+86-159 9860 6917
info@geofantex.com
geofantex@gmail.com
+86-400-8266163-44899
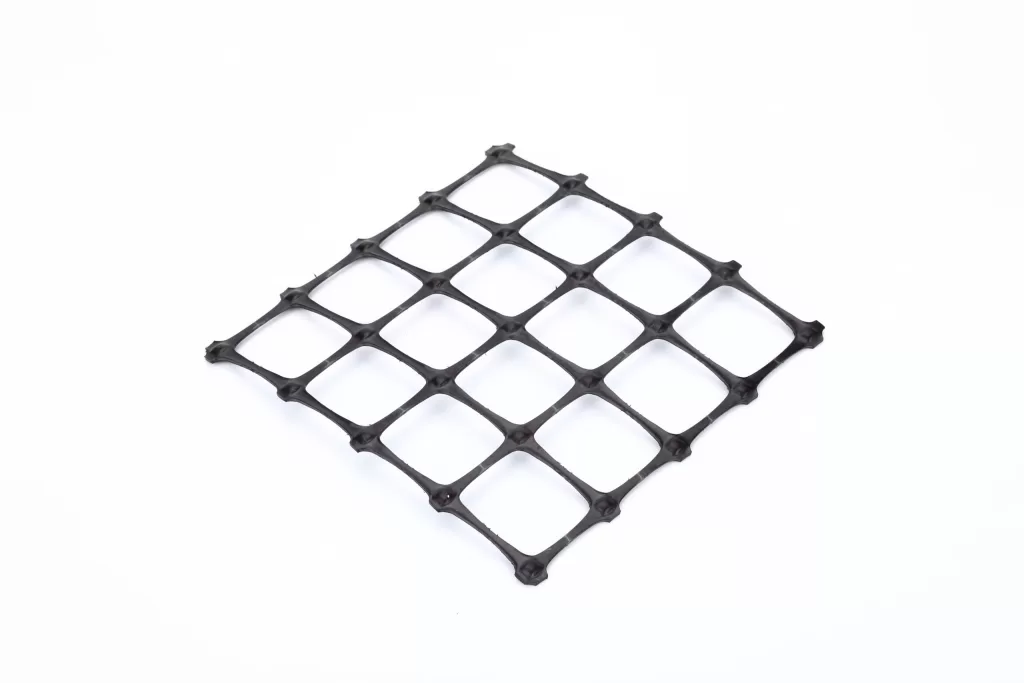
If your project involves stabilizing slopes or retaining earth, you will need geogrid. Geogrid is a synthetic, flexible mesh designed for these purposes, available in various materials, strengths, and sizes. Made from woven polyester or high-tensile strength plastic, it comes in rolls and is available in both uniaxial and biaxial forms. Biaxial geogrid, most commonly used for retaining walls under 10 feet, can be rolled in both directions while maintaining its reinforcement properties, unlike uniaxial geogrid, which can only be rolled out in one direction.
How Does Geogrid Work?
Definition: A geogrid is a synthetic material used in civil engineering for soil stabilization and reinforcement. It is typically made from polymers such as polyethylene, polypropylene, or polyester. Geogrids have an open-grid design, which allows soil to interlock within their apertures, creating a composite material with enhanced strength and stability.
Applications
- Road Construction: Geogrids are used to reinforce subgrade soils, reducing the risk of deformation and rutting. They distribute loads more evenly, increasing the road’s lifespan and reducing maintenance costs.
- Retaining Walls: By stabilizing the backfill, geogrids provide additional strength to retaining walls, allowing for steeper slopes and reducing the need for extensive foundation work.
- Pavement Design: Geogrids help to prevent cracks and extend the durability of pavement by reinforcing the base layers and reducing the need for thick layers of aggregate.
Materials
Geogrids are manufactured using high-strength polymers like:
- Polypropylene: Lightweight and resistant to chemical degradation, often used in softer soils.
- Polyester: Known for high tensile strength and used in heavy-load applications.
- High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE): Offers excellent durability and flexibility, suitable for varied environments.
The choice of material depends on project requirements such as load-bearing needs, environmental conditions, and compatibility with the soil.
Mechanisms of Action
- Interlocking: The open-grid structure of geogrids allows soil particles to lock into the apertures. This interlocking effect increases the composite material’s load-bearing capacity.
- Load Distribution: Geogrids distribute loads over a wider area, reducing localized pressure on the soil and preventing deformation.
- Shear Resistance: They provide resistance against lateral shear forces, improving stability on slopes and in embankments.
- Erosion Control: Geogrids reduce soil movement, protecting against erosion in areas with water flow or heavy rainfall.
Geogrids are indispensable in modern civil engineering projects. They enhance the performance and longevity of infrastructure by stabilizing soils, preventing deformation, and reducing construction costs. Their versatility in various applications, combined with their adaptability to different soil types and load requirements, makes them a critical component in construction and geotechnical projects.
