+86-159 9860 6917
info@geofantex.com
geofantex@gmail.com
+86-400-8266163-44899
In the realm of civil engineering and landscaping, ensuring the longevity and stability of structures is paramount. A geocomposite drainage retaining wall is an innovative solution that combines durability with efficient water management. This article delves into the intricacies of geocomposite drains, explores the best drainage options for retaining walls, discusses the necessity of drainage systems, and answers other pertinent questions related to this advanced engineering solution.
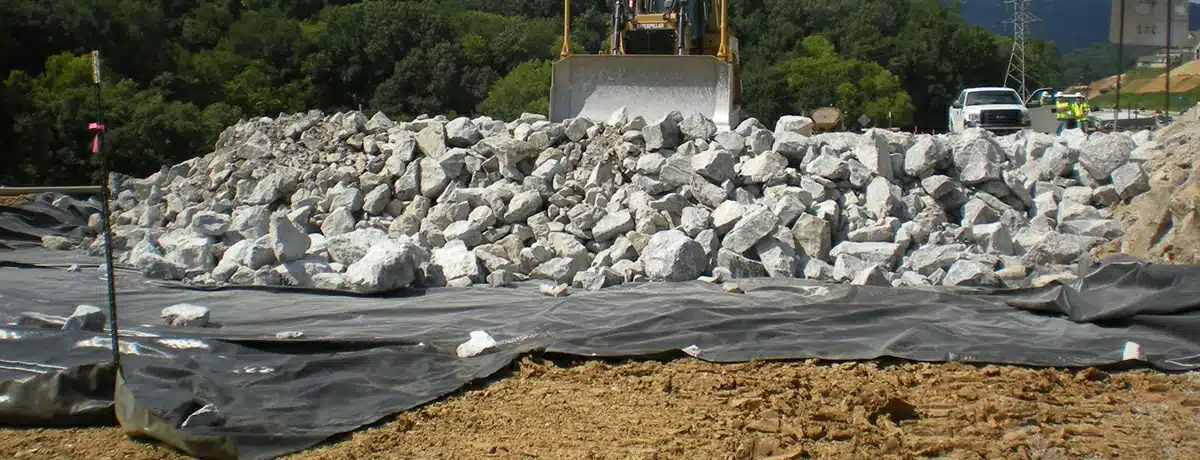

What is a geocomposite drain?
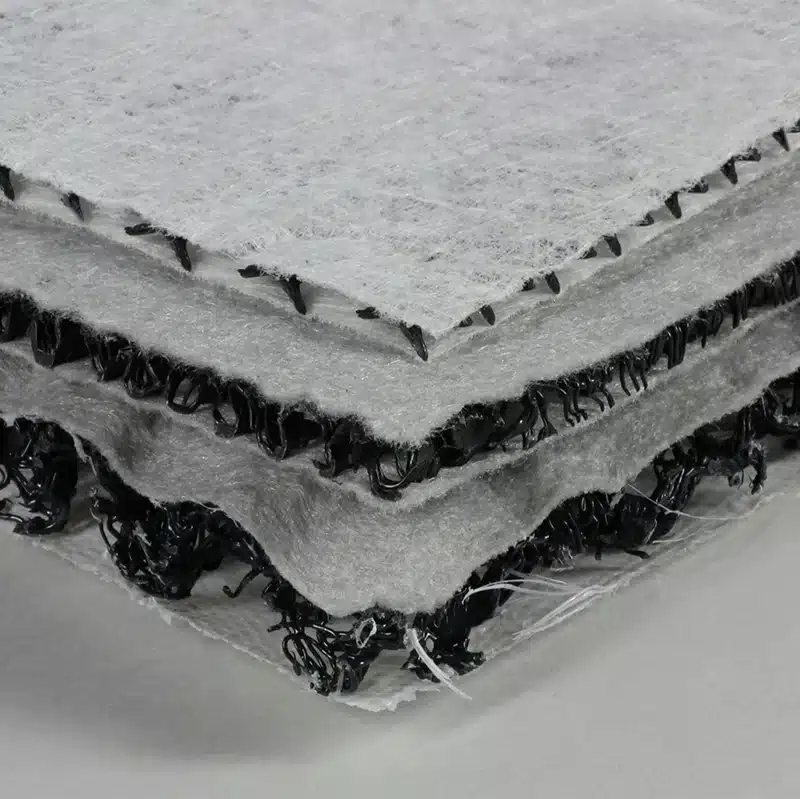
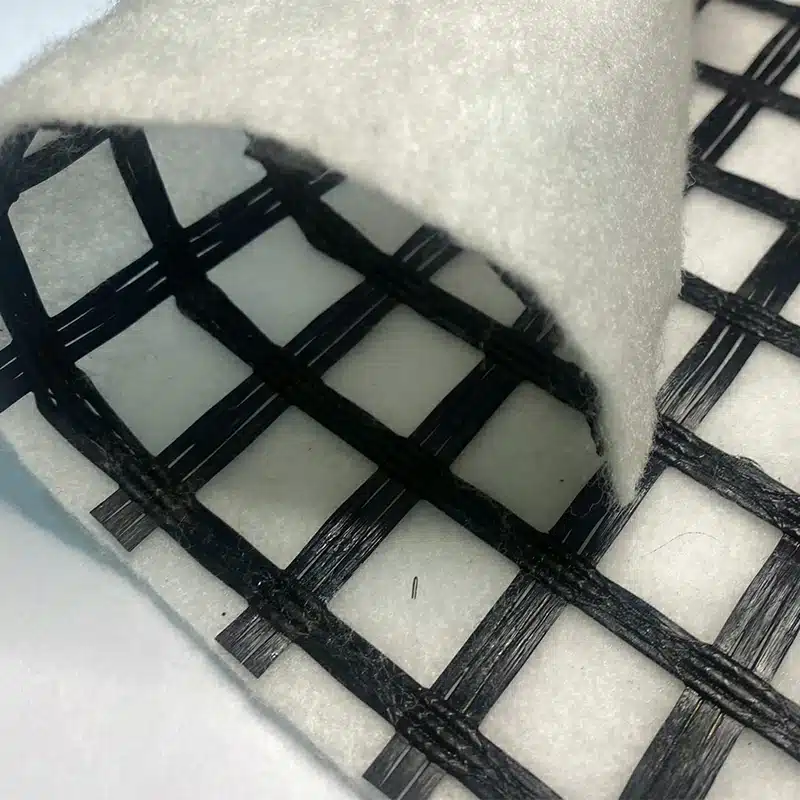
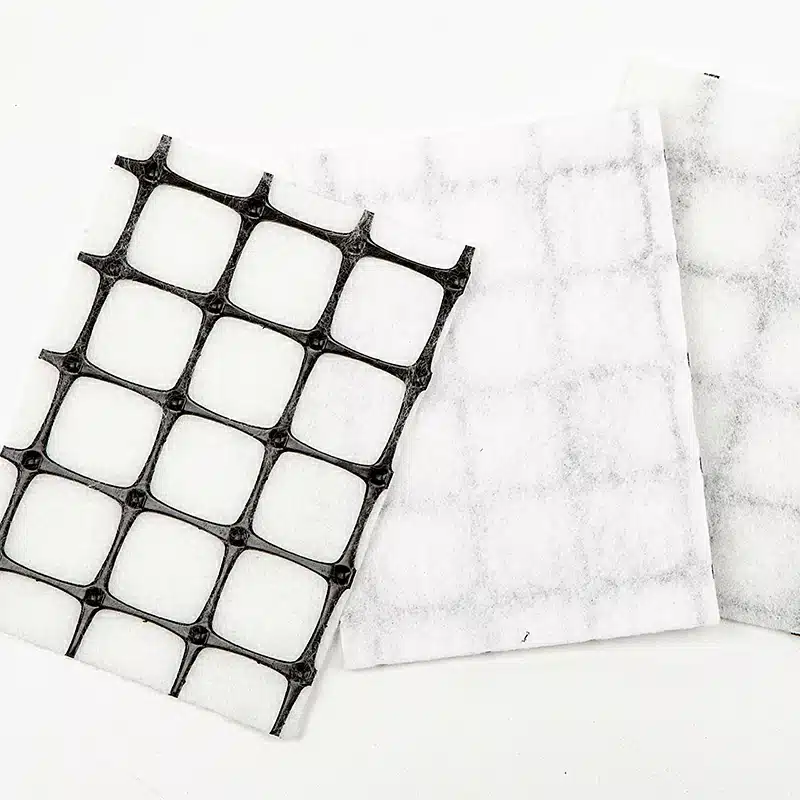
A geocomposite drain is an engineered drainage system combining different geosynthetic materials to manage fluid and gas flow effectively. Here is a detailed explanation:
- Geotextile: A permeable fabric allowing water to pass through while filtering soil particles.
