces (Parking lots, roads): A combination of smaller gravel (10-25mm) and larger gravel (up to 50mm) is recommended to support higher loads.
Gravel Types:
- Crushed Stone: Best for most geocell applications because it locks well into the cellular structure and provides excellent load distribution.
- Rounded Gravel: Less ideal due to its tendency to move within the cells, reducing the stabilization effect.
Geocell Configurations:
- Cell Size: Larger cells may accommodate larger gravel sizes, but ensure that the gravel pieces are not too large to prevent excessive movement within the cell.
- Height of Geocell: Taller geocells may require larger gravel for more support, especially in heavy-load applications.
Additional Considerations:
- Drainage: Proper drainage is critical. Ensure that the chosen gravel type supports the permeability requirements of your project.
- Compatibility: The type of gravel used should be compatible with the geocell’s material to prevent puncturing or damaging the cells over time.
What is the Weld Spacing for Geocell?
Weld spacing in geocells refers to the distance between the individual weld points that connect the strips of the polymer material, forming the honeycomb structure. Standard weld spacing for geocells used in road construction is typically around 14.0 in ± 0.12 in (355 ± 3 mm). This spacing is designed to balance flexibility and strength, allowing the geocell to conform to the ground’s contours while maintaining its structural integrity. Proper weld spacing is essential to ensure the geocell can effectively distribute loads and withstand the stresses imposed by traffic and environmental factors.
How to Install Geocell?
Installing geocell for road reinforcement involves several key steps:
- Site Preparation: Begin by preparing the subgrade. Ensure it is level, compact, and free of debris. This foundational layer should be stable to support the geocell and infill materials. Once your base is complete, you’re ready to add geocell to your project.
- Geocell Deployment: To add geocell, first trim the material to fit the area properly. Next, lay the geocell across the excavated area and secure it with stakes. To separate geocells from other ground layers, geotextile fabric can be used. Secure the edges using stakes or other anchoring methods to prevent movement during infill placement.
- Infill Placement: Fill the geocell with the appropriate gravel size, ensuring even distribution across all cells. Overfill slightly to account for compaction. Compaction Compact the infill material using a vibrating plate compactor or similar equipment. This step is crucial for achieving maximum density and stability.
- Surface Layer: Depending on the road design, add additional layers of gravel or other paving materials on top of the compacted geocell to complete the road structure.
Proper installation is key to maximizing the performance benefits of geocells in road construction.
Geocells are a vital component in modern road reinforcement, offering enhanced load distribution, stability, and erosion control. Understanding the correct gravel size, weld spacing, and installation process is essential for leveraging the full benefits of geocell technology. By incorporating geocells into road construction, engineers can create more durable and resilient roadways capable of withstanding the demands of heavy traffic and adverse environmental conditions.

Get Free Sample
We’ll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)






















