+86-159 9860 6917
info@geofantex.com
geofantex@gmail.com
+86-400-8266163-44899
Geomembranes are an integral component in modern engineering, offering versatile solutions to problems in environmental, hydraulic, and geotechnical applications. Among the various types of geomembranes, sand-finish geomembranes stand out due to their unique texture and enhanced performance in certain applications. This article delves into the specifics of sand finish geomembranes, exploring their uses, types, installation methods, and ideal application scenarios.
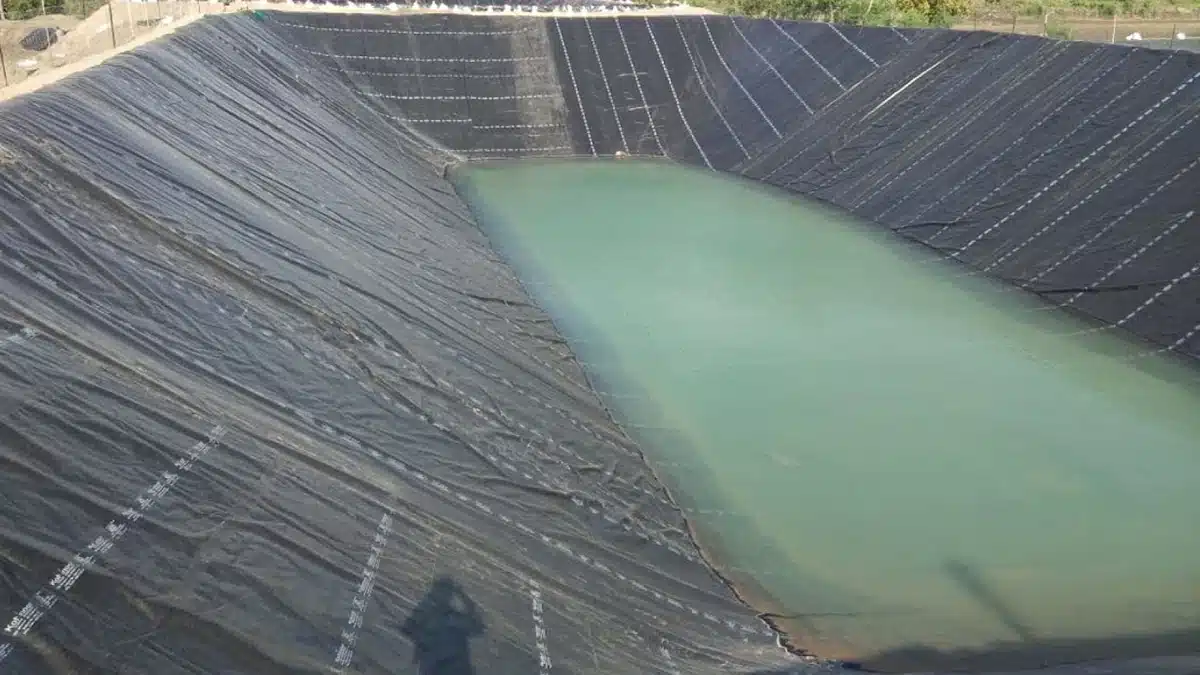
What is a geomembrane used for?
Geomembranes are synthetic membranes primarily used in containment applications to control fluid and gas migration in various engineering projects. They are typically made from flexible materials such as high-density polyethylene (HDPE), polyvinyl chloride (PVC), or ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM). Geomembranes are used for:
Lining Landfills: To prevent leachate (a liquid that has percolated through a solid and leached out some of its constituents) from entering the soil and groundwater, thus protecting the environment from contamination.
- Pond and Canal Linings: To line ponds, reservoirs, canals, and other water containment structures to prevent seepage and control water flow.
- Mining Applications: As liners for tailings ponds and heap leach pads to contain mining by-products and prevent environmental contamination.
- Water and Wastewater Treatment: Used in tanks, lagoons, and secondary containment structures to manage liquid waste and ensure environmental compliance.
- Aquaculture: Lining fish ponds and aquaculture facilities to control water seepage and maintain water quality.
- Tunnels and Underground Structures: Used in tunnel waterproofing and underground construction to prevent water ingress and protect structures.
- Geomembrane Liners: Used in combination with geotextiles and other geosynthetic materials as composite liners for enhanced containment performance.
Geomembranes provide a durable barrier against chemicals, gases, and liquids, making them essential in modern civil engineering and environmental protection projects.

What are the three types of geomembranes?
The three main types of geomembranes commonly used are:
- HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene): Known for its durability and chemical resistance, HDPE geomembranes are widely used in applications such as landfill liners, mining, and pond liners.
