Management of Sludge and Wastewater
Geosynthetics are integral in sludge and wastewater management, serving roles in containment, filtration, reinforcement, and drainage. Geomembranes line containment structures to prevent leakage, while geotextiles aid in filtration and separation, allowing water passage while retaining solids. Geotube and geocells reinforce soil structures, enhancing stability and load-bearing capacity. Geocomposites facilitate efficient drainage, removing excess water from treatment processes. These versatile materials improve infrastructure durability and environmental sustainability in wastewater treatment and sludge management.
The Main Functions of Various Geosynthetics:
Geotextiles play a significant role in the management of sludge and wastewater within the realm of environmental engineering and geotechnical infrastructure. These materials are part of a larger category known as geosynthetics, and they are specifically designed to address various challenges in soil stability, filtration, protection, and drainage. In the context of sludge and wastewater management, geotextiles serve several key functions:
- Filtration and Separation: Geotextiles act as filters that allow water to pass through while retaining solid particles. This is crucial in wastewater treatment processes where separating liquid from solid phases is essential. The permeability of the geotextile fabric can be selected based on the size of particles it needs to retain, making it a versatile solution for various applications. This filtration process helps in clarifying water before it is discharged or further treated for reuse.
- Dewatering and Sludge Removal: One of the primary uses of geotextiles in sludge management is for dewatering. Sludge, a by-product of wastewater treatment, contains a significant amount of water, making it difficult to handle, transport, and dispose of. Geotextiles can be used in the form of geotextile tubes or bags that are filled with sludge. The water is then allowed to seep out through the fabric, leaving behind a more solidified material. This method significantly reduces the volume of sludge, lowering handling and disposal costs.
- Erosion Control and Protection: Geotextiles are also used to protect wastewater treatment infrastructure from erosion and sedimentation. They can be used to stabilize embankments, protect geomembranes in landfills, and prevent soil erosion in areas disturbed by construction activities. This helps in maintaining the integrity of the infrastructure and prolonging its lifespan.
- Drainage: In addition to filtration, geotextiles also facilitate drainage. They can be used to wrap around drainage pipes or incorporated into the design of leachate collection systems in waste disposal sites. This ensures that excess water is efficiently removed, preventing the buildup of hydrostatic pressure and enhancing the overall performance of the waste management system.
- Reinforcement: Though more related to their mechanical properties, geotextiles can also reinforce the soil. This can be beneficial in the construction of embankments or landfills where increased soil stability is required. By improving the soil’s mechanical properties, geotextiles help in creating a more stable and durable infrastructure for wastewater and sludge management.
Geosynthetic Clay Liners (GCLs) play a crucial role in the management of sludge and wastewater, integral to environmental protection, waste management, and water quality preservation. Comprising a layer of bentonite clay sandwiched between two layers of geotextiles or bonded to a geomembrane, GCLs leverage the natural healing properties of bentonite to provide an effective barrier against the migration of contaminants. Here’s how GCLs function in the context of sludge and wastewater management:
- Containment and Isolation: In the management of sludge and wastewater, GCLs serve as a barrier to contain the waste material and prevent the leachate (the liquid that drains or ‘leaches’ from a landfill or sludge bed) from contaminating the surrounding soil and groundwater. The bentonite clay swells when it comes into contact with water, creating a dense, low-permeability layer that traps contaminants.
- Leakage Reduction: The low permeability of the bentonite layer within GCLs significantly reduces the risk of leachate leakage. This property is particularly important in facilities like sludge drying beds and wastewater treatment ponds, where the potential for liquid seepage must be minimized to protect groundwater and surrounding ecosystems.
- Self-Healing: A notable feature of GCLs is their ability to ‘self-heal’. When punctured or torn, the bentonite clay within the liner can swell to fill small holes or gaps, thereby restoring its integrity and continuing to provide an effective barrier against liquid migration. This self-healing capability ensures the long-term effectiveness of containment systems, even when minor damage occurs.
- Chemical Resistance: The bentonite in GCLs is resistant to many of the chemical components found in sludge and wastewater, maintaining its sealing properties in a variety of chemical environments. This resistance ensures that GCLs remain effective as barriers, even in settings where the contained material may have high levels of chemical contaminants.
