+86-159 9860 6917
info@geofantex.com
geofantex@gmail.com
+86-400-8266163-44899
Geogrids are a vital component in modern road construction, playing a crucial role in reinforcing and stabilizing the roadbed. These grid-like structures are made from polymers such as polypropylene, polyethylene, or polyester, and are used to enhance the strength and durability of roadways. In this article, we will explore the use of geogrids in road construction, their purpose, when they should be used, and their specific application in rigid pavements.
What is the use of geogrid in road construction?
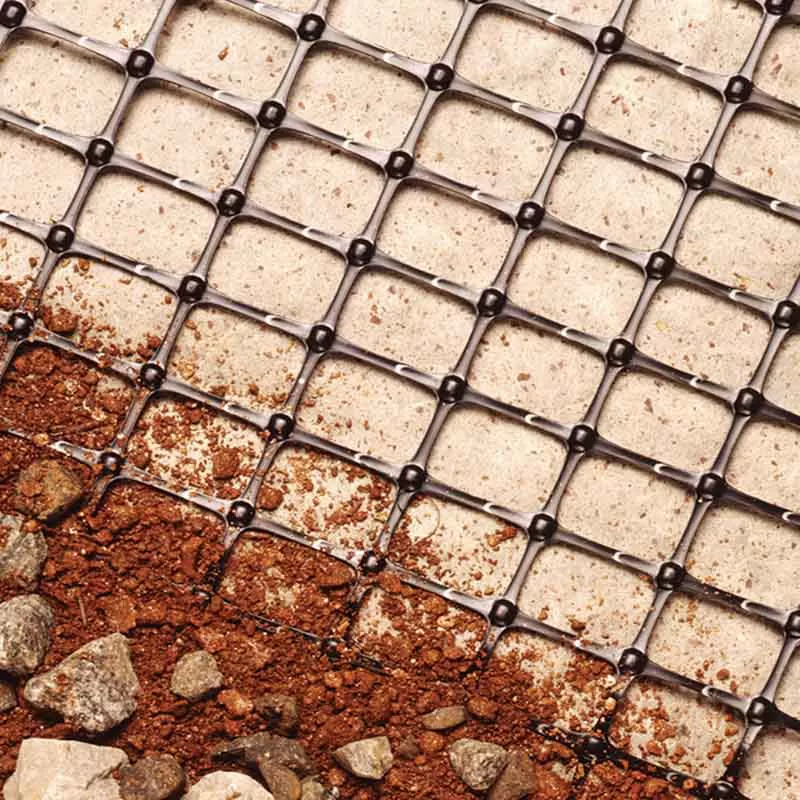
Geogrids are essential synthetic materials used in civil engineering and road construction for ground stabilization and reinforcement. Made from polymers such as polypropylene or polyester, geogrids consist of open, grid-like structures that provide excellent load distribution. Their application in road construction helps manage soil movement, maintain road integrity, and extend the lifespan of the structure.
Applications of Geogrids in Road Construction
- Soil Stabilization and Base Reinforcement: Geogrids are placed between subgrade and aggregate layers to improve load distribution. They help reinforce weaker soils by confining and stabilizing the base material, reducing rutting and other common road deformations.
- Subgrade Improvement: In areas with soft or unstable soils, geogrids enhance the bearing capacity of the subgrade. They help control deformation by creating a stronger platform, essential for roads subjected to heavy traffic.
- Pavement Reinforcement: Geogrids are also used within the pavement layers to improve the load-bearing capacity, ensuring that the road structure can withstand heavy loads without deteriorating.
Benefits of Using Geogrids in Road Construction
- Enhanced Load Distribution: By distributing loads more evenly, geogrids reduce stress on the subgrade and underlying layers, minimizing the risk of subsurface failure.
- Increased Durability and Reduced Maintenance: Geogrids improve the durability of roads by reducing rutting, cracking, and potholes, which leads to lower maintenance costs over time.
- Reduced Construction Costs and Time: By reinforcing weaker soils, geogrids allow for thinner layers of aggregate and other materials, reducing the amount of material and labor required during construction.
Types of Geogrids and Example Use Cases
- Uniaxial Geogrids: These are primarily used for retaining walls and in applications requiring high tensile strength in one direction.
- Biaxial Geogrids: Commonly used in road construction, biaxial geogrids provide strength in two directions, making them ideal for stabilizing bases and subgrades.
- Triaxial Geogrids: With multi-directional strength, these geogrids are well-suited for heavy-duty roads and are highly effective in distributing loads from multiple directions.
Example Case Study
In a project in California, using biaxial geogrids for base stabilization on a major highway reduced rutting by 30% over five years, highlighting geogrids’ effectiveness in reducing maintenance needs and prolonging road life.