Installing Geogrid with AB Aztec or AB Europa Walls
Geogrid reinforcement is a critical component when constructing AB Aztec or AB Europa retaining walls. Proper installation enhances the wall’s stability, prevents soil erosion, and ensures long-term durability. This guide provides a detailed process for incorporating geogrid into these retaining wall systems
Step-by-Step Installation
- Foundation Preparation: Excavate and level the base trench for the retaining wall, ensuring it is compacted and stable. Lay the first course of blocks on a level bed of compacted crushed stone, checking alignment with a level.
- Placement of the Geogrid: Measure the required length of geogrid based on the wall height and the manufacturer’s specifications. Cut the geogrid to the appropriate size using a utility knife or scissors.
- Positioning the GeogridLay the geogrid on top of the backfilled soil directly behind the first course of wall blocks. The geogrid should extend into the backfill perpendicularly to the wall face. Ensure that the geogrid is placed with the correct side facing up, as indicated by the manufacturer.
- Securing the Geogrid: Place the next course of blocks on top of the geogrid, pulling the geogrid taut before securing it in place. Backfill with crushed stone or gravel to the level of the geogrid. Compact the fill to eliminate air gaps and create a solid reinforcement layer.
- Repetition: Continue the process for additional layers of the wall. Add geogrid at specified intervals, typically every two to three courses of blocks, based on wall height and load requirements.
Tips and Precautions
- Follow Manufacturer Guidelines: Always adhere to the geogrid manufacturer’s specifications for spacing, overlap, and orientation.
- Avoid Wrinkles: Ensure the geogrid is taut and flat to maximize its reinforcing capability.
- Edge Safety: Trim any protruding geogrid to prevent it from interfering with adjacent landscaping.
- Proper Backfill: Use well-graded gravel or crushed stone for optimal drainage and compaction.
- Weather Considerations: Avoid installation during extreme weather conditions to maintain soil and block stability.
Installing geogrid reinforcement with AB Aztec or AB Europa retaining walls requires precision and adherence to proper techniques. By following this structured guide, you can build a sturdy, long-lasting retaining wall system that effectively resists pressure and environmental stress.
Compacting and Backfilling
Compacting and Backfilling is a critical process in construction and civil engineering, primarily used for soil stabilization, structural integrity, and the successful completion of foundation works, roads, retaining walls, and various types of infrastructure projects. These methods help ensure that the soil or fill material is packed tightly enough to support loads and prevent future subsidence or erosion. Here’s an overview of both terms and their importance in construction:
What is Backfilling?
Backfilling refers to the process of filling excavated areas with material after the installation of underground utilities, foundations, or structures. It helps restore the ground to its original level or prepares the site for further construction. The backfill material can range from soil, sand, gravel, or even specific engineered materials like geosynthetics depending on the project’s needs.
Key Types of Backfill Material:
- Native Soil: Excavated soil that’s reused.
- Granular Fill: Sand or gravel used for drainage or stability.
- Cohesive Fill: Clay or silt that binds together to form a solid layer.
What is Compacting?
Compacting is the process of increasing the density of the backfill material by applying mechanical force. The goal is to reduce the void spaces between particles and increase the material’s stability and load-bearing capacity. It’s achieved using specialized equipment like vibratory rollers, plate compactors, or tampers.
Why is Compaction Important?
- Prevents Settlement: Proper compaction ensures that the backfilled material does not settle over time, causing future instability.
- Improves Load-Bearing Capacity: It strengthens the base material to handle heavier loads without shifting.
- Reduces Water Flow: Well-compacted layers minimize water infiltration, which could lead to erosion or structural damage.
What Are the Common Methods of Compacting?
- Static Compaction: Involves applying a steady force to the material using rollers or flat surfaces.
- Vibratory Compaction: Uses vibrations to rearrange particles and decrease air voids.
- Impact Compaction: Involves high-energy impacts, often using heavy tamping equipment to densify the soil.
How is Compaction Tested?
To ensure the material is properly compacted, construction teams use tests such as:
- Proctor Test: Determines the maximum dry density and optimum moisture content of the material.
- Nuclear Density Test: Uses a portable nuclear device to measure the density of compacted soils.
- Sand Cone Test: Measures the in-place density of the soil after compaction.
Best Practices for Backfilling and Compacting:
- Layering: Backfill in thin layers (typically 4-6 inches), compacting each layer before adding the next.
- Moisture Control: Ensure the soil is not too dry or too wet for optimal compaction.
- Equipment Selection: Use the correct equipment for the type of soil and project requirements (e.g., vibratory roller for granular material, plate compactor for smaller areas).
- Avoid Overcompaction: Overcompaction can damage sensitive structures like pipes, which can lead to cracking or deformation.
Compacting and backfilling are essential techniques that contribute to the durability and stability of construction projects. Proper execution of these processes ensures the longevity of the structure, prevents future soil movements, and guarantees that utilities and infrastructure are protected from future settlement or erosion. Whether for roads, foundations, or retaining walls, backfilling and compacting lay the groundwork for safe, long-lasting construction.