Concrete blankets significantly manage sludge and wastewater by providing a stable, impermeable layer that prevents leachate seepage, mitigates contamination risks, and promotes containment. Here’s a detailed look at how they contribute:
- Containment of Sludge and Wastewater: Concrete blankets provide a durable, impermeable layer that effectively contains sludge and wastewater in designated areas, minimizing the risk of contamination to surrounding soil and groundwater. This containment is essential for sludge lagoons, ponds, or holding areas where leaks could lead to environmental hazards.
- Prevention of Leachate Seepage: One of the major issues in sludge and wastewater management is the potential for leachate—contaminated water that has seeped through waste materials—to escape into the environment. Concrete blankets help prevent this seepage, as they are designed to be impermeable, significantly reducing the chance of leachate penetration into the surrounding ecosystem.
- Stability and Erosion Control: Concrete blankets offer structural stability, which prevents erosion in wastewater containment areas. When applied to sloped or uneven areas, these blankets ensure that sludge and wastewater remain securely contained, especially during heavy rain or adverse weather. This also helps maintain the integrity of surrounding land and water sources.
- Facilitation of Sludge Drying and Decomposition: Concrete blankets also contribute to the drying process of sludge. When sludge is allowed to dry, its volume reduces, making it easier to handle and process. Concrete surfaces create a controlled environment that promotes faster drying and can enhance the natural decomposition of organic components in sludge, which is beneficial for wastewater treatment facilities.
- Compatibility with Geosynthetic Liners: Concrete blankets can work in conjunction with geosynthetic liners, such as geomembranes or geocomposites, to create an even stronger barrier system. This combined approach improves resistance to chemical contaminants and increases durability, making it an effective choice for long-term sludge and wastewater management projects.
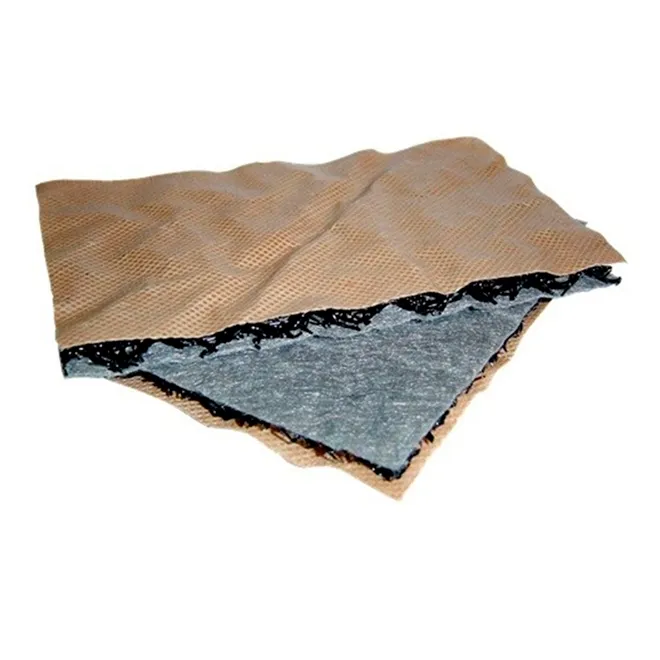
Geonets, like geotextiles, are a type of geosynthetic material, but they serve a distinct function in the management of sludge and wastewater. Geonets are formed by a network of integrally connected ribs over a large area, creating a high-porosity material that is used primarily for drainage purposes. In the context of sludge and wastewater management, geonets play several crucial roles:
- Drainage Enhancement: The primary function of geonets is to enhance drainage. They are often used in conjunction with geotextiles, where the geotextile functions as a filter layer to prevent the passage of soil particles into the geonet, which serves as a drainage layer. This combination is particularly effective in managing leachate and excess moisture in landfill sites, including those designated for sludge disposal. By facilitating rapid drainage of leachate away from the waste material, geonets help minimize the potential for groundwater contamination.
- Gas Ventilation: In the decomposition of organic matter within sludge, gases are produced, which need to be vented to prevent buildup and potential damage to landfill covers or other containment structures. Geonets can be used to form gas venting layers within landfill covers, facilitating the safe and efficient removal of gases such as methane and carbon dioxide from the decomposition of organic material in sludge.
- Erosion Control: While not their primary function, geonets can also contribute to erosion control measures, especially in landfill capping systems. By facilitating proper drainage, they prevent water from accumulating and causing erosion or instability in the covered soil. This is particularly important in the management of sludge and wastewater residuals disposed of in landfills, where maintaining the integrity of the cap is crucial for environmental protection.