- Geonet: A three-dimensional polymeric structure providing a pathway for water flow.
- Geomembrane: An impermeable barrier often included to contain fluids and prevent leakage.
- Geogrid: A reinforcement grid is sometimes integrated for added structural support.
Function
- Water Management: Facilitates the efficient collection and discharge of water from various sources, preventing soil erosion and structural damage.
- Filtration: The geotextile component filters out soil particles, preventing clogging and maintaining system functionality.
- Gas Venting: In landfill applications, geocomposite drains can also manage gas buildup by providing a pathway for gas to escape.
Typical Applications
- Civil Engineering Projects: Used in road and railway construction for subgrade drainage and stabilization.
- Landfills: Employed to manage leachate and gas, ensuring environmental safety and compliance.
- Retaining Walls: Assists in relieving hydrostatic pressure, and enhancing wall stability.
- Green Roofs: Utilized to manage water drainage, promoting healthy vegetation growth.
Benefits
- Efficiency: Combines multiple functions (drainage, filtration, containment) in a single system, improving installation speed and performance.
- Durability: Made from robust materials resistant to environmental degradation, extending the system’s lifespan.
- Cost-Effective: Reduces the need for multiple separate products and complex installations.
What is the best drainage for a retaining wall?
When planning the drainage for a retaining wall, several key factors must be taken into account to ensure effectiveness and efficiency. Here’s a structured approach to consider:
Type of Soil: Evaluate the soil type behind the retaining wall. Different soils have varying water retention capabilities. For example, clay holds water, while sandy soil drains more easily.
Grading: Proper grading ensures water flows away from the retaining wall. A slope of at least 2% away from the wall is recommended to direct water away from the structure.
Drainage Materials:
- Gravel: Use gravel or crushed stone to create a drainage layer behind the wall. This layer helps water to flow freely and reduces pressure on the wall.
- Filter Fabric: Place a filter fabric between the soil and the gravel to prevent soil from clogging the drainage layer.
Drainage Pipes:
- Perforated Drain Pipes: Install perforated drainage pipes (also known as weep holes) at the base of the retaining wall. These pipes should be surrounded by gravel and covered with filter fabric to ensure proper water flow.
- Outlet Pipes: Ensure that the drainage pipes lead to a proper outlet, such as a storm drain or a downhill slope, to effectively remove water from behind the wall.
Waterproofing: Apply a waterproofing membrane on the backside of the retaining wall to prevent water infiltration that can weaken the structure over time.
Maintenance: Regularly inspect and maintain the drainage system. Clear any blockages in the pipes and ensure the gravel layer remains effective.
Do you always need drainage behind the retaining wall?
Most retaining walls, especially those over 3-4 feet or in wet areas, need drainage to prevent water buildup and structural damage. Yes, which means you need backfill too. Drainage reduces hydrostatic pressure and the risk of water damage, benefiting even smaller walls. It’s best to evaluate your site’s specific conditions and consult a professional to understand the required drainage and backfill for your wall.
How does a geocomposite drainage system extend the life of a retaining wall?
A geocomposite drainage system extends the life of a retaining wall by efficiently managing water flow and reducing hydrostatic pressure against the structure. It acts as a barrier, preventing soil erosion, waterlogging, and freeze-thaw cycles that can weaken the wall over time. By maintaining a dry and stable environment behind the wall, geocomposite drains mitigate the risks of cracking, bulging, or collapsing. Additionally, they are resistant to clogging and biological degradation, ensuring long-term performance and less need for maintenance or repairs.
Geocomposite drainage retaining walls represent a significant advancement in engineering and construction, offering a robust solution for managing hydrostatic pressure and ensuring the longevity of structures. By understanding the role and benefits of geocomposite drains, selecting the appropriate drainage system, and recognizing the importance of drainage in retaining wall construction, engineers and builders can enhance the stability, efficiency, and durability of their projects. Whether in residential landscaping or large-scale civil engineering, incorporating geocomposite drainage systems is a wise investment in the future of infrastructure.


Get Free Sample
We’ll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)






















