Slopes and Walls
+86-159 9860 6917
info@geofantex.com
geofantex@gmail.com
+86-400-8266163-44899
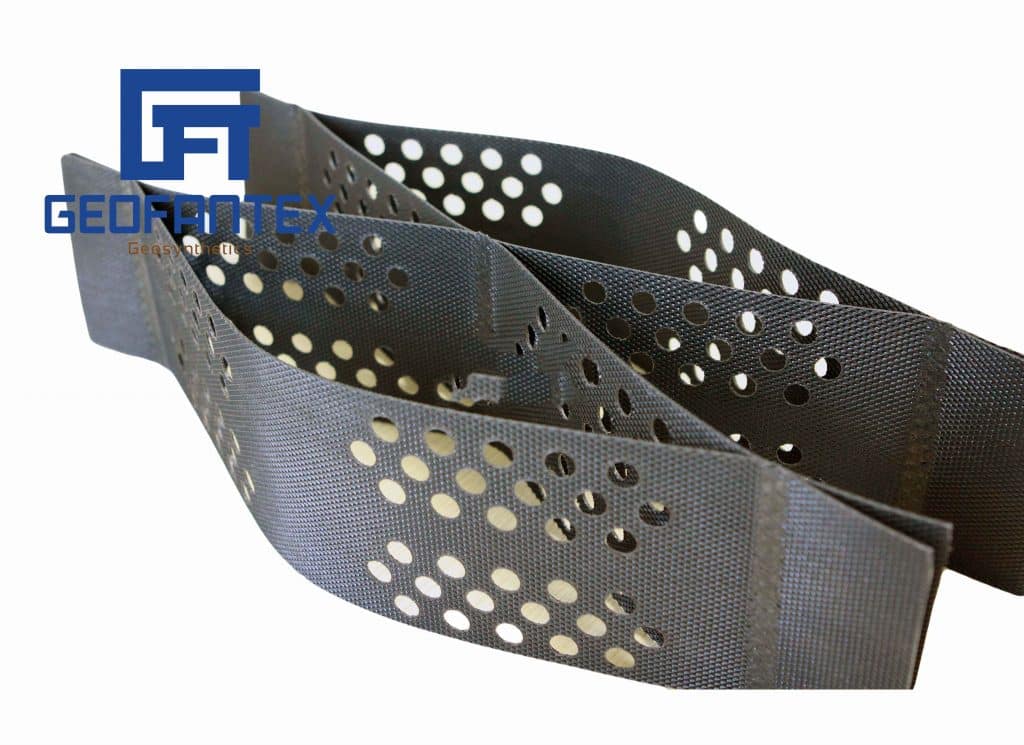
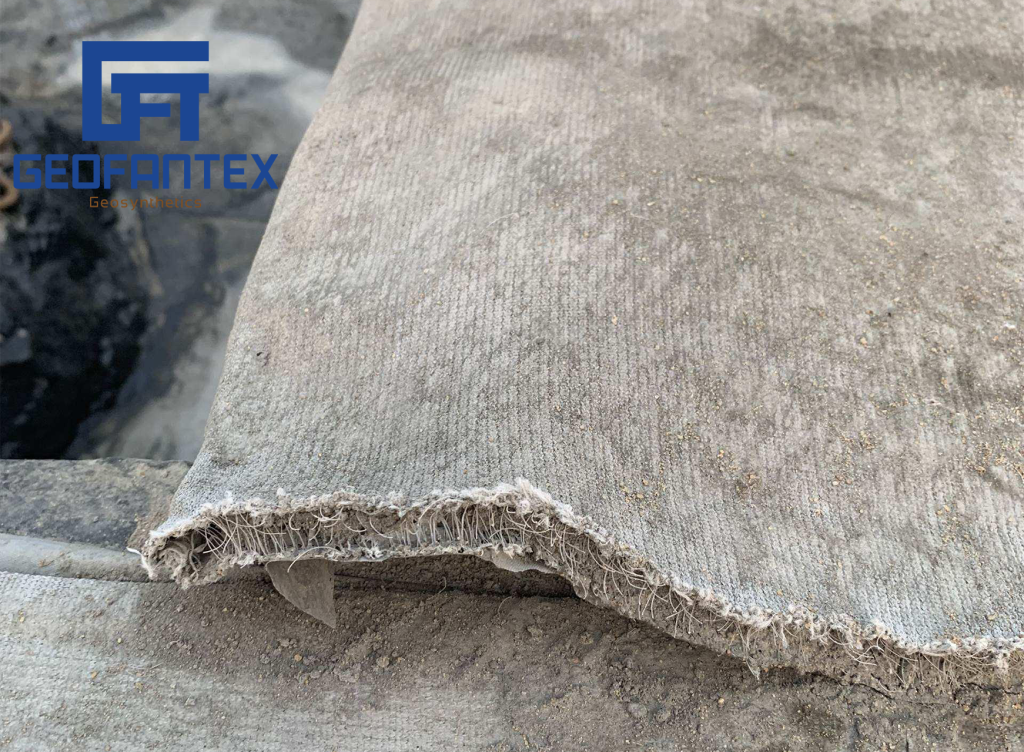
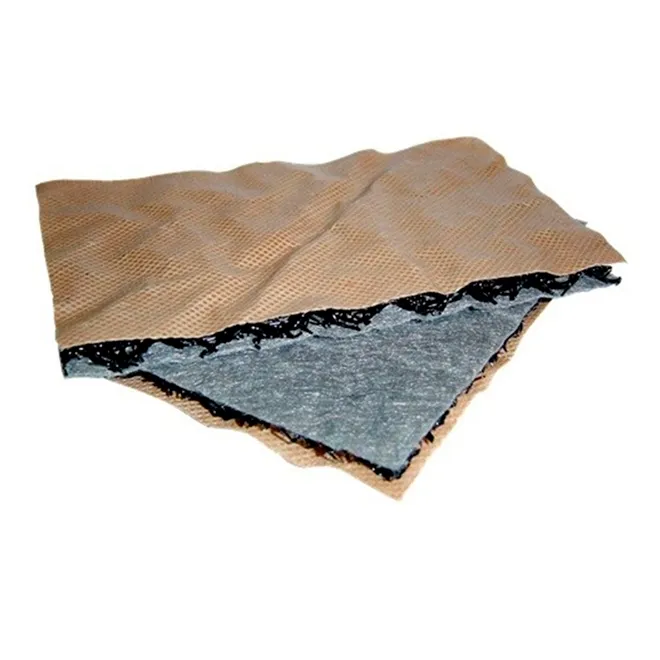
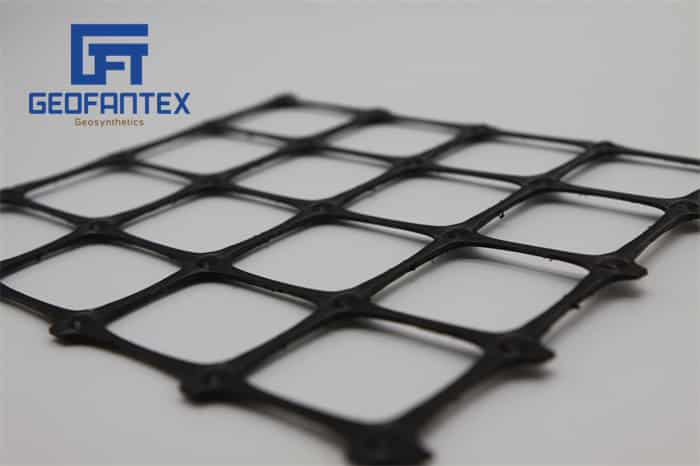
Geofantex offers a variety of products for building walls or modifying slopes to create more usable space, preserve unstable slopes, or enhance aesthetic appeal. These treatments typically involve soil-reinforced gabions with metal mesh panels or geosynthetic geogrids as reinforcing elements. Geosynthetic geogrid products are typically used for long-term retaining applications, and the choice of finish depends on aesthetic requirements and the angle of the slope or wall to be constructed.
The Main Functions of Various Geosynthetics:
| SEPARATION | REINFORCEMENT | FILTRATION | DRAINAGE | WATERPROOF | PREVENTION | POLLUTION PREVENTION | PROTECTION | CONSOLIDATE | |
| GEOTEXTILE | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||
| GEOMEMBRANE | √ | √ | √ | ||||||
| GEOGRID | √ | √ | |||||||
| GEONET | √ | ||||||||
| GEOTUBE | √ | ||||||||
| GEOCELL | √ | √ | |||||||
| GCL | √ | √ | |||||||
| GEOCOMPOSITE | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||
| GEOCONCRETE BLANKET | √ | √ | √ | ||||||
| Drainage Board B | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||
| Storage and Drainage Board | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||
| Grass Paver | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||
| Macmat | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||
| GeoFanTex®GD 2L | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||
| GeoFanPipe® FP | √ | ||||||||
| GeoFanDrain® BC | √ | √ | √ | ||||||
| GeoFanPipe® DCP | √ | √ | |||||||
| GeoFanTRM® Geomantles | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ |
Get Free Sample
We’ll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)