- Channeling and Containment: Geonets can be used to create channels for the directed flow of leachate or treated wastewater within containment areas. This is beneficial in complex landfill or treatment site geometries where controlling the flow paths of liquids is necessary to ensure they are directed toward treatment or collection facilities.
- Foundation Protection: In the context of wastewater treatment plants and related infrastructure, geonets can be used beneath protective geomembranes to ensure efficient drainage. This protects the foundation of these structures from waterlogging and the associated problems, such as differential settlement or structural failure.
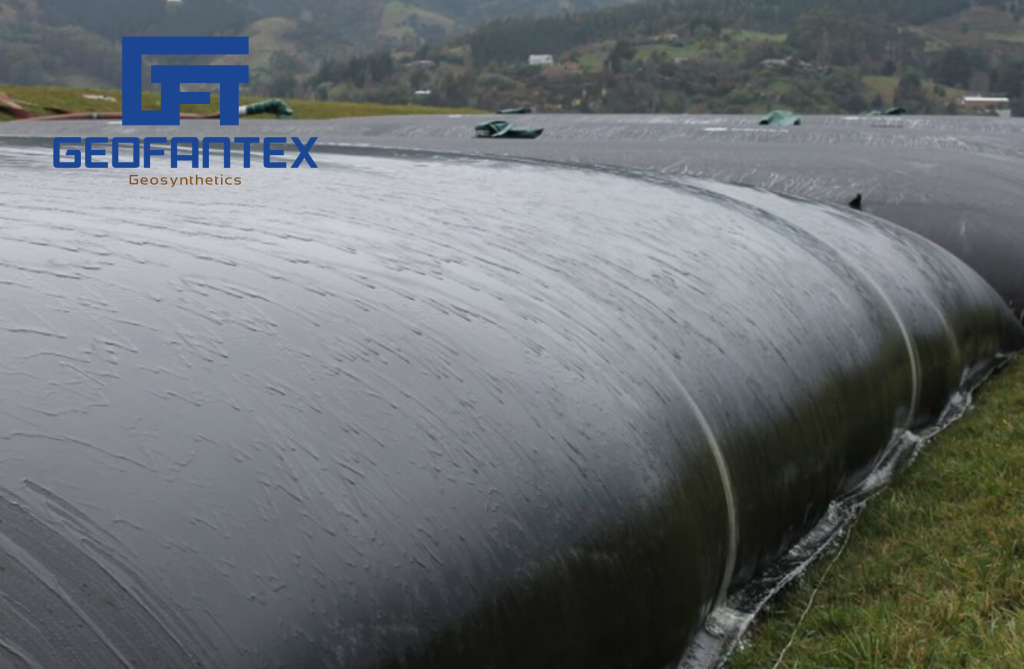
Geotubes are a specific application of geotextile technology designed for the dewatering and containment of sludge and other semi-solid materials, including those generated in wastewater treatment processes. They are large tubular containers made from high-strength, permeable geotextiles. The role and function of geotubes in the management of sludge and wastewater are multifaceted and highly valuable for environmental engineering and geotechnical infrastructure projects. Here’s a closer look at their key contributions:
- Dewatering of Sludge: The primary function of geotubes is the dewatering of sludge. This process involves pumping the sludge into the geotube where the geotextile fabric traps the solid particles, while the water permeates through the fabric and is expelled. This significantly reduces the volume of the sludge, making it easier to handle, transport, and dispose of or apply as a soil amendment, depending on its composition and environmental regulations.
- Containment and Stabilization: Once filled and dewatered, the sludge within the geotube is contained in a stable, manageable form. The high-strength fabric of the geotube ensures that the contained sludge is securely held, reducing the risk of leakage and environmental contamination. This containment system is particularly useful for hazardous or contaminated sludge that requires careful management to protect public health and the environment.
- Sludge Management: Geotubes offer a cost-effective alternative to traditional sludge dewatering and disposal methods, such as mechanical dewatering systems or the use of drying beds. Their operational simplicity, low maintenance requirements, and efficiency in volume reduction can lead to significant savings in sludge management projects.
- Shoreline Protection and Erosion Control: Beyond sludge management, geotubes have applications in shoreline protection and erosion control. They can be filled with sand or other materials and used as part of coastal defense systems, reinforcing embankments, and preventing soil erosion. addressing a range of geotechnical and environmental challenges.
The main functions of Drainage Board B typically include:
- Water Management – Regulating water flow to prevent flooding and ensure proper drainage in designated areas.
