+86-159 9860 6917
info@geofantex.com
geofantex@gmail.com
+86-400-8266163-44899
In the world of civil engineering, the use of innovative materials to enhance the longevity and durability of infrastructure is critical. Geogrid fabric for roads represents a significant advancement in this domain, offering solutions to common challenges in road construction and maintenance. This article explores the fundamental aspects of geogrid fabric, its types, functioning, and its specific application in road construction, providing insights into why it’s becoming a staple in modern engineering projects.
What is the difference between geogrid and geotextile fabric?
Geogrids and geotextile fabrics are both geosynthetics used in civil engineering, but they serve different functions.
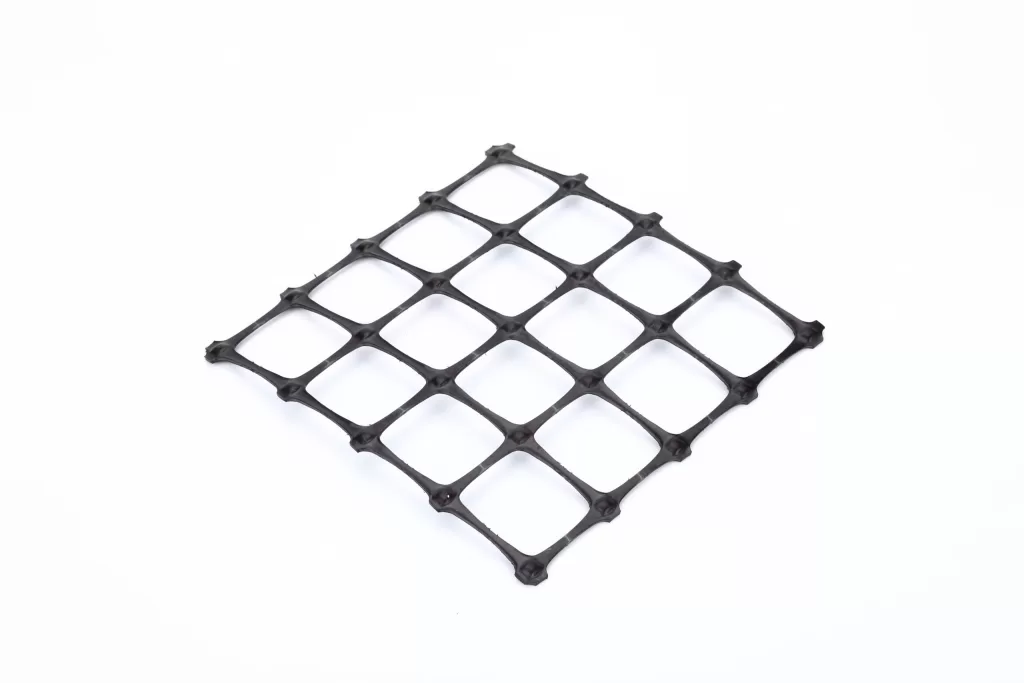
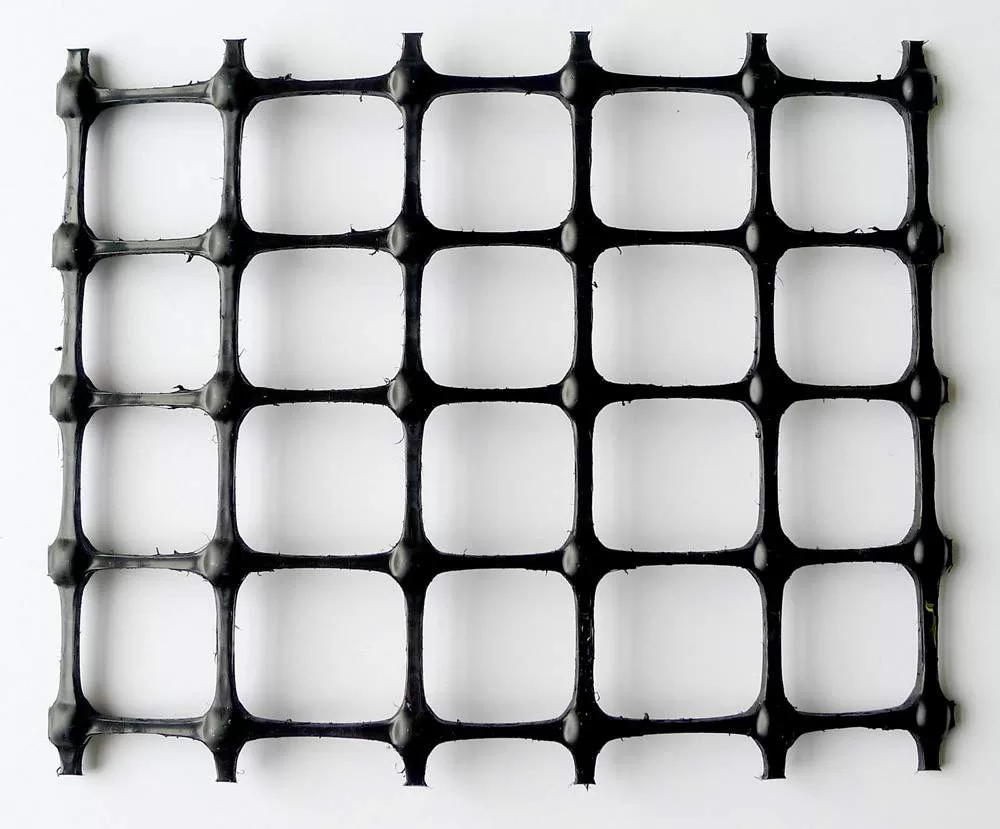
- Geogrids are stiff, grid-like structures made from polymers, primarily used for soil reinforcement. Their open mesh allows soil or aggregate to interlock, improving load distribution and stability in applications like road bases, retaining walls, and slopes.
