+86-159 9860 6917
info@geofantex.com
geofantex@gmail.com
+86-400-8266163-44899
In construction and environmental projects, managing water flow through drainage layers is critical to prevent structural damage, erosion, and waterlogging. Geonets, a type of geosynthetic material, are designed to control water movement effectively. A key feature of geonets is their transmissivity, which refers to the ability to transmit water across a layer within a drainage system. This article delves into the concept of geonet transmissivity, its importance in engineering applications, and how it contributes to sustainable, resilient construction practices.
What is geonet transmissivity?
Geonet transmissivity is the measure of a geonet’s ability to allow water to flow horizontally across its structure. Essentially, it quantifies how efficiently water can move through the geonet, which is crucial in drainage applications. Geonets are typically installed in layers where water needs to be channeled away, preventing buildup and ensuring structural stability. High transmissivity means the geonet can handle significant water flow, making it effective for areas with heavy water load, such as landfills, roadways, and retaining walls.
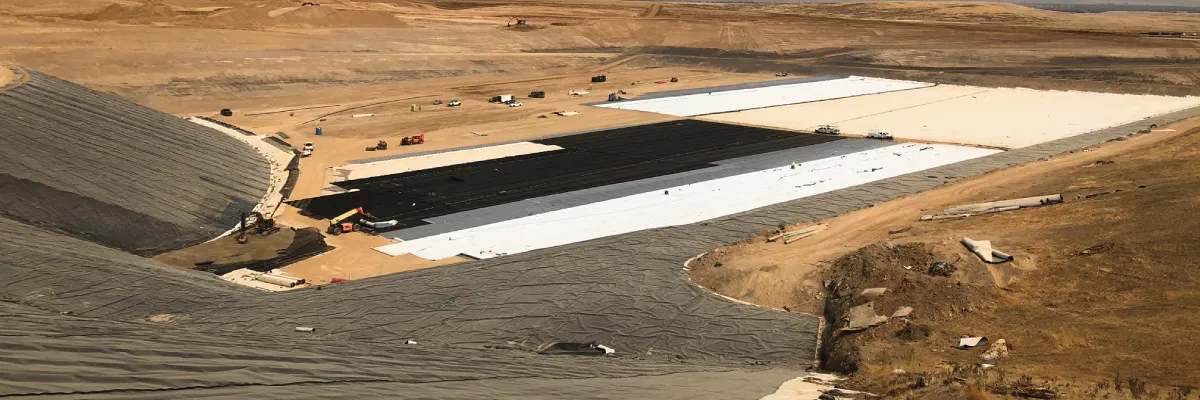

How is geonet transmissivity tested?
Testing geonet transmissivity involves subjecting the material to simulated environmental conditions to measure water flow. Typically, the geonet is placed under specific pressures, replicating the weight it would experience in situ. A known amount of water is introduced, and the flow rate is measured. The test results determine the transmissivity rate, helping engineers select the right geonet based on site-specific water management needs. Accurate transmissivity testing is essential for ensuring long-term performance in drainage systems.
Why is geonet transmissivity important in construction?
Geonet transmissivity is vital in construction because it ensures effective water drainage, which is essential to prevent erosion, flooding, and structural instability in applications like landfills, high transmissivity geonets channel leachate efficiently, reducing environmental contamination. In roadways, geonets help drain water away from pavement layers, maintaining the road’s durability and safety. Proper water management through transmissivity-focused geonets extends the life of structures and minimizes maintenance costs, especially in water-sensitive projects.
What factors affect geonet transmissivity?
Several factors impact geonet transmissivity, including material type, thickness, and environmental conditions. The geonet’s material composition, often HDPE or polypropylene, affects its resistance to pressure and chemical exposure. Thicker geonets generally have higher transmissivity due to increased space for water flow, though this varies based on structural design. Environmental conditions like soil pressure and temperature also influence transmissivity, as they affect water flow and material stability. Engineers must consider these factors to select the optimal geonet for each project.
Geonet transmissivity is a fundamental property that ensures efficient water drainage in construction and environmental applications. By understanding the role of transmissivity, engineers can design effective drainage systems that support the longevity and stability of infrastructure. Factors like material composition, thickness, and environmental conditions all influence transmissivity, making it crucial to select geonets suited to specific project needs. As part of sustainable construction, high-transmissivity geonets provide effective water management, reduce erosion, and enhance the resilience of projects across industries.

Get Free Sample
We’ll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)






