- Maintenance of Drainage Systems – Cleaning and repairing ditches, channels, and pipelines to maintain efficient water movement.
- Erosion Control – Implementing measures to reduce soil erosion and maintain land stability.
- Environmental Protection – Ensuring water quality and preventing pollution in drainage systems.
- Land Use Coordination – Working with local authorities and stakeholders to plan and manage water drainage in urban and rural areas.
- Emergency Response – Addressing drainage-related issues during heavy rains or natural disasters to minimize damage.
Management of Sludge and Wastewater Storage and Drainage Boards
Sludge Management:
- Storage: Sludge tanks, drying beds, geomembrane liners.
- Treatment: Thickening, dewatering (centrifuges, filter presses), stabilization (digestion, lime).
- Disposal/Reuse: Land application, incineration, or landfill.
Wastewater Management:
- Storage: Retention ponds, tanks, and basins.
- Drainage: Drainage boards (geocomposite, dimpled) and perforated pipes.
- Treatment: Primary, secondary, and tertiary processes.
Integrated Systems:
- Combine sludge dewatering with drainage boards.
- Separate solids from liquids for targeted treatment.
- Recover resources (biogas, reusable water).
Benefits:
- Prevents environmental contamination.
- Enables resource recovery (water, energy, nutrients).
- Reduces disposal costs.
Installation/Maintenance:
- Use durable, corrosion-resistant materials.
- Regular inspection and cleaning for efficiency.
These systems ensure sustainable and efficient handling of sludge and wastewater.
Grass pavers can be an effective solution for managing sludge and wastewater by enhancing drainage, filtration, and soil stabilization in treatment facilities, industrial sites, and environmentally sensitive areas.
Key Benefits in Sludge & Wastewater Management:
- Natural Filtration: Grass pavers allow water to percolate through soil, filtering contaminants and reducing surface runoff.
- Erosion Control: Prevents soil degradation in areas exposed to wastewater discharge or sludge accumulation.
- Load-Bearing Capability: Supports vehicles and equipment used in wastewater treatment and sludge processing.
- Reduced Runoff & Flooding: Enhances groundwater recharge, minimizing standing water issues.
Applications:
- Bioswales & Drainage Fields: Used in conjunction with wetlands or swales to manage stormwater and effluent.
- Sludge Drying Beds: Reinforced surfaces can stabilize drying areas while allowing natural filtration.
- Permeable Access Roads: Provides durable access paths in wastewater treatment plants without disrupting natural water flow.
For best performance, grass paver systems should be installed with proper sub-base layers and maintained to prevent clogging with sludge residues. Would you like recommendations on specific paver systems suited for wastewater applications?
Macmat is a specialized solution for managing sludge and wastewater in treatment plants. It offers effective filtration, dewatering, and stabilization, helping to reduce environmental impact.
How Macmat Works
- Filtration: Separates solids from wastewater.
- Dewatering: Reduces sludge volume for easier disposal.
- Stabilization: Prevents recontamination and enables safe reuse.
Applications
- Municipal Wastewater: For treating residential and industrial sewage.
- Industrial Waste: Used in sectors like food processing and chemicals.
- Agricultural Waste: Helps manage runoff and wastewater from farms.
Benefits
- Cost-effective: Reduces disposal and chemical treatment costs.
- Sustainable: Minimizes environmental impact and allows safe reuse of treated sludge.
- Efficient: Speeds up treatment processes, improving operational efficiency.
Macmat provides a reliable, sustainable solution for sludge and wastewater management, enhancing both environmental safety and operational efficiency.
