+86-159 9860 6917
info@geofantex.com
geofantex@gmail.com
+86-400-8266163-44899
Geonet material is a critical component in many civil and environmental engineering projects. These polymeric materials, often made from virgin high-density polyethylene (HDPE), are used in drainage and filtration systems to provide efficient flow pathways for liquids and gases. Geonets are lightweight, durable, and versatile, making them indispensable in applications like landfill liners, road construction, and erosion control. In this article, we will explore what geonets are made of, their differences from geotextiles, and their specific uses.
What is Geonet made of?
Geonets are typically made from high-density polyethylene (HDPE), derived from polyethylene resin, although other polymers like polypropylene (PP) may also be used in certain applications. The structure of geonets consists of intersecting ribs that form a grid-like pattern, creating channels for fluid or gas flow. HDPE, produced from polyethylene resin, is the most common material due to its excellent chemical resistance, UV stability, and durability, making geonets highly effective in challenging environmental conditions.
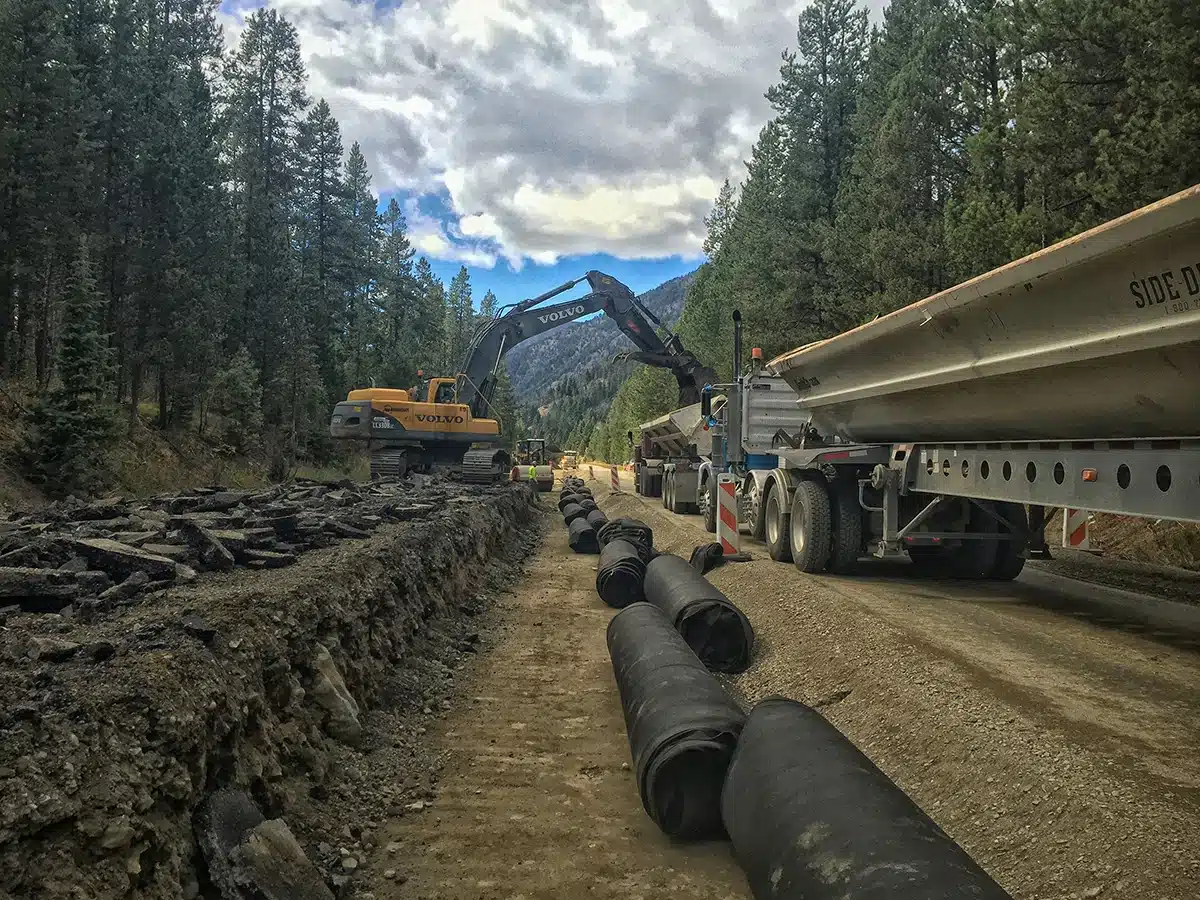

What is the difference between geotextile and Geonet?
While both geotextiles and geonets are used in civil engineering projects, they serve different purposes and are made from different materials. Geotextiles are typically fabrics—either woven or non-woven—designed to separate, filter, reinforce, or protect soil. Geonets, on the other hand, have a grid-like structure and are primarily used for drainage and filtration. The geonet provides drainage while the geotextile provides separation and strength, working together to manage fluid movement and maintain soil stability. Unlike geotextiles, which are primarily focused on soil interaction, geonets create pathways for water or gas movement in applications like landfill liners and drainage systems.
What are the uses of geonets?
Geonets are widely used in applications requiring efficient fluid drainage or gas venting. Common uses include road construction, road widening, and asphalt work, building construction and foundations, retaining walls, dams, artificial ponds, and water reservoirs, and many more. Specific applications include:
| Landfill liners | Geonets are placed between layers of geomembranes and other materials to allow for the drainage of leachate and gases. |
| Road construction | Geonets help drain excess water away from road bases, preventing water accumulation and maintaining road integrity. |
| Erosion control | In slope stabilization and coastal protection, geonets assist in water drainage, reducing soil erosion and improving overall stability. |
| Underground drainage systems | Geonets provide efficient drainage for structures like retaining walls and basements. |
These versatile uses make geonets essential in a wide range of civil engineering and environmental projects.
Is HDPE a geotextile?
No, HDPE (high-density polyethylene) is not a geotextile. While HDPE is commonly used to manufacture geonets, geomembranes, and other geosynthetic materials, geotextiles are typically made from materials like polypropylene or polyester. The geomembrane is made of high-density polyethylene, which is used to prevent seepage, while the geotextile is made of non-woven fabric, designed for filtration and soil stabilization. Geotextiles are fabric-like, whereas HDPE is used in grid structures like geonets or as sheet-like barriers in geomembranes. Geotextiles and geonets often complement each other in projects, with geotextiles used for filtration and stabilization, and geonets used for drainage.
Geonet material, primarily made from HDPE, plays a vital role in various drainage and filtration applications in civil and environmental engineering. It differs from geotextile in structure and function, with geonets providing fluid and gas pathways, while geotextiles focus on soil interaction. From landfill liners to erosion control, geonets are essential in ensuring proper drainage and maintaining structural stability in complex projects.

Get Free Sample
We’ll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)






