- Geotextile fabrics, on the other hand, are flexible sheets (woven or non-woven) used mainly for separation, filtration, and drainage. They allow water to pass while preventing soil migration and are commonly used under roads, in drainage systems, and for erosion control.
- In short, use geogrids when you need structural strength and geotextiles when you need water flow control, soil separation, or filtration.
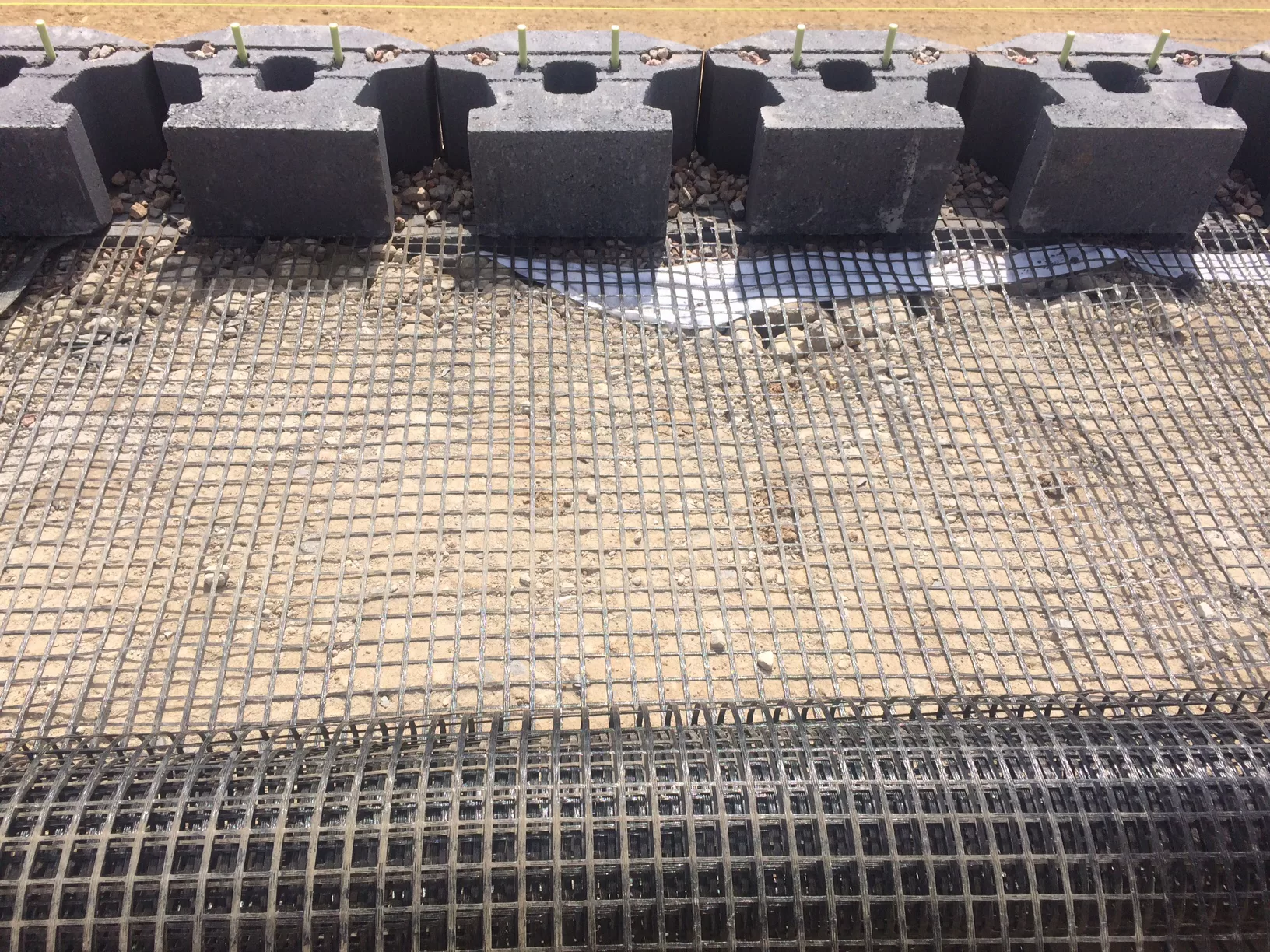

What are the different types of geogrid material?