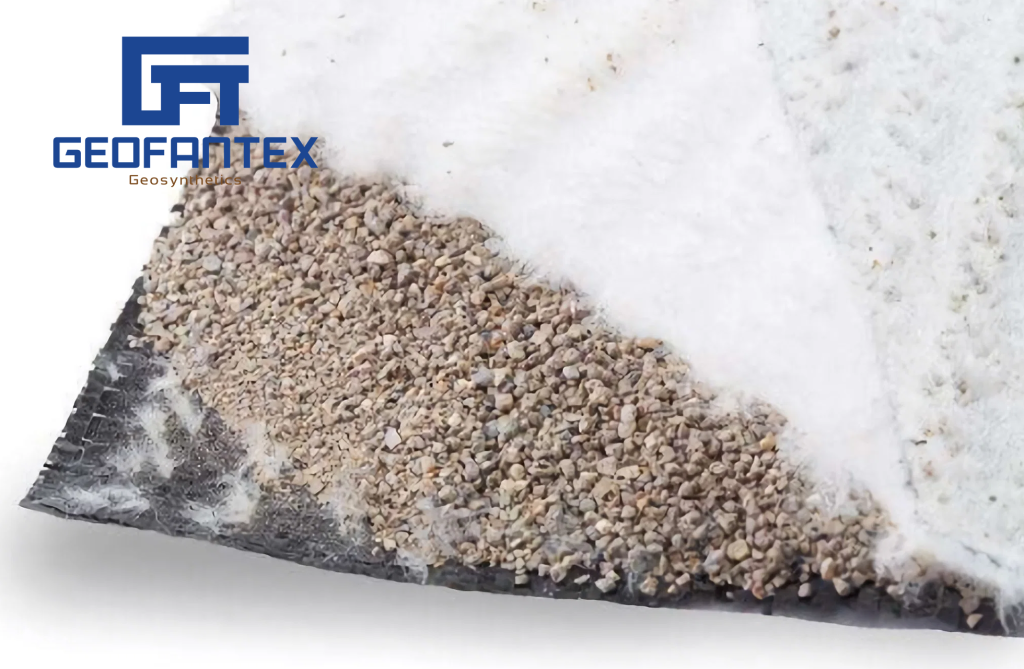
GeoFanTex®GD 2L is a drainage geocomposite engineered for efficient filtration and separation in sludge dewatering and wastewater treatment systems. Its HDPE geonet core, laminated with nonwoven geotextiles on both sides, provides high flow capacity while preventing clogging from fine particles and organic matter.
Key Applications:
- Sludge dewatering beds and lagoons
- Wastewater treatment containment systems
- Separation and drainage layers in biosolid drying areas
Benefits:
- High permeability for consistent drainage
- Chemically resistant to aggressive waste environments
- Prevents soil and sludge migration
- Enhances system lifespan and performance efficiency
GeoFanPipe® FP – Advanced Solution for Sludge and Wastewater Management
GeoFanPipe® FP is an innovative system designed to meet the growing demands of efficient sludge and wastewater management in industrial, agricultural, and municipal settings. This geosynthetic-based solution combines durability, functionality, and environmental responsibility, offering a reliable approach to handling and treating waste materials. Key features include:
- Efficient Filtration and Separation: The system utilizes high-performance geotextile materials that effectively filter out solids while allowing water to pass through, ensuring cleaner discharge and reduced environmental load.
- Reinforced Containment: GeoFanPipe® FP strengthens the structural integrity of sludge dewatering units, enhancing their ability to contain large volumes of waste without leakage or failure.
- Environmental Sustainability: By minimizing leachate and promoting water reuse, the system supports eco-friendly waste management practices and helps industries comply with environmental regulations.
- Cost-Effective Operation: Its design reduces the need for frequent maintenance and secondary treatment processes, lowering long-term operational costs and improving overall efficiency.
- Versatile Applications: Suitable for use in sewage treatment plants, mining operations, agricultural waste containment, and industrial processing facilities.
GeoFanPipe® FP stands out as a comprehensive and sustainable solution for modern sludge and wastewater challenges, delivering performance, reliability, and environmental stewardship in one integrated system.
- Used as a drainage and dewatering layer in sludge drying beds, lagoons, or wastewater treatment basins.
- Installed beneath or within sludge to accelerate water removal by providing a continuous drainage path.
- The three-dimensional thermoplastic core maintains high flow capacity even under heavy, saturated sludge loads.
- The outer geotextile filter fabric allows water to pass through while retaining fine particles and organic matter.
- Eliminates or reduces the need for gravel drainage layers, resulting in lighter structures and faster installation.
- Enhances drying efficiency in sludge treatment processes, reducing operational time and energy consumption.
- Resistant to chemical attack and biological degradation, making it suitable for long-term exposure to wastewater and biosolids.
- Can be used in both fixed beds and portable dewatering systems, adapting to different plant designs.
- Supports environmental compliance by improving leachate control and minimizing the risk of contamination.
- Improves overall performance in sludge stabilization, drying, and reuse processes.