The use of geogrids in road construction significantly enhances structural stability, reduces costs, and extends the life of road surfaces. As road infrastructure continues to face increased load demands, geogrids offer an efficient solution for supporting stable, long-lasting roadways.
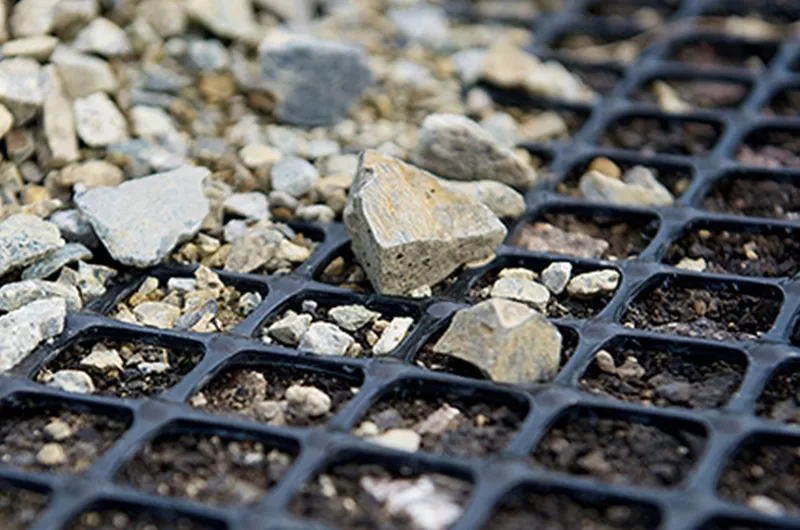

What is the purpose of a geogrid?
Geogrids are specialized synthetic materials used widely in civil engineering to reinforce and stabilize soil. Their primary purpose is to provide structural support in various applications, including roads, retaining walls, and slopes. Here’s a detailed overview of their role and benefits:
Purpose of Geogrids in Construction
Geogrids serve to improve the structural integrity of soil by providing reinforcement. Their open, grid-like structure allows them to interact with the soil particles, enhancing load-bearing capacity and improving stability. This makes geogrids essential in construction projects where soil conditions may otherwise be inadequate to support heavy loads.
Key Functions of Geogrids
- Soil Stabilization: Geogrids prevent soil movement and displacement, which is crucial in unstable soils or sloped terrains. By holding the soil in place, they reduce the risk of erosion and sliding, making them ideal for steep embankments and retaining walls.
- Load Distribution: Geogrids distribute loads more evenly across the soil. This helps prevent surface deformation or rutting under heavy loads, such as in roadways or parking areas. By spreading the load, geogrids reduce pressure on any single area of the soil, increasing the lifespan of the structure.
- Reduction in Fill Requirements: In construction, geogrids often reduce the amount of fill material needed. This lowers material costs and minimizes environmental impacts, especially in remote or sensitive locations.
Applications of Geogrids
- Road Construction: Geogrids reinforce the subbase and subgrade layers in roads, allowing them to carry heavier loads and reducing maintenance costs due to rutting and cracking.
- Retaining Walls: In retaining walls, geogrids improve the wall’s stability, especially in areas with soft or unstable soil. They increase the wall’s load-bearing ability and resistance to lateral forces.
- Slope and Embankment Reinforcement: Geogrids stabilize slopes and embankments, preventing landslides and erosion. They are particularly useful in areas prone to heavy rainfall or erosion.
Materials Used in Geogrids
Geogrids are commonly made from polymers such as polypropylene (PP), polyethylene (PE), and polyester. These materials are durable, resistant to chemicals and weather, and offer flexibility with adequate strength. The material selection depends on the project’s specific requirements, with polyester often chosen for high-strength needs, while polyethylene is favored for more cost-effective applications.
Benefits of Using Geogrids
- Increased Structural Stability: Geogrids enhance the overall stability of structures by reinforcing the soil, reducing settling and deformation.
- Cost Savings: By reducing fill requirements and extending the lifespan of structures, geogrids offer significant cost savings.
- Environmental Benefits: By minimizing the need for additional fill and preventing erosion, geogrids contribute positively to environmental sustainability.
Geogrids are invaluable in enhancing soil strength, load distribution, and durability in construction projects. They offer long-term benefits through cost savings, environmental support, and improved structural integrity across a range of applications.
When should you use Geogrid?
Geogrids should be used in road construction when the underlying soil is weak or unstable, or when there is a need to increase the load-bearing capacity of the road. They are particularly effective in areas with soft soils, such as clay or silt, where traditional construction methods may not provide adequate support. Geogrids are also beneficial in heavy traffic areas, where the road is subjected to significant loads that could cause deformation over time. Furthermore, they are used in the construction of embankments, retaining walls taller than three to four feet, and other structures where soil reinforcement is necessary to ensure stability and prevent erosion.
