+86-159 9860 6917
info@geofantex.com
geofantex@gmail.com
+86-400-8266163-44899
Waterproofing geomembranes have become a cornerstone in various construction and environmental protection projects. One of the most commonly used materials in this domain is High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) geomembrane. Here, we will explore the waterproofing capabilities of geomembranes, the differences between geomembrane and HDPE, the concept of HDPE waterproofing, and the typical thickness of HDPE waterproofing materials.
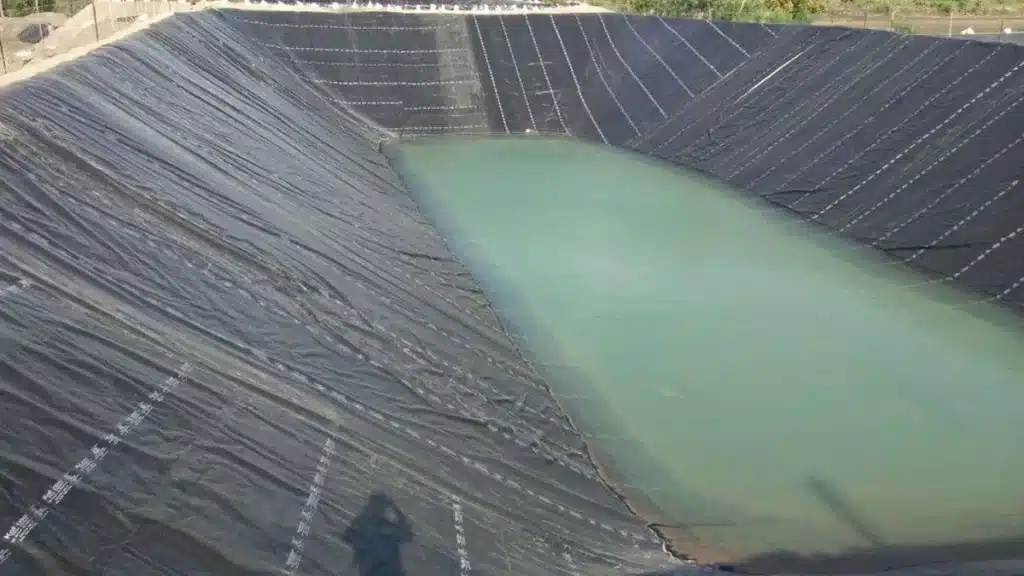

Is geomembrane waterproof?
Yes, geomembranes are inherently waterproof materials. A geomembrane is a synthetic membrane, often made from materials like polyethylene, polypropylene, or PVC, that is waterproof by design to provide a reliable waterproof barrier. They are widely used in various applications, including landfill liners, pond liners, and reservoirs, to prevent the passage of liquids and protect the environment from contamination.
What is the difference between geomembrane and HDPE?
Geomembrane and HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene) are related but distinct terms. PVC geomembranes are flexible and relatively easy to handle, while HDPE geomembranes are tough and non-flexible.HDPE is a type of geomembrane, and the primary difference lies in the material itself. HDPE geomembrane is specifically made from high-density polyethylene, a type of plastic known for its excellent strength and durability. Geomembrane, on the other hand, is a broader term encompassing various synthetic membrane materials used for containment and waterproofing purposes.
What is HDPE waterproofing?
HDPE waterproofing refers to the use of High-Density Polyethylene geomembrane as a waterproofing solution in construction and environmental projects. HDPE geomembranes are exceptionally resistant to chemical, UV, and environmental degradation, making them a preferred choice for applications requiring long-lasting waterproofing. They are commonly used in landfill liners, ponds, and reservoirs, as well as in tunnel and basement waterproofing, where they are used to attach to the main structure of the building.
How thick is HDPE waterproofing?
The thickness of HDPE geomembranes can vary depending on the specific project requirements and the level of waterproofing needed. HDPE geomembranes typically come in various thicknesses, including 0.5, 1.0, 1.2, 1.5, and 1.8 millimeters (20 to 120 mils). The choice of thickness depends on factors such as the type of application, the depth of the structure, and the expected levels of stress and environmental exposure.
- 0.5 to 1.0 mm (20 to 40 mils): Used for lighter applications such as decorative ponds and landscaping projects.
- 1.0 to 2.0 mm (40 to 80 mils): Suitable for applications like landfill liners and reservoirs.
- 2.0 to 3.0 mm (80 to 120 mils): Used for heavy-duty applications, such as industrial chemical containment and high-stress environments.

In conclusion, waterproofing geomembranes, particularly HDPE geomembranes, are indispensable in a wide range of construction and environmental projects. They offer excellent waterproofing capabilities, ensuring the protection of structures and the environment from water intrusion and contamination. The choice of HDPE geomembrane thickness should align with the specific project requirements to provide optimal waterproofing and durability.


Get Free Sample
We’ll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)






