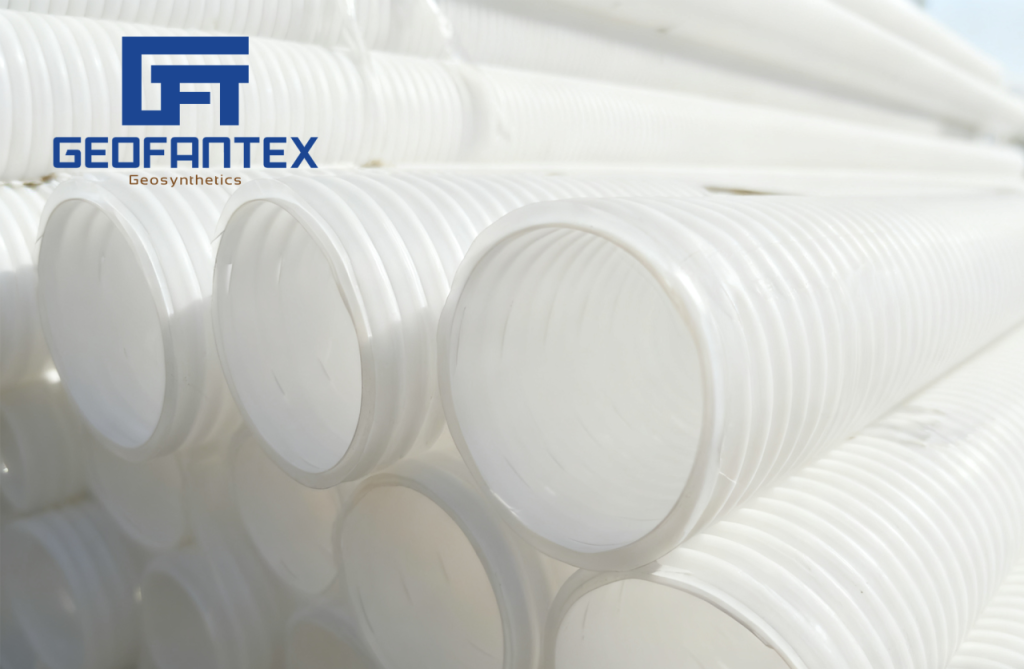
Municipal Drainage & Sewerage
- Scope: Urban rainwater networks, domestic sewage pipelines, municipal stormwater systems.
- Advantages: High ring stiffness resists road/soil pressure (no deformation under heavy traffic); smooth inner wall prevents clogging, ensuring efficient drainage during peaks.
Industrial Wastewater Drainage
- Scope: Non/low-corrosive wastewater drainage (machinery, electronics, food plants) and pre-treated industrial sewage pipelines.
- Advantages: PP/PE material offers strong chemical resistance (against mild acids/alkalis/salts); impact resistance endures on-site construction stress.
Agricultural Irrigation & Drainage
- Scope: Farmland drainage (anti-waterlogging, soil moisture control) and rural irrigation pipelines.
- Advantages: 50+ year underground service life reduces replacement needs; leak-proof connections save water and prevent soil salinization.
Residential & Commercial Drainage
- Scope: Residential rainwater, commercial plaza sewage, community green belt drainage.
- Advantages: Compact design fits narrow spaces; non-toxic, recyclable PP/PE aligns with green building standards.
Road & Highway Drainage
- Scope: Highway side ditches, rural road subgrades, tunnel auxiliary drainage.
- Advantages: Withstands road/vehicle pressure (no cracking); temperature resistance ensures stability in extreme climates.
| SEPARATION | REINFORCEMENT | FILTRATION | DRAINAGE | WATERPROOF | PREVENTION | POLLUTION PREVENTION | PROTECTION | CONSOLIDATE | |
| GEOTEXTILE | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||
| GEOMEMBRANE | √ | √ | √ | ||||||
| GEOGRID | √ | √ | |||||||
| GEONET | √ | ||||||||
| GEOTUBE | √ | ||||||||
| GEOCELL | √ | √ | |||||||
| GCL | √ | √ | |||||||
| GEOCOMPOSITE | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||
| GEOCONCRETE BLANKET | √ | √ | √ | ||||||
| Drainage Board B | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||
| Storage and Drainage Board | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||
| Grass Paver | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||
| Macmat | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||
| GeoFanTex®GD 2L | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||
| GeoFanPipe® FP | √ | ||||||||
| GeoFanDrain® BC | √ | √ | √ | ||||||
| GeoFanPipe® DCP | √ | √ | |||||||
| GeoFanTRM® Geomantles | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ |
Get Free Sample
We’ll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)