+86-159 9860 6917
info@geofantex.com
geofantex@gmail.com
+86-400-8266163-44899
Geogrids are synthetic materials used in civil engineering and construction projects to reinforce soil, improve stability, and increase the lifespan of structures. These materials are vital in various applications, including retaining walls, roadways, and slopes, providing a cost-effective solution for soil reinforcement. Understanding how to use geogrid correctly can help enhance the efficiency of construction projects and provide long-term support for infrastructure.
How do you use geogrid?
To use geogrid, start by preparing the surface where it will be installed. Step 1: Excavate Soil Area. Before the geogrid can be placed, you must excavate the entire area to ensure a stable foundation. The soil must be leveled and compacted to create a solid base. Step 2: Cut Geogrid. After excavation is complete, it’s time to cut the geogrid to fit the area. Once the area is ready, the geogrid is unrolled and laid across the surface. Step 3: Install Geogrid by positioning it evenly across the foundation. Depending on the application, it is then pinned or secured into place with stakes, ensuring tension is evenly distributed. Step 4: Secure Geogrid and Place Backfill to lock the geogrid in place. For retaining walls or slopes, the geogrid is layered between compacted soil, reinforcing the structure and preventing erosion or slippage.
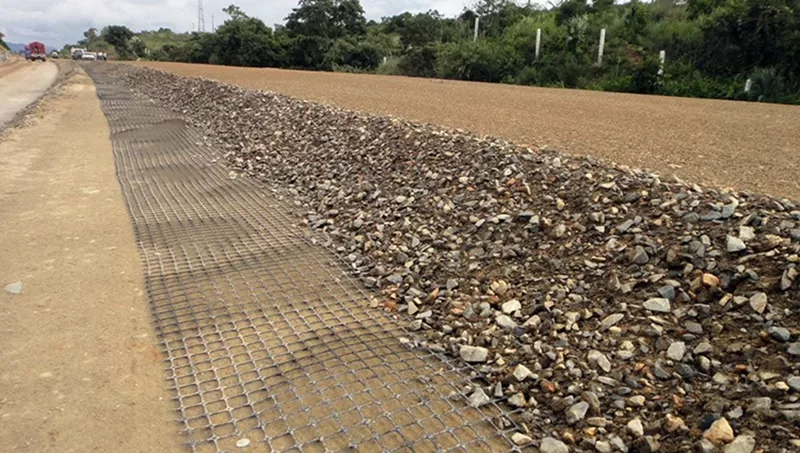

When should geogrid be used?
Geogrid is ideal for projects requiring soil stabilization or reinforcement, such as building retaining walls, especially those taller than three to four feet, stabilizing slopes, and creating road foundations. It is commonly used in construction where load distribution or resistance against shifting is critical. For example, if soil conditions are weak or if a structure must bear heavy loads, geogrid provides the necessary reinforcement to prevent deformation and enhance overall stability.
How many layers of geogrid do I need?
The number of geogrid layers required depends on the specific project and the height of the structure. For retaining walls, multiple layers of geogrid are typically used, with spacing between each layer determined by the height and type of wall. A general rule of thumb is to install one layer for every 2 to 4 feet of height for walls, often placing geogrid every second block layer. However, exact recommendations vary depending on soil conditions, load requirements, and engineering specifications.
Which way to lay a geogrid?
The number of geogrid layers required depends on the specific project and the height of the structure. For retaining walls, multiple layers of geogrid are typically used, with spacing between each layer determined by the height and type of wall. A general rule of thumb is to install one layer for every 2 to 4 feet of height for walls, often placing geogrid every second block layer, ensuring it is laid perpendicular and lengthwise to the face of the wall. However, exact recommendations vary depending on soil conditions, load requirements, and engineering specifications.
Geogrids are versatile tools for reinforcing soil in construction projects. From retaining walls to road stabilization, using geogrids correctly ensures that structures remain stable and long-lasting. Proper installation, including determining the number of layers and correct orientation, is key to maximizing their effectiveness. Understanding when and how to use geogrid can significantly improve the success of infrastructure projects.


Get Free Sample
We’ll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)






















