+86-159 9860 6917
info@geofantex.com
geofantex@gmail.com
+86-400-8266163-44899
In the quest for sustainable construction and land management practices, the importance of soil stabilization cannot be overstated. Among the myriad of solutions available, the geogrid universal soil stabilization grid stands out as a revolutionary approach. This innovative technology not only promises to transform the landscape of civil engineering but also offers a beacon of hope for environmental conservation. In this article, we delve into the world of geogrids, exploring their functionality, application, and the science behind their effectiveness.
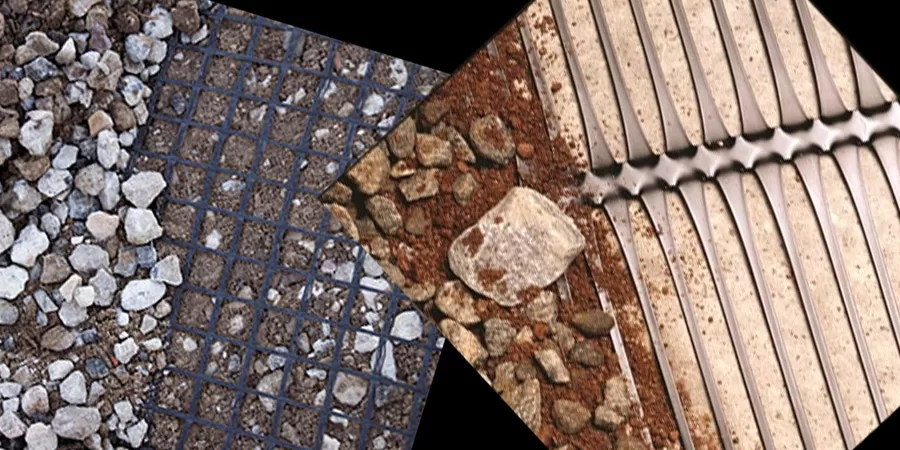
What is Geogrid Soil Stabilization?
Geogrid Soil Stabilization:
Purpose: Geogrid soil stabilization is a technique used to improve soil stability and strength, particularly in construction and civil engineering projects. Its primary purpose is to reinforce soil, making it more stable and able to support structures like roads, embankments, retaining walls, and foundations.
How It Works:
- Material: Geogrids are synthetic materials made from polymers such as polyester, polyethylene, or polypropylene. They are designed in a grid-like pattern with openings (apertures) between the longitudinal and transverse ribs.
- Installation: Geogrids are laid on the soil surface or between layers of soil. They are typically used in layers to create a reinforcing effect.
- Mechanism: The grid structure of geogrids interacts with the soil, providing confinement and distributing loads over a larger area. This interaction enhances the soil’s shear strength and prevents lateral displacement.
- Integration: Geogrids can be combined with other materials like geomembranes or geotextiles for additional stabilization and separation functions.
Benefits:
- Increased Load-Bearing Capacity: Geogrids enhance the soil’s ability to support heavy loads, which is crucial for the stability of roads, parking lots, and other structures.
- Erosion Control: By reinforcing the soil, geogrids help prevent erosion, especially on slopes and embankments.
- Reduced Material Costs: The use of geogrids can reduce the amount of fill material required, leading to cost savings in construction projects.
- Improved Durability: Structures built with geogrid-stabilized soil tend to have a longer lifespan due to enhanced soil stability.
- Versatility: Geogrids can be used in various soil types and conditions, making them a versatile solution for many geotechnical challenges.
Geogrid soil stabilization is a vital technique in modern construction and civil engineering, offering numerous benefits in terms of soil stability, erosion control, and cost efficiency. By understanding its purpose and mechanism, engineers and builders can effectively utilize geogrids to enhance the durability and safety of their projects.
How is Geogrid Used?
Geogrid is a geosynthetic material used widely in construction and civil engineering projects. Here’s a detailed explanation of its applications, functions, and benefits:
Applications of Geogrid
Road Construction
- Base Reinforcement: Geogrid is used to reinforce the base layer of roads, providing a stable foundation and preventing deformation.