Geogrid materials, typically made from polymers such as polyester, polyvinyl alcohol, polyethylene, or polypropylene, can be classified based on their manufacturing processes and the orientation of their ribs. The three primary types are:
- Uniaxial Geogrids: These are manufactured by stretching a polymer sheet in one direction, enhancing strength in that direction, which is ideal for applications like retaining walls, where tension is predominantly in one direction.
- Biaxial Geogrids: These geogrids are stretched in both longitudinal and transverse directions, providing strength and stability in both axes. They are typically used in pavement and road applications, where equal stress distribution is necessary in multiple directions.
- Triaxial Geogrids: With a multi-directional structure, triaxial geogrids offer enhanced interlocking capabilities and are effective in situations requiring multidirectional load distribution, such as in large-area roadbeds.
How does geogrid fabric work?
Geogrid fabric works by providing reinforcement to soil structures, including retaining walls, slopes, and road bases. It improves the stability and load-bearing capacity of the soil by distributing stresses over a wider area. Here’s how it works in different applications:
- Soil Reinforcement: Geogrid fabric typically consists of a polymer-based material that is either woven or welded into a grid pattern. When used in soil stabilization, the geogrid’s structure interlocks with the surrounding soil particles. This interlocking creates a more stable matrix that resists shear forces, preventing soil from shifting or eroding under stress.
- Retaining Wall Applications: In retaining walls, geogrid is placed in layers, with each layer being embedded in the soil behind the wall. The geogrid provides tensile strength, preventing the wall from collapsing or shifting due to pressure from the retained soil. The geogrid fabric also helps distribute loads across the entire wall structure, improving the overall stability.
- Slope Reinforcement: For slope stabilization, geogrid fabric is laid over the soil surface, often in a series of layers. It anchors the soil in place, preventing erosion, landslides, and surface runoff. The geogrid creates a “reinforced soil mass” by combining the tensile strength of the fabric with the frictional resistance of the soil.
- Pavement Design and Road Construction: Geogrids are also used in road construction to reinforce the subgrade, preventing deformation and cracking. The geogrid fabric helps distribute traffic loads, reducing the pressure on underlying soil, which can otherwise cause rutting and shifting over time.
In summary, geogrid fabric works by providing tensile strength, preventing shifting and erosion, and distributing loads in soil reinforcement and stabilization projects.
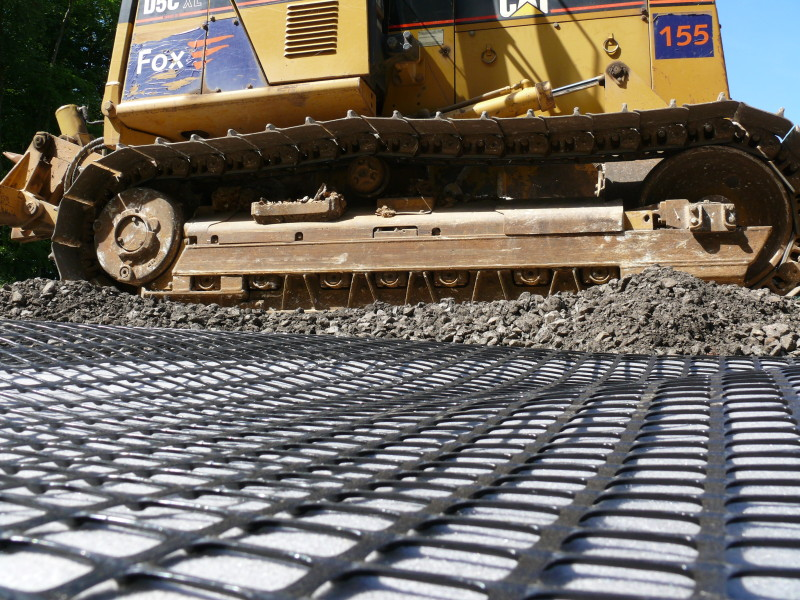

What is a geogrid road?
Geogrids and geotextile fabrics are both geosynthetic materials widely used in civil engineering, but they have distinct functions.
Geogrids are rigid, grid-like structures made from polymers such as polyester, polypropylene, or polyethylene. They are primarily used for soil reinforcement, with an open mesh design that allows soil or aggregate to interlock. This improves load distribution, stability, and structural strength in applications like road bases, retaining walls, and slopes.
Geotextile fabrics, in contrast, are flexible sheets—either woven or non-woven—designed for separation, filtration, and drainage. They allow water to pass through while preventing soil migration, making them ideal for use under roads, in drainage systems, and for erosion control.
In short, choose geogrids when structural reinforcement and load-bearing strength are required, and choose geotextiles when water management, soil separation, or filtration is the main objective.
Geogrid fabric is a transformative element in modern road construction, offering unmatched benefits in terms of durability and stability. By understanding the differences between geogrid and geotextile, the types of geogrid materials, their mechanisms of action, and their specific applications in geogrid roads, engineers and construction professionals can better implement these solutions in their projects. As infrastructure demands evolve, so too will the technologies to support them, with geogrid fabric leading the way in ground reinforcement technology.


Get Free Sample
We’ll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)






















