+86-159 9860 6917
info@geofantex.com
geofantex@gmail.com
+86-400-8266163-44899
Soil-geogrid interaction is crucial in civil engineering and construction. This article delves into three key aspects: (i) friction at soil–geogrid interfaces, (ii) soil–soil shear strength in apertures, and (iii) transverse rib resistance. These elements play a vital role in soil reinforcement and are essential for understanding this relationship.

What is the Interaction Between Soil and Geogrid?
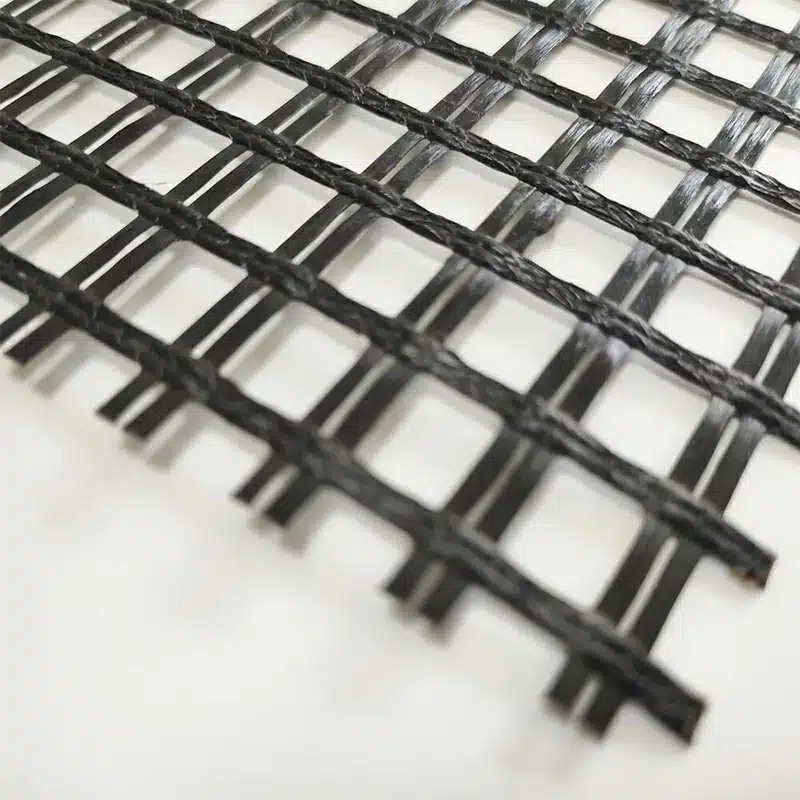
The interaction between soil and geogrid refers to the interlocking and mechanical bonding that occurs when a geogrid material is placed within or on the surface of soil. Geogrids are typically made of high-strength polymers or synthetic materials. When installed in soil, they distribute loads, reduce soil movement, and enhance soil stability. This interaction is crucial for reinforcing soil structures, such as retaining walls, slopes, and embankments.
What is Geogrid Soil Reinforcement?
Geogrid soil reinforcement is the process of using a geosynthetic material, made of polymers, to strengthen soil behind retaining walls. When geogrids are added to the soil, they boost its tensile strength and resistance to deformation. This reinforcement enables the soil to handle heavier loads, making it suitable for various civil engineering purposes like road construction, foundation support, and erosion control.
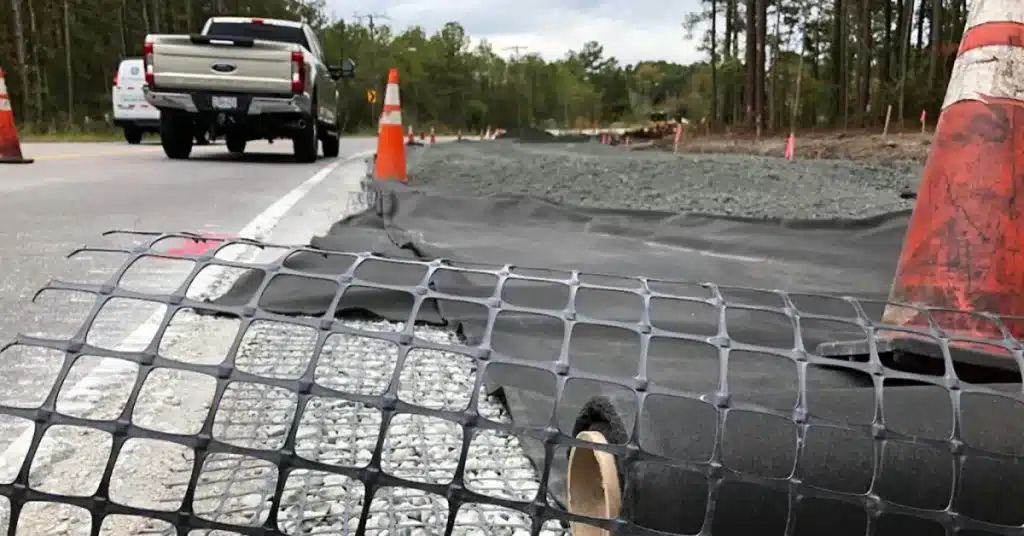

How is Geogrid Used in Soil Stabilization?
Geogrids serve as a key solution in soil stabilization to halt soil shifting, manage erosion, consolidate aggregate, carry variable loads, and ensure the dispersal of tensile forces. They are typically installed in layers within the soil, forming a reinforced area that minimizes both lateral and vertical movement. Geogrids are highly effective in stabilizing slopes, embankments, and roadbeds, enhancing the long-term stability and safety of these structures while also reducing the formation of ruts and deformation caused by frictional forces.
What is the Mechanism of Geogrid?
The geogrid mechanism combines several functions:
- Reinforcement: Geogrids spread loads, easing soil stress.
- Confinement: They hold soil particles in place, limiting lateral movement.
- Interlocking: Geogrid apertures link with soil, boosting stability through friction.
- Tension Resistance: Geogrids provide soil with tensile strength, averting shearing or sliding while also creating a tensioned membrane effect.
In conclusion, soil-to-geogrid interaction is a fundamental aspect of civil engineering, enabling the reinforcement and stabilization of soil in various construction projects. Understanding this interaction and following the requirements are essential for the successful implementation of geogrid soil reinforcement solutions.


Get Free Sample
We’ll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)






















