+86-159 9860 6917
info@geofantex.com
geofantex@gmail.com
+86-400-8266163-44899
When it comes to soil stabilization and erosion control, geogrid and fabric are two commonly used solutions. In this article, we will explore the differences between geogrid and fabric, and their requirements to help you make an informed choice for your specific project.
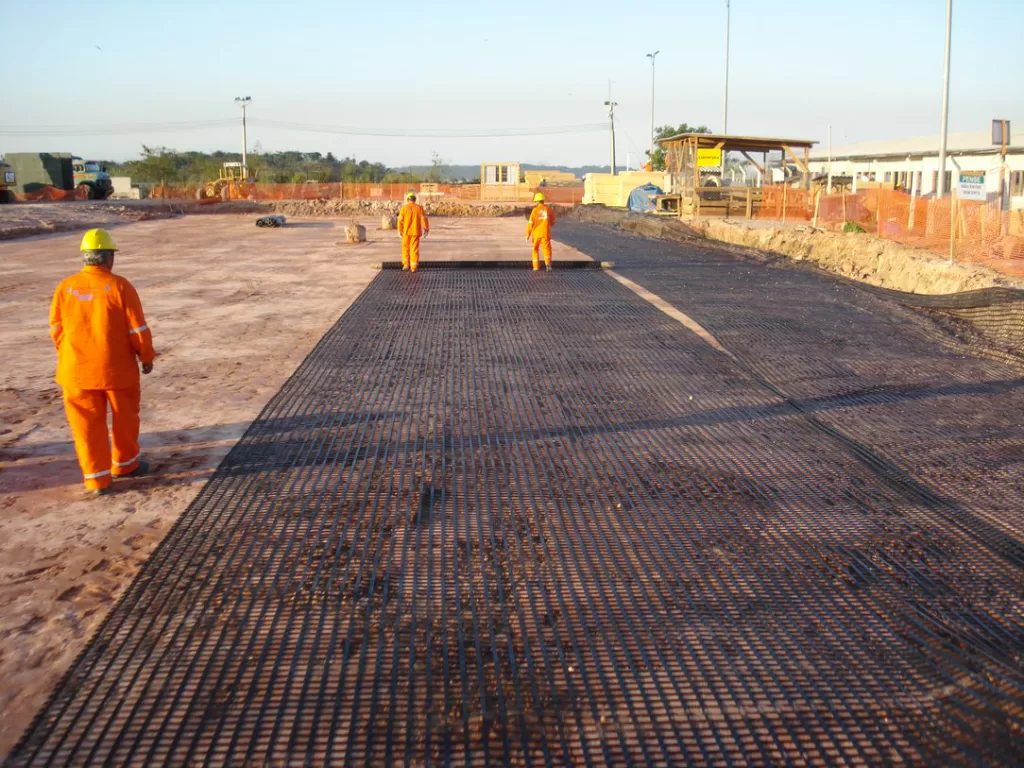

What Is Geogrid, and How Does It Work?
Geogrid is a geosynthetic material designed to reinforce soil, improve load distribution, and enhance structural stability in civil engineering and construction projects.
Key Functions of Geogrid:
- Reinforcement: The grid structure provides a framework that stabilizes soil and increases shear strength, making it ideal for retaining walls, embankments, and road bases.
- Load Distribution: Spreads applied loads evenly across a larger area, reducing stress on underlying soil and preventing deformation or failure.
- Soil Interlock: Soil penetrates the open grid apertures, creating mechanical interlock that enhances stability and resists soil movement and erosion.
- Tension Resistance: Highly tensile, geogrids withstand significant pulling forces, preventing stretching or tearing under heavy loads.
- Flexibility and Durability: Conforms to uneven ground contours and differential settlement while remaining resistant to chemical, biological, and environmental degradation.
Geogrids strengthen soil by reinforcing, distributing loads, and improving interlock, making them an essential component for projects requiring enhanced soil stability, erosion resistance, and long-term durability. They are widely used in roads, slopes, embankments, and retaining walls to ensure reliable structural performance.
What is Geofabric, and What Are Its Applications?
Geofabric, also known as geotextile, is a permeable fabric used in civil engineering and construction, made from synthetic materials like polyester or polypropylene. It comes in two main forms: woven and non-woven, each with specific properties and uses.
Applications of Geofabric:
- Soil Separation: Geofabric is used to separate different layers of soil, gravel, and stones, preventing them from mixing. This separation is crucial in road construction, where it prevents the intermixing of subgrade soil and the gravel base, maintaining the structure’s integrity.
- Erosion Control: It’s used to prevent soil erosion in areas susceptible to water or wind erosion. By covering soil surfaces, geo fabric prevents the displacement of soil particles, thus protecting the landscape and maintaining soil health.
- Drainage: Geofabric aids in drainage by allowing water to pass through while preventing soil erosion. This feature is particularly useful in the construction of retaining walls, drainage ditches, and landscaping to manage water flow and prevent waterlogging.
- Reinforcement: While not as robust as geogrids in terms of load distribution, geofabrics can still provide additional strength to soil, helping to stabilize embankments, slopes, and other earth structures.
- Filtration: In applications like road construction and drainage systems, fabric acts as a filter, allowing water to pass through while preventing soil and other particles from clogging drainage systems.
- Protection: It is used to protect geomembranes in landfill and pond lining applications. Geofabric prevents punctures or damage to these liners, ensuring their longevity and effectiveness.
- Landscaping: In landscaping, fabric is used to suppress weeds while allowing water and nutrients to reach plant roots. It’s also used in creating paths and retaining structures within gardens.
In summary, fabric is a versatile material in civil engineering and environmental projects, offering solutions for soil separation, erosion control, drainage, filtration, reinforcement, protection, and landscaping. Its ability to perform multiple functions makes it a valuable component in a wide range of construction and environmental applications.
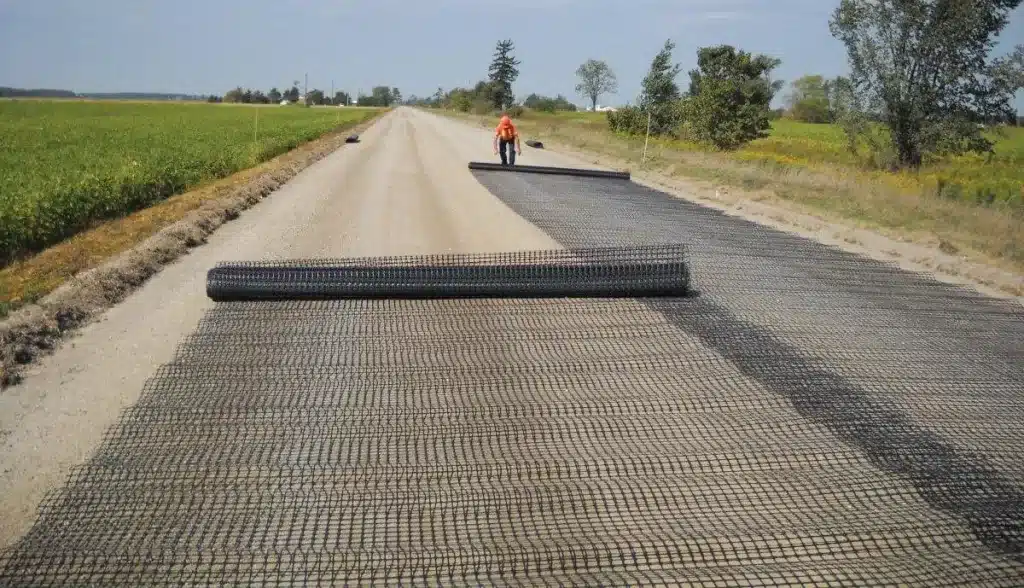