- Pavement Reinforcement: It helps distribute loads and reduce rutting and cracking in pavements.
Retaining Walls
- Soil Stabilization: Geogrid is used to reinforce the soil behind retaining walls, increasing the wall’s stability and load-bearing capacity.
- Erosion Control: It helps in controlling erosion by stabilizing the soil.
Embankments and Slopes
- Slope Reinforcement: Geogrid is employed to reinforce slopes and prevent landslides by increasing the shear strength of the soil.
- Embankment Stability: It stabilizes embankments constructed over weak or compressible soils.
Railway Construction
- Track Bed Stabilization: Geogrid is used to stabilize the track bed, reducing maintenance needs and improving the longevity of railway tracks.
Landfills
- Liner Reinforcement: Geogrid reinforces the liner systems in landfills, providing additional stability and preventing leakage.
- Waste Containment: It helps in the containment and stabilization of waste materials.
Functions of Geogrid
- Reinforcement: Geogrid enhances the structural integrity of soils and aggregates by providing tensile strength, which the soil alone cannot achieve.
- Separation: It prevents the intermixing of different soil layers, maintaining the integrity and functionality of each layer.
- Filtration: Geogrid can allow for the passage of water while preventing soil particles from migrating, thus reducing erosion.
Benefits of Using Geogrid
- Increased Load-Bearing Capacity: Geogrid improves the load-bearing capacity of soils, allowing for the construction of more robust and durable infrastructure.
- Cost Efficiency: It reduces the need for excavation and replacement of poor soils, leading to lower construction costs.
- Durability and Longevity: Geogrid enhances the durability and longevity of structures by preventing common issues like settlement, deformation, and erosion.
- Environmental Benefits: By stabilizing soil and preventing erosion, geogrid contributes to environmental conservation and reduces the environmental impact of construction projects.
Impact on Infrastructure
- Performance: Incorporating geogrid significantly improves the performance of infrastructure by enhancing stability and reducing maintenance requirements.
- Longevity: Geogrid extends the lifespan of structures by mitigating issues such as soil movement and erosion, leading to more sustainable and resilient infrastructure.
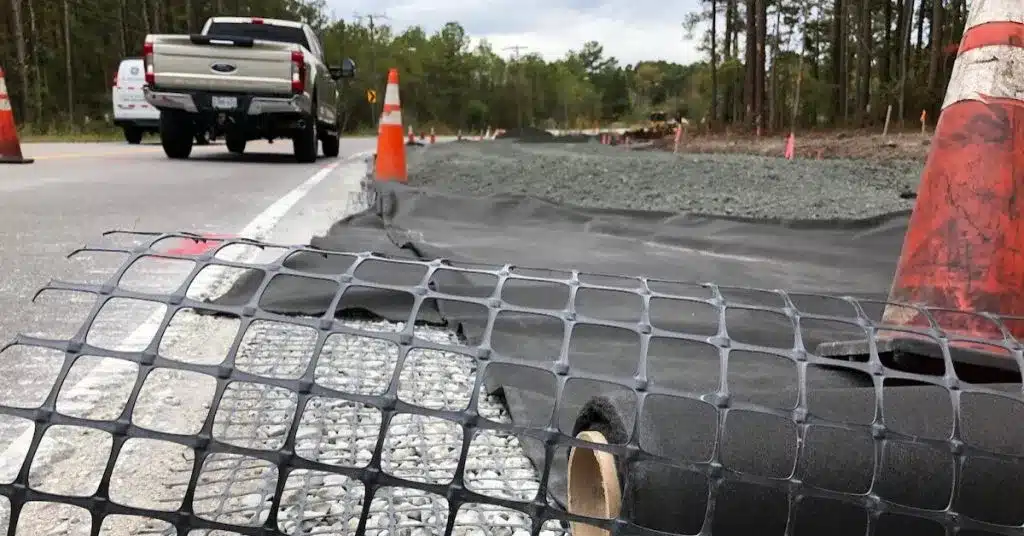

Why do you need Geogrid?
Geogrid is essential for various engineering and construction projects due to its unique properties and applications. Here are the specific purposes and benefits of using Geogrid:
Soil Stabilization:
- Function: Geogrid helps in stabilizing soil by providing a strong foundation.