- LLDPE (Linear Low-Density Polyethylene): LLDPE geomembranes are flexible and offer good puncture resistance. They are often used in applications where flexibility and conformability to uneven surfaces are required, such as in secondary containment and agriculture.
- PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride): PVC geomembranes are known for their chemical resistance and are commonly used in applications such as decorative ponds, irrigation reservoirs, and tunnels.
Each type of geomembrane has specific advantages and is chosen based on the requirements of the application, including factors such as chemical compatibility, environmental conditions, and installation method.
When to use a geomembrane?
A geomembrane is a synthetic barrier widely used in construction, civil engineering, and environmental protection. It’s highly durable, impermeable, and used to control fluid movement or create barriers. Here are common scenarios where geomembranes are essential:
- Landfill Liners and Caps: Geomembranes are used as liners at the base and as caps over landfills to prevent toxic leachate from contaminating groundwater and to manage gas emissions. The impermeability of the geomembrane is key in ensuring containment.
- Pond and Reservoir Liners: When constructing artificial ponds, reservoirs, or lagoons, a geomembrane is used to prevent water seepage. This is particularly important in arid regions where water conservation is critical.
- Mining Operations: Geomembranes line tailings dams, heap leach pads, and other containment systems in mining to prevent contamination of surrounding areas from hazardous chemicals and leachates.
- Wastewater Treatment Ponds: In wastewater treatment plants, geomembranes are applied as liners to prevent the escape of contaminated water into the environment and to maintain system integrity.
- Canal and Tunnel Liners: Geomembranes are used in canals and tunnels to reduce water loss through seepage and to protect structural elements from erosion.
- Erosion Control and Slope Stabilization: In situations where soil stabilization and erosion control are required, such as slopes and embankments, geomembranes are used to reinforce the surface and prevent water infiltration.
- Secondary Containment: nFor industries dealing with chemicals and hazardous materials, geomembranes are installed under storage tanks and containment areas to safeguard against spills.
Each of these applications leverages the geomembrane’s impermeability, chemical resistance, and durability.
How are geomembranes installed?
Geomembranes are essential components in environmental and civil engineering projects, providing a reliable barrier against the infiltration of liquids and gases. These synthetic membranes, typically made of materials like high-density polyethylene (HDPE), low-density polyethylene (LDPE), or polyvinyl chloride (PVC), are widely used in landfills, reservoirs, and pond liners. Their installation process is critical to ensuring their functionality and long-term performance.
- Site Preparation: The installation of geomembranes begins with thorough site preparation. The ground must be leveled and free from sharp objects, debris, and any potential hazards that could puncture the membrane. A smooth, even surface helps ensure the integrity of the geomembrane once installed.
- Geomembrane Unrolling and Positioning: After the site is prepared, the geomembrane is unrolled across the surface. The process requires careful handling to avoid stretching, tearing, or damaging the material. Installers usually follow a pre-determined layout to ensure efficient coverage, with sections of the geomembrane overlapping at the edges to enable secure seams.
- Seaming and Welding: One of the most crucial steps in the installation process is seaming, where adjacent geomembrane sheets are bonded together. This is typically done using heat-based welding techniques, such as extrusion welding or hot wedge welding. In some cases, chemical bonding may also be used. The seams must be airtight and watertight to prevent leaks and ensure the durability of the installation.
- Inspection and Testing: After the geomembrane is laid and seams are welded, inspection and testing are conducted to verify the installation’s integrity. This includes visual inspections to check for damages and non-destructive testing, such as air pressure testing for seams. Any issues discovered during this phase must be repaired immediately.
- Covering and Finalization: Once the geomembrane passes inspection, it is often covered with a protective layer, which could be soil, gravel, or concrete, depending on the application. This helps protect the geomembrane from environmental factors like UV exposure and mechanical damage. The final stage includes securing the edges to ensure the membrane stays in place during operation.
The installation of geomembranes involves careful site preparation, precise positioning, reliable seaming techniques, and thorough inspections. Proper installation ensures the membrane functions effectively as a barrier, providing long-term protection in applications such as landfills, reservoirs, and containment systems.
Sand finish geomembranes represent a crucial development in the field of synthetic barriers, providing effective solutions to environmental challenges. Whether it’s managing waste, securing water resources, or ensuring the safety of civil engineering structures, these geomembranes play a pivotal role in safeguarding our natural and built environments. With their unique sand finish, they offer added stability and efficiency, making them a preferred choice for challenging applications. Understanding when and how to use these materials is key to leveraging their benefits in various industrial and environmental contexts.


Get Free Sample
We’ll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)






