What Is the Difference Between Geofabric and Geogrid?
Geofabric and geogrid differ mainly in structure, function, and engineering performance:
- Structure: Geofabric is a flexible woven or non-woven synthetic sheet with controlled permeability, while geogrid has a rigid or semi-rigid open grid structure made from polymer ribs.
- Primary function: Geofabric focuses on soil separation, filtration, drainage, and erosion control, whereas geogrid is designed for soil reinforcement, load transfer, and structural stabilization.
- Load capacity: Geofabric provides limited tensile contribution and is not intended for heavy load-bearing, while geogrid offers high tensile strength to improve bearing capacity and reduce deformation.
- Soil interaction: Geofabric works by allowing water to pass while retaining fine soil particles, whereas geogrid relies on mechanical interlock between soil or aggregate and its apertures.
- Typical applications: Geofabric is commonly used in road subgrade separation, drainage systems, erosion control, and liner protection, while geogrid is widely applied in road bases, retaining walls, slopes, and embankments.
- Selection principle: Choose geofabric when water management and soil preservation are critical, and choose geogrid when structural strength and long-term stability are required.
Can I use both Geogrid and Geofabric together?
Yes, you can use both geogrid and fabric together in many construction and engineering projects. Combining these materials often leverages the strengths of each, leading to enhanced performance and durability of the engineered structure. Here’s how they can complement each other:
- Layered System: In applications like road construction, a layered system can be created where fabric is used at the bottom layer for separation and filtration, preventing the mixing of subgrade soil with the gravel or aggregate layer. Above this, a geogrid can be placed to provide reinforcement and load distribution.
- Erosion Control and Slope Stabilization: For slope stabilization and erosion control, fabric can be used to prevent soil erosion and promote vegetation growth, while geogrid can provide structural stability to the slope.
- Retaining Walls: In the construction of retaining walls, fabric can be used to facilitate drainage and prevent the buildup of hydrostatic pressure, while geogrids can reinforce the soil, enhancing the overall stability of the wall.
- Drainage Systems: In drainage applications, fabric can act as a filter layer to prevent the clogging of drainage channels with fine soil particles, while geogrid can provide structural support to the drainage system.
- Pavement Construction: For pavement construction, the combination can be particularly effective. Geofabric can act as a separator and filter, while geogrid can reinforce the base and sub-base layers, improving load-bearing capacity and extending the pavement’s lifespan.
When using both materials together, it’s important to consider the specific properties and installation requirements of each. The design should ensure that the functions of both materials are optimized without compromising their individual performance. Proper overlap, anchoring, and layering techniques are crucial for the effectiveness of the combined system. Consulting with a civil engineer or a geosynthetic specialist can provide guidance on the best practices for using geogrid and fabric together in a particular project.
In conclusion, the choice between Geogrid and Geofabric depends on the specific requirements of your project. Geogrids offer structural support and load distribution, while Geofabrics excel in erosion control and soil preservation. Analyzing your site conditions and design goals will help you make an informed decision, ensuring the success of your soil stabilization and erosion control project.


Get Free Sample
We’ll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)






