- Example: In road construction, Geogrid is used to prevent the road from sinking by distributing the load over a wider area.
Reinforcement:
- Function: It reinforces retaining walls and slopes, making them more durable and resistant to environmental forces.
- Example: Geogrid is often used in the construction of embankments to prevent erosion and collapse.
Load Distribution:
- Function: Geogrid distributes loads more evenly, reducing the stress on individual soil particles.
- Example: In airport runways, Geogrid ensures that the load from aircraft is spread out, preventing damage to the surface.
Reduction in Material Costs:
- Function: By using Geogrid, less aggregate material is needed, leading to cost savings.
- Example: In building foundations, the use of Geogrid can reduce the amount of concrete required.
Enhanced Performance:
- Function: It enhances the overall performance and lifespan of construction projects.
- Example: Geogrid in railway track beds improves stability and reduces maintenance costs over time.
Environmental Benefits:
- Function: Geogrid usage can reduce the environmental impact of construction projects.
- Example: Using Geogrid in green roofs helps in water retention and supports plant growth.
What is the mechanism of geogrid?
Geogrid is a geosynthetic material used in civil engineering and construction projects to reinforce soil and other granular materials. Here’s a detailed explanation of how geogrid works and its mechanism:
Structure of Geogrid:
- Material: Geogrids are typically made from polymers such as polypropylene or polyester.
- Design: They consist of a network of integrally connected ribs with apertures (open spaces) that form a grid-like structure. This can be uniaxial (strength in one direction), biaxial (strength in two directions), or triaxial (strength in three directions).
Mechanism of Action:
- Load Distribution: Geogrids help distribute loads over a larger area, reducing the stress on the underlying soil. This is particularly useful in applications like road construction and embankments.
- Soil Reinforcement: The grid structure interlocks with the surrounding soil, creating a composite material that improves the overall strength and stability. The soil particles are confined within the grid apertures, preventing lateral movement.
- Improved Bearing Capacity: By restricting the lateral displacement of soil, geogrids enhance the bearing capacity of the soil, allowing it to support heavier loads without excessive settlement.
- Reduction of Differential Settlement: Geogrids help in achieving more uniform settlement by evenly distributing loads, thus reducing the risk of differential settlement which can lead to structural damage.
Applications:
- Road Construction: Geogrids are used to stabilize road bases and subbases, improving the longevity and performance of roadways.
- Retaining Walls: They provide reinforcement in retaining wall systems, allowing for steeper wall angles and greater wall heights.
- Railway Ballast Stabilization: Geogrids help stabilize railway tracks by reinforcing the ballast layer, reducing maintenance requirements.
- Landfills: They are used to reinforce the foundation layers of landfills, ensuring stability and preventing differential settlement.
Installation Process:
- Surface Preparation: The surface is prepared by removing vegetation and leveling the area.
- Geogrid Placement: The geogrid is laid out flat on the prepared surface, with overlapping sections as required for continuous coverage.
- Backfilling: Soil or aggregate material is placed over the geogrid and compacted to ensure proper interlocking with the grid structure.
Advantages:
- Cost-Effective: Reduces the amount of material needed for construction by enhancing soil properties.
- Durability: Made from durable polymers, geogrids have a long lifespan and can withstand harsh environmental conditions.
- Environmental Benefits: By reducing the need for excavation and material transportation, geogrids contribute to more sustainable construction practices.
The geogrid universal soil stabilization grid represents a significant advancement in the field of civil engineering and environmental management. Its ability to reinforce soil, prevent erosion, and support sustainable construction practices makes it a critical tool in the modern world. By understanding the principles behind geogrid soil stabilization, its applications, and the necessity of its use, we can better appreciate the value it brings to our efforts in creating resilient and durable infrastructures. As we continue to face the challenges of soil degradation and environmental sustainability, the role of geogrids in our construction practices becomes ever more crucial, offering a path towards a more stable and sustainable future.


Get Free Sample
We’ll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)






