Installing Geogrid with AB Fieldstone Walls
When installing geogrid with AB (Allen Block) fieldstone walls, the geogrid plays a crucial role in reinforcing the structure and enhancing its stability, especially for retaining walls that must withstand lateral forces and soil pressure. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to properly install geogrid with AB fieldstone walls:
Preparing the Foundation
- Excavation: Dig a trench to the required depth based on the wall height and design specifications. Ensure the base is level and compacted to provide a solid foundation.
- Base Layer: Add a layer of gravel or crushed stone to create a stable base for the wall and geogrid. This layer should be about 4-6 inches thick and compacted for stability.
Installing the First Course of AB Fieldstone
- Set the First Block: Lay the first row of AB fieldstone blocks in a straight line. Make sure each block is level and securely placed. This row will support the geogrid and future courses.
- Leveling: Continuously check the level and alignment of the blocks during installation to maintain a uniform base for the geogrid.
Laying Geogrid
- Placement: Lay the geogrid over the base material and the first course of AB blocks. Geogrid should extend horizontally and into the soil behind the wall, typically at a 90-degree angle to the wall face.
- Overlap: Ensure the geogrid overlaps properly, extending beyond the footprint of the block for optimal reinforcement. Typically, each layer should extend 12-18 inches into the backfill area.
- Securing: The geogrid may need to be anchored using pins or stakes to keep it in place as you continue building the wall.
Backfilling
- Add Backfill: Place backfill material (gravel, sand, or other engineered fill) behind the wall in layers, compacting each layer as you go. This prevents shifting and ensures stability.
- Geogrid Layering: As you add backfill, lay additional geogrid layers, ensuring that each new layer is placed on top of the previous one and extends further into the backfill. The geogrid should remain taut and wrinkle-free for maximum strength.
Installing Additional Courses
- Stacking Blocks: As each layer of geogrid is placed, add another course of AB fieldstone blocks on top of the previous one. Offset the seams of each course to create a staggered pattern for added strength.
- Repetition: Continue adding layers of geogrid and fieldstone until the desired wall height is reached.
Final Backfilling and Compaction
- Top Layer: Once the final course of blocks is in place, backfill the top with soil and compact it to ensure the wall’s integrity. Make sure the top layer is leveled and slightly sloped away from the wall to promote drainage.
Drainage Considerations
- Weep Holes: Install weep holes or drainage pipes behind the wall to allow water to escape and prevent hydrostatic pressure from building up behind the wall.
- Drainage Fabric: Place a layer of geotextile fabric between the geogrid and the backfill to prevent fine soil particles from clogging the geogrid and to promote drainage.
Installing geogrid with AB fieldstone walls enhances the strength and longevity of retaining walls. The geogrid reinforcement helps distribute the weight and pressure across a larger area, preventing wall failure due to soil movement. Proper installation of both the geogrid and the fieldstone blocks is crucial to ensure the wall performs as designed and can resist external forces.
Creating Patterned Retaining Walls
- Design and Installation: Patterned walls offer a unique look, blending different block sizes to create a hand-laid stone appearance. You can use preset patterns or design your own. For curved or reinforced walls, use a two-procedure pattern.
- Craftsmanship and Detail: Creating a hand-laid wall look requires craftsmanship and attention to detail. Allow extra time, especially if it’s your first attempt. Use either the AB Europa or AB Collection for preset or irregular patterns, refer to the Pattern Chart for details. Ensure a level surface on the reinforced wall for irregular patterns to properly install the geogrid.
Biaxial Geogrid: Applications and Benefits
Biaxial geogrids are crucial for creating stable landscapes that resist erosion. They are composite or plastic lattice structures used to reinforce roads, retaining walls, and slopes. Providing stability in both latitudinal and longitudinal directions, biaxial geogrids are durable and made from punched or extruded polymers, preventing soil erosion effectively.

Geogrid Properties
Geogrids have several properties that make them useful for construction:
- Tensile Strength: Resistance to breaking under tension.
- Radial Stiffness: Load distribution in all directions.
- Confinement: Prevents granular material like soil from shifting.
By locking soil particles in place, geogrids create long-lasting, erosion-resistant soil structures, reducing maintenance needs.

Common Applications
Geogrids are widely used in:
- Road Construction: Increasing roadway lifespan by strengthening the subgrade and evenly distributing vehicle weight.
- Retaining Walls: Reinforcing soil behind walls to reduce pressure and prevent failure.
- Slope and Soil Stabilization: Allowing steeper slope construction by stabilizing layers of soil with geogrid.
Biaxial geogrids, with their ability to lock soils and add strength in multiple directions, are invaluable for construction projects. Ensure your projects stand the test of time by incorporating biaxial geogrid.


Get Free Sample
We’ll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)






