What is the geogrid in rigid pavement?
In rigid pavement construction, geogrids are used to reinforce the base or subbase layers beneath the concrete slab. By providing additional support to these layers, geogrids help to distribute loads more evenly across the pavement, reducing the risk of cracking and extending the lifespan of the road. Geogrids can reduce deformation better than extremely thick aggregate base sections, offering a more efficient solution for maintaining pavement integrity. The use of geogrids in rigid pavement also improves the overall stability of the pavement structure, making it more resistant to environmental factors such as temperature changes and moisture. This results in a more durable and long-lasting pavement that requires less maintenance over time.
Geogrids are an essential tool in road construction, offering significant benefits in terms of reinforcement, stability, and longevity. Whether used in flexible or rigid pavements, geogrids help to distribute loads, prevent deformation, and extend the lifespan of the road. Their application is particularly crucial in areas with weak soils or heavy traffic, where traditional construction methods may fall short. By understanding the role and purpose of geogrids, engineers and construction professionals can make informed decisions to enhance the performance and durability of roadways.
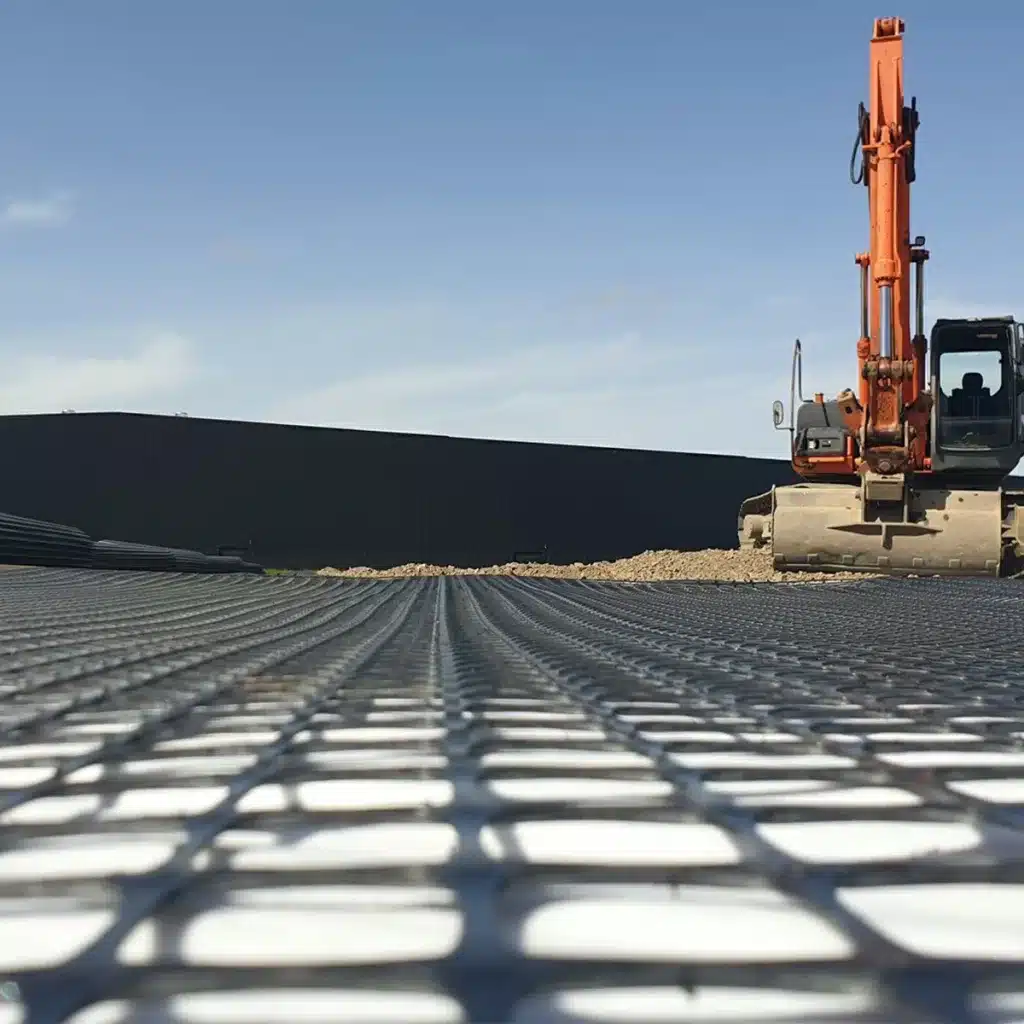


Get Free Sample
We’ll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)






